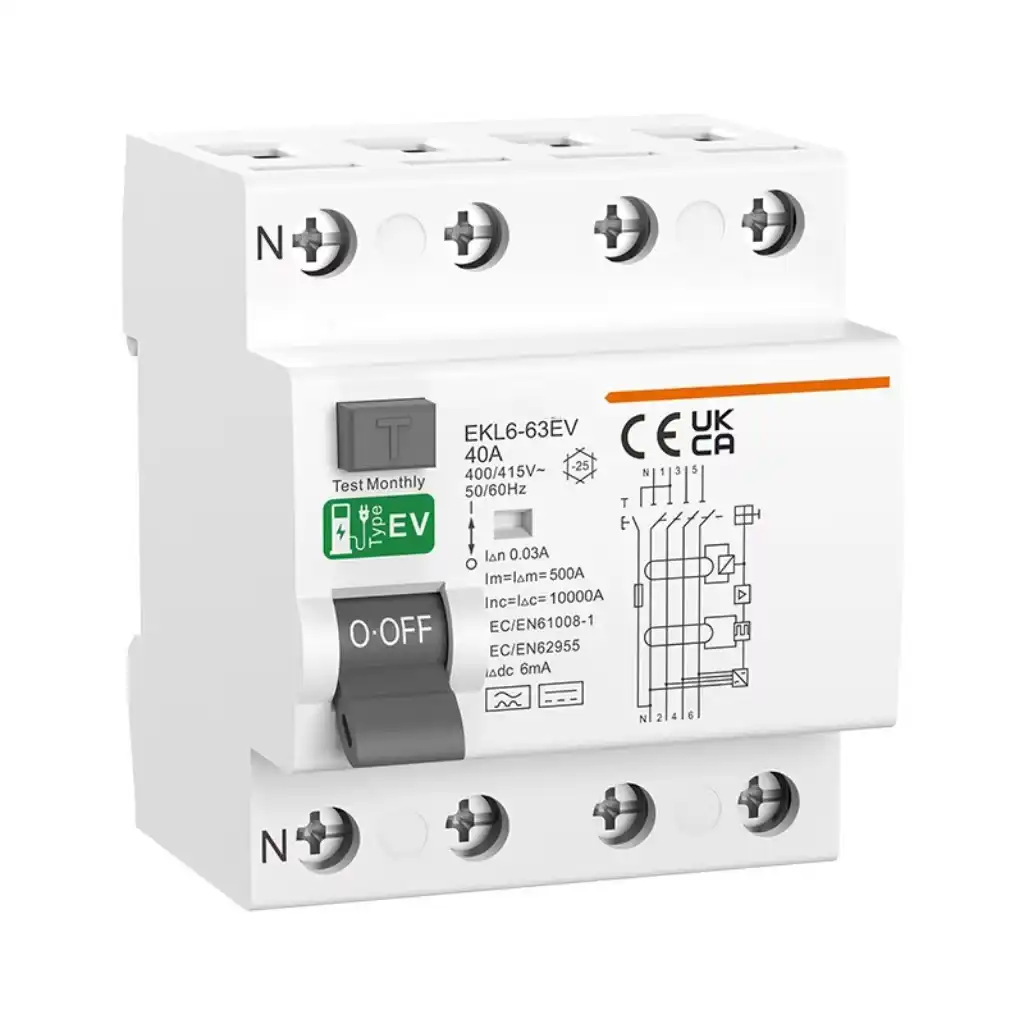
You can find several main types of residual current circuit breaker type options. The residual current circuit breaker type AC detects normal AC faults. The residual current circuit breaker type A detects both AC and pulsing DC faults. The residual current circuit breaker type F works with mixed-frequency and smooth DC up to 10 mA. Residual current circuit breaker type B and B+ cover many types, including high-frequency and smooth DC. Residual current circuit breaker type Bqf is designed for special equipment. Residual current circuit breaker type S features a time delay. The RCBO provides both residual current circuit breaker type protection and overcurrent protection. Choosing the right residual current circuit breaker type is crucial because each type responds differently to various fault currents.
| Residual Current Circuit Breaker Type | Detection Capability | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| AC | Sinusoidal AC | Standard outlets |
| A | AC + Pulsating DC | Appliances with electronics |
| F | Mixed-frequency, smooth DC | Variable speed drives |
| B/B+ | AC, DC, high-frequency | PV systems, EV charging |
Selecting the wrong residual current circuit breaker type may cause it to miss faults or trip unnecessarily. This issue is especially significant in circuits with harmonics or power electronics.
