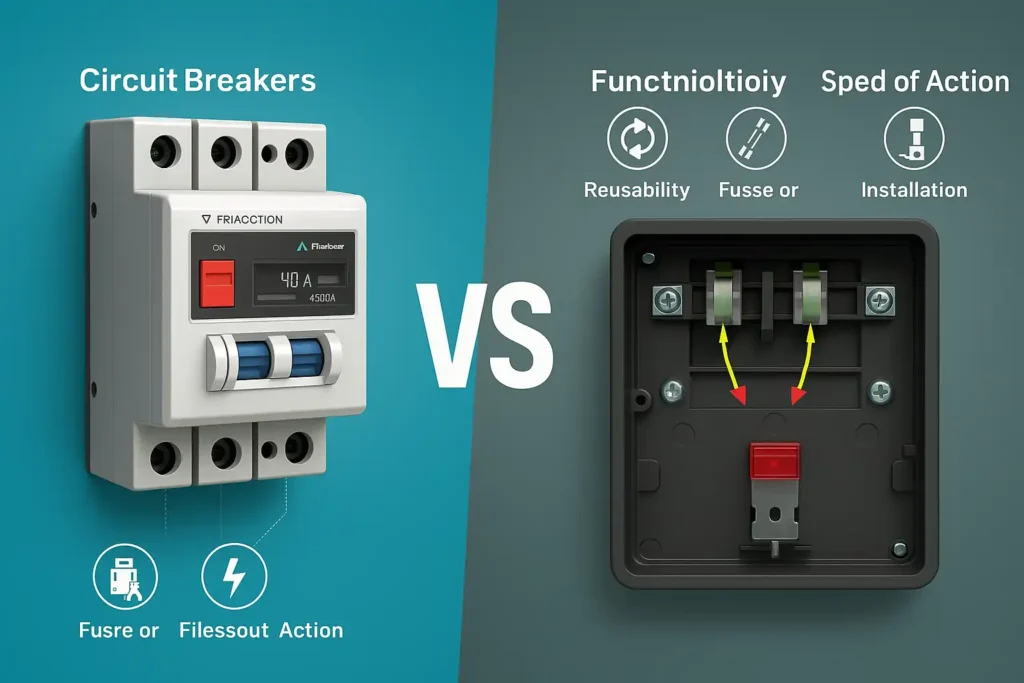
Two popular choices for circuit protection are circuit breakers and fuses. Both serve the same function – preventing electrical overload and short circuit – but with different working mechanisms and distinct advantages.
So how do they differ? A fuse is a single-use safety device that will melt when excessive current flows, thereby breaking the power supply. A circuit breaker is a reusable switch that trips when overloaded and can be manually reset. This tutorial will provide a comprehensive overview of their differences, advantages, and when to use them.
What is a circuit breaker and what is its function
Circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect circuits from damage caused by current exceeding the safe carrying capacity of the equipment (overcurrent). Its basic function is to interrupt current to protect equipment and prevent fires. Unlike fuses that must be replaced after a single operation, circuit breakers can be reset (manually or automatically) to restore normal operation.
Circuit breakers are usually installed in distribution boards. In addition to safety purposes, circuit breakers are often used as main switches to manually disconnect (“pull out”) and connect (“pull in”) power to the entire electrical sub network.
What is a fuse and what is its function
A fuse is an electrical safety device used to provide overcurrent protection for circuits. Its basic components are metal wires or metal strips. When excessive current flows, the metal wires or strips will melt, thereby stopping or interrupting the current.
It is a sacrificial device; Once the fuse is activated, it becomes a circuit breaker and must be replaced or rewired according to its type.
Circuit breakers and fuses: main differences
| Feature | Circuit Breaker | Fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Trips and cuts off power during overload or short circuit. | Melts and breaks the circuit when overloaded. |
| Reusability | Reusable (manually/automatically resettable). | Single-use (requires replacement after burnout). |
| Response Speed | Delayed tripping (0.1-5 seconds) to avoid nuisance trips. | Instantaneous cutoff (millisecond-level). |
| Installation | Requires panel mounting and professional wiring (compatible with DIN rails). | Plug-and-play (e.g., glass tube fuses) or screw-in (e.g., Edison bases). |
| Application | Ideal for homes, industrial systems, and high-current environments (10A-4000A). | Used in low-power devices (e.g., small appliances, automotive circuits). |
| Safety & Maintenance | Includes self-test buttons; lifespan up to 10,000 cycles. | No self-test feature; requires troubleshooting after burnout. |
| Environmental Impact | Long-term use reduces waste. | Generates metal waste after burnout. |
Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of circuit breakers and fuses
Circuit breaker
√Reusable (reset after tripping)
√More durable, suitable for long-term use
√Suitable for high-power applications
×High upfront costs
×Trip slightly delayed (less sensitive than fuses)
Fuse
√Quick action (immediately cut off power)
√Cheaper than circuit breakers
√Installation is simpler
×After blowing, it needs to be replaced
×Unable to reset, inconvenient maintenance
Application scenarios of circuit breakers and fuses
Application of Circuit Breaker:
- Home power system: suitable for main circuit or large appliances at home, such as air conditioning, water heaters, etc.
- Industrial equipment protection: for overload protection for electrical equipment of high power, such as power distribution systems of factories.
- Commercial buildings: Circuit breakers have extensive applications in large electrical equipment and systems in commercial buildings also.
Application of fuses:
- Small household appliances: Fuses are commonly used as a safety measure in household appliances such as televisions, refrigerators, and microwaves.
- Automotive Circuit: Fuses in motor vehicles mainly protect the electrical circuit of a vehicle from damage due to short circuit.
- Fuses are widely used as an inexpensive protection measure in small electrical appliances such as fans, lamps, and other low-power appliances
Can a circuit breaker be used instead of a fuse?
Circuit breakers can replace fuses in some situations, but not all situations are applicable. Circuit breakers can provide overload and short-circuit protection, suitable for application scenarios that require flexible parameter adjustment
The core advantage of fuses is their ability to quickly cut off short-circuit currents, making them particularly suitable for high short-circuit current environments or current sensitive equipment. Due to their different protection mechanisms, they cannot be completely equivalent.
- An alternative scenario is that circuit breakers are more convenient and cost-effective in low voltage and low current scenarios.
- The situation that cannot be replaced is that in industrial high short-circuit current systems, equipment that requires quick protection, or areas where fuses are mandatory by regulations, fuses must be retained.
Conclusion
In the choice of fuses and circuit breakers, the difference is in reusability, speed of operation, and convenience. Circuit breakers are gaining popularity as they can be reset and have a longer lifespan. Although fuses react faster and are cheaper, they have to be replaced constantly.
If you still use fuses, you may need to replace them with circuit breakers for increased safety and efficiency. If you need high-quality circuit breakers and fuses, please visit ONESTO, a professional electrical circuit breaker factory.
FAQ
What is the greatest difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker?
Circuit breakers are reusable and can be reset, while fuses must be replaced once melted.
Is purchasing circuit breakers pricey?
Compared to fuses, circuit breakers are pricey, but they are reusable and reliable.
Will the circuit breaker be damaged?
Circuit breakers can malfunction due to overload and other reasons after a long period of use, but otherwise are highly durable.
Is the fuse suitable for industrial use?
Fuses are suitable for low-power equipment, and for large industrial electrical systems, circuit breakers are generally chosen.
Here are some information that you may have just been interested in:
What are fuses in electrical systems?
What Fuse Size Is Best for a 200W Solar Panel
How to determine if your solar inverter is functioning correctly