Key Takeaways
- Different RCCB types find different fault currents. Some find simple AC leaks. Others find complex DC and high-frequency faults.
- Pick Type AC for basic AC-only loads. Pick Type A for homes with electronics. These electronics make pulsing DC currents.
- Type F protects machines with changing speeds. It finds mixed-frequency currents. Type B finds all fault types. It also finds smooth DC.
- Type S adds a time delay. This stops unnecessary power outages in big buildings. It lets selective tripping happen.
- RCBOs give earth leakage and overcurrent protection in one device. They give fast and reliable safety for each circuit.
Type AC
Detection
Type AC residual current circuit breaker type finds only AC faults. It works with sinusoidal AC at 50 or 60 Hz. This device can sense sudden or slow AC leaks. It does not notice DC or pulsed DC faults. International rules set how sensitive and tough it must be. The table below shows how Type AC works in different tests:
| Disturbance Type | Test Waveform / Level | Immunity Level / Test Result for Type AC RCDs |
|---|---|---|
| Harmonics | 1 kHz sinusoidal | Up to 8 × rated residual current (I∆n) |
| Lightning induced overvoltage | 1.2/50 µs pulse | 4.5 kV between conductors, 5.5 kV to earth |
| Lightning induced current | 8/20 µs pulse | 5 kA peak |
| Switching transient | 0.5 µs / 100 kHz “ring wave” | 400 A peak |
| Surge arrester operation | 10 ms pulse | 500 A |
| Inductive load switching | Repeated bursts | 5 kV at 2.5 kHz, 4 kV at 400 kHz |
| RF conducted waves | 150 kHz to 230 MHz | 30 V, 250 mA (15 kHz to 150 kHz) |
| RF radiated waves | 80 MHz to 1 GHz | 30 V/m |
Type AC devices follow strict rules for safety and strength. You can trust them in homes and factories.
Applications
Type AC residual current circuit breaker type is used with simple loads. These are things like lights, ovens, and heaters without electronics. Type AC is also used in:
- Electrical vehicle chargers
- Control panel assemblies
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Medical machinery and laboratory equipment
- Marinas and boatyards
- Deicing systems
Type AC devices keep people and machines safe from shock and fire. They are common in homes and factories. They are used in sub-panels and big buildings. They help stop system problems and lower fire risk.
Features
Type AC devices have some key features:
- They only find AC sinusoidal leaks.
- You do not need to check DC fault response on-site. Makers test AC detection before selling.
- Installers use a test button to check if it works. If it does not trip, you must replace it.
- Type AC devices meet IEC and national rules for speed and sensitivity.
- They can handle surges and electrical noise as the rules say.
Note: If you think DC faults might happen, check if Type AC is still right.
Type A
Detection
Type A residual current circuit breaker type can find AC and pulsing DC faults. It works well with things like washing machines and induction cooktops. These devices sense problems from both AC and pulsed DC currents. This gives better safety in homes with modern electronics. Type A devices act fast when they find dangerous leaks. They help stop electric shock and fire.
Type A devices can find some faults that Type AC cannot. This is important when electronics make pulsing DC currents.
Applications
Type A devices are used where there are many electronic loads. You see them in:
- Homes with washing machines or induction stoves
- Offices with computers and printers
- Workshops with power tools that change speed
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Solar panel systems with inverters
Type A works well where both AC and pulsed DC leaks can happen. Pick Type A if your building has lots of electronics.
Features
Type A devices have some important features:
- They find both AC and pulsed DC leaks.
- They lower the chance of missing faults from new appliances.
- They help stop false trips from normal electronics.
- They follow strict rules for safety and reliability.
Lab tests show Type A devices work well with household electronics. Five makers tested them and found they work even if voltage or network changes. Harmonics from things like chargers can change how sensitive they are. High-frequency currents above 2 kHz do not make them trip by mistake. Fast changes from switching loads might cause false trips, but Type A still finds real faults. Big European makers agree with these results. You can trust Type A devices for most homes and offices today.
Type F
Detection
Type F devices can find tricky fault currents. They sense AC and pulsed DC faults. They also notice mixed-frequency currents. This makes them different from Type AC and Type A. Type F works well with machines that change speed. These machines often make currents with odd shapes. Type F reacts fast to these strange currents. This helps stop electrical dangers.
Makers test Type F using the BS EN 62423 standard. They check how quickly the device trips with different currents. Tests use AC, pulsed DC, and mixed waveforms. The device must trip in 300 milliseconds or less. This makes sure Type F protects new appliances well.
Applications
Use Type F for appliances with motors that change speed. Some examples are:
- Dishwashers
- Washing machines
- Air conditioners with variable speed drives
These machines can make tricky fault currents. Other devices might not catch these faults. Type F is also good for sensitive electronics. It works well for equipment that changes speed or load. If you use advanced home or factory systems, Type F gives more safety.
Features
Type F has many helpful features. It comes in many current and sensitivity levels. It works in cold and hot places from -25°C to +55°C. There is a test button to check if it works. You can see a contact position indicator for quick checks. Type F works with auto-reclosing units. This helps your power come back after a trip. The device meets big international rules and has green certificates.
Here is a table with important performance facts:
| Performance Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Rated Current Range | 16 A to 125 A |
| Sensitivity Range | 10 mA to 1000 mA |
| Detection Capability | Detects mixed frequency and pulsed loads |
| Operating Temperature Range | -25°C to +55°C |
| Safety Features | Bidirectional clamps, contact position indicator |
| Compliance | Meets major international standards |
| Additional Functionalities | Test button, auto-reclosing compatibility |
| Environmental Compliance | PEP ecopassport® certified |
Pick Residual current circuit breaker type F if you want strong protection for machines with changing speeds or mixed-frequency loads.
Type B
Detection
Type B devices give the most protection. They can find AC, pulsed DC, and smooth DC faults. These devices also sense high-frequency currents up to 1,000 Hz. Type B works well with new machines that use power electronics. They can spot faults that other types might not catch. If your equipment makes smooth DC or mixed-frequency currents, you need this type. Type B trips fast when it finds any dangerous current.
Type B helps keep you safe when using advanced machines or renewable energy.
Applications
You should use Type B for special electrical loads. These include:
- Photovoltaic (solar) power systems
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Medical imaging equipment like MRI machines
- Elevators and escalators with frequency converters
- Industrial machines with variable speed drives
Type B protects people and equipment from shock and fire. It also helps you follow safety rules in modern buildings. Type B works best with loads that make smooth DC or high-frequency currents. You often see these in commercial and industrial places.
Features
Type B has many advanced features:
- It finds AC, pulsed DC, smooth DC, and high-frequency currents
- It is strong against electrical noise and surges
- There is a test button for easy safety checks
- LED lights show the device status
- It meets international standards like IEC 61008-1 and IEC 62423
You can get Type B in different current ratings and sensitivities. Some models have remote signaling or auto-reset features. These help you stay safe and lower downtime. If you want the best protection, pick Type B for your system.
Tip: Always check your equipment’s manual to see if you need Type B. Using the right type keeps your system safe and working well.
Type B+ and Bqf
Detection
Type B+ and Bqf devices can find many types of faults. Type B+ finds AC, pulsed DC, and smooth DC faults. It also finds high-frequency currents up to 1,000 Hz. Type Bqf can sense even more special waveforms from complex machines. Both types act fast when they find dangerous currents. They protect you from faults that other devices might not catch.
Type B+ and Bqf help keep you safe with new machines or solar power.
Applications
You should use Type B+ and Bqf for advanced electrical systems. These types work well in:
- Solar power systems with inverters
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Industrial robots and automation lines
- Medical equipment with strong magnets or imaging
- Elevators and escalators with frequency converters
Type Bqf is best for special machines with unique current shapes. You might see these in research labs or factories with custom gear. Type B+ is good for places with strict safety rules. You can use it in hospitals, airports, or big office buildings.
Features
Type B+ and Bqf have many useful features. You get:
- High sensitivity to all fault current types
- Fast response to AC and DC faults
- Good at ignoring electrical noise and surges
- LED lights show the device status
- Test buttons make safety checks easy
Some models let you check status from a control room. Many meet tough international standards. You can pick from different current ratings and ways to install.
| Feature | Type B+ | Type Bqf |
|---|---|---|
| Max Frequency | 1,000 Hz | Custom/Extended |
| Special Waveform Sense | Yes | Advanced |
| LED Indicators | Yes | Yes |
| Remote Monitoring | Optional | Optional |
Tip: Always read your equipment’s manual. Choose the right device for your system.
Type S
Detection
Type S devices find earth leakage currents like other RCCBs. They have a special time delay. This means they do not trip right away. When a fault happens, they wait a bit before turning off the power. This helps other devices closer to the problem trip first. It stops power from going out in big areas for no reason. Type S is good for systems with many layers of protection.
You can check how Type S works in different situations by looking at the table below. The I²t numbers show how much energy is needed to melt fuse parts. These numbers help you see how Type S works with other safety devices.
| Fuse Link Reference | Pre-arcing I²t (A²s) | Total I²t at 415V | Total I²t at 550V | Total I²t at 660V | Nominal Watts Loss at Full Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125N | 30,000 | 52,000 | 75,000 | 150,000 | 12 |
| 160N | 67,000 | 120,000 | 170,000 | 335,000 | 13 |
| 200N | 120,000 | 210,000 | 300,000 | 590,000 | 15 |
| 250N | 220,000 | 390,000 | 550,000 | 1,100,000 | 19 |
| 315N | 340,000 | 600,000 | 870,000 | 1,700,000 | 25 |
| 355P | 490,000 | 870,000 | 1,250,000 | 2,450,000 | 28 |
| 400P | 670,000 | 1,200,000 | 1,700,000 | 3,350,000 | 32 |
Type S uses these numbers to make sure it trips at the right time and keeps your system safe.
Applications
You use Type S when you want only the device closest to the problem to trip. This is called selective protection. Type S works best in:
- Main panels in big buildings
- Factories with lots of smaller panels
- Apartment buildings with many floors
- Hospitals and schools with many safety layers
Type S helps stop blackouts in large places. It keeps most circuits working if there is a problem. You often see Type S as the main RCCB, with regular RCCBs on smaller circuits.
Features
Type S has some important features:
- Time delay built in for better selectivity
- Does not trip easily by mistake
- Works well even with strong starting currents
- Follows world safety rules
- Easy-to-read labels for quick checks
You can test Type S with a simple button. Many models have lights or signs to show if they are working. Type S helps you make safer and stronger electrical systems, especially in big buildings.
Tip: Pick Type S if you want to keep important circuits on during a problem. This makes your system safer and cuts down on power loss.
RCBO
Detection
An RCBO keeps you safe from two types of problems. It can find earth leakage and overcurrent. This means it looks for leaks and too much current. If the RCBO finds a dangerous current, it shuts off power fast. This helps stop fires and shocks. Rules like IEC 61009 and the National Electrical Code say how fast and sensitive RCBOs must be. These rules make sure RCBOs trip even for small leaks. They must act in less than 0.1 seconds. You can trust RCBOs to keep homes, offices, and hospitals safe.
RCBOs put earth fault and overcurrent protection together. This makes your system safer and more dependable.
Applications
RCBOs work in many places. You can use them in homes, schools, offices, and factories. Each RCBO protects just one circuit. If there is a problem, only that circuit turns off. The rest of the building keeps working. This is good for safety and business. You often see RCBOs in:
- Home panels for kitchens, bathrooms, and outside plugs
- Office buildings to protect computers and lights
- Factories to keep motors and machines safe
- Solar power and electric car charging systems
Modern RCBOs are small and easy to fit. Some let you upgrade old panels without replacing everything. You can pick special RCBOs for things like time delay or high-frequency loads.
Features
RCBOs have many helpful features in one device. You get:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Overload Protection | Stops power if too much current flows |
| Leakage Protection | Finds earth faults to stop shocks |
| Short Circuit Protection | Shuts off fast if wires touch |
| Voltage Protection | Guards against sudden voltage changes |
| Lightning Protection | Extra safety during storms |
| Fast Action | Trips in less than 0.1 seconds |
| Multiple Ratings | Works with many circuit sizes (6A to 63A) |
| Universal Tripping | Type C fits most uses |
You can test RCBOs with a button on the front. Some have lights to show if they work. RCBOs save space because you do not need two devices. They make wiring easier and give better safety.
Tip: Pick RCBOs if you want every circuit protected and less trouble when something goes wrong.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker Type Comparison
It can be tough to pick the right residual current circuit breaker type. The table below helps you compare each type quickly. You can see what each type finds, where it is used, and what makes it different.
| Type | Detection Capability | Typical Applications | Unique Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC | AC only | Simple outlets, lighting | Basic protection |
| A | AC + Pulsed DC | Homes with electronics, offices | Handles modern appliances |
| F | AC, Pulsed DC, Mixed-frequency | Variable speed drives, appliances | Detects tricky currents |
| B | AC, Pulsed DC, Smooth DC, High-freq | PV, EV charging, medical, industry | Full-spectrum detection |
| B+ | AC, Pulsed DC, Smooth DC, High-freq | Hospitals, airports, advanced systems | Extra sensitivity |
| Bqf | Advanced waveform detection | Custom industrial, research labs | Special equipment compatibility |
| S | AC, Pulsed DC (with delay) | Main panels, large buildings | Time delay for selectivity |
| RCBO | AC, Pulsed DC + Overcurrent | Homes, offices, factories | Combines two protections |
Selection Guide
You should always pick the right type for your needs. If you have simple lights or outlets, Type AC is enough. For homes with lots of electronics, Type A is better. Type F is good for machines with motors that change speed. If you use solar panels or charge electric cars, you need Type B or B+. Type S is best for big buildings where you want only the right breaker to trip. RCBOs protect one circuit and add extra safety for too much current.
When you choose, think about these things:
- Check what kind of load you have. Does it use electronics, motors, or inverters?
- Look at the pole setup. Single-pole is for most homes. Four-pole is for three-phase systems.
- Pick the right sensitivity. Most homes use 30 mA. Some places need 10 mA or 100 mA.
- Follow your local rules. Some places need special types to meet safety codes.
Tip: Always read your equipment manual and local rules before picking a device. The right choice keeps people and things safe.
Each residual current circuit breaker type works best with certain loads and faults. The table below helps you see which types fit different electronic loads.
| Electronic Load Architecture / Fault Current Type | Suitable RCD Types |
|---|---|
| Phase control | AC, A, F, B |
| Burst control | AC, A, F, B |
| Single-phase rectifier | A, F, B |
| Two-pulse bridge | A, F, B |
| Frequency inverter with two-pulse bridge | F, B |
| Single-phase with smoothing | B |
| Three-phase star | B |
Picking the right residual current circuit breaker type keeps your system safe. It also helps you follow the rules. Always choose a device that matches your equipment and the risks. This gives you the best protection.
FAQ
What is the main difference between Type AC and Type A RCCBs?
Type AC detects only AC faults. Type A detects both AC and pulsed DC faults. You should use Type A if your equipment has electronics or creates pulsed DC currents.
What should you check before choosing an RCCB type?
You should check the type of load, the presence of electronics, and local safety codes. Always read your equipment manual. This helps you pick the right RCCB for your needs.
What does the test button on an RCCB do?
The test button lets you check if the RCCB works. When you press it, the device should trip. If it does not trip, you need to replace the RCCB.
What makes Type B RCCBs special?
Type B RCCBs detect AC, pulsed DC, smooth DC, and high-frequency faults. You need them for solar systems, EV chargers, or machines with inverters. They give you the widest protection.
What happens if you use the wrong RCCB type?
If you use the wrong type, the RCCB might miss faults or trip too often. This can put people and equipment at risk. Always match the RCCB type to your application.
The following information may be of interest to you
RCBO and RCCB Explained for Beginners
Meaning of Surge Protector Parameters
Why is Type A AC RCD not suitable for electric vehicle charging equipment?
What are the detection methods for circuit breakers
Understanding a and b Contacts in Circuit Breakers

Purchase-miniature-circuit-breakers-1024x683.webp)



