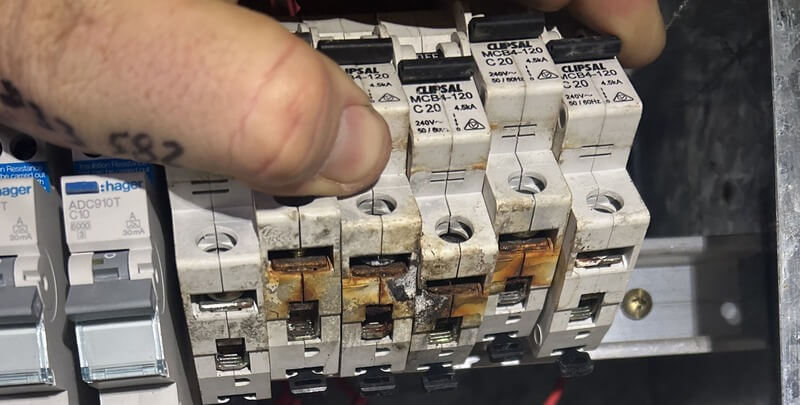
When the current flowing in the circuit exceeds its specified processing capacity, there is circuit overload, and this can result in dangerous effects such as fire or electrical burnout. Understanding how circuit overload occurs and how to repair such problems is vital in maintaining the safety and operational integrity of electrical systems. This article will assist you in detecting, preventing, and repairing circuit overloads.
What is circuit overload
When the rate of current passing through the circuit is greater than its safe carrying capacity, the circuit becomes overloaded. Every circuit has a limit, usually the size of the circuit breaker or fuse that it is connected with. When several appliances or gadgets are connected to the same circuit, the circuit may become overloaded. This causes the circuit to overheat, damages electrical appliances, and can even start a fire
4 common signs of circuit overload
Circuit overload refers to the situation where the current exceeds the carrying capacity of the circuit or equipment, which may result in heating, short circuit, or even fire. The following are typical signs:
Frequent tripping of circuit breakers or blowing of fuses
This is the most evident overload sign. When the current in the circuit exceeds the rating of the circuit breaker or fuse, the protective device will automatically cut off the power supply to prevent danger. If the circuit cannot be closed right away after tripping, or if the circuit trips once more following closing for a brief period, it indicates that there is a persistent overload in the circuit
Overheating of the circuit or the equipment
When overloaded, current increases and wires and appliances generate more heat due to effects of resistance. Manifesting in the form of sockets, switches, or electrical enclosures feeling warm or even hot to touch, or discovering that the insulation layer of wires softens, becomes discolored, or even melts due to high temperature
The lights flicker or dim
If some appliances flicker or dim when turned on, it may indicate circuit overload. When the circuit is overloaded, it is difficult to provide sufficient power, which can cause a voltage drop and make the lights appear darker than usual.
Abnormal odor or sound
Overload is usually accompanied by an odor of melted plastic or smell of thermal breakdown of wire insulation. Concurrently, loose or poorly secured points of connection within the circuit will produce buzzing or sparking noises when plugging in or un-plugging plugs or turning on devices
Reasons for circuit overload
The risk and harm of circuit overload
Fire risk
Overloading may cause wires to overheat and even melt insulation layers, leading to fires. Especially if the circuit does not have overload protection devices or circuit breakers, the consequences of overload can be very serious.
Electrical damage
When the current is too high, the circuit board or electrical components inside the appliance may be damaged. Long term overload use can also shorten the service life of electrical appliances, leading to frequent malfunctions.
Unstable power supply
In the case of overloading of the circuit, the power supply will become unstable, causing irregular power failure and even unstable phenomenon such as lightning in electrical appliances, disrupting the normal operation of the equipment.
How to repair circuit overload
Once it is determined that the circuit is overloaded, it is necessary to know how to safely repair it.
Unplug excess devices
Reset circuit breaker
Upgrade circuit breaker
Contact an electrician
How to prevent circuit overload
Accurately calculate the load
When installing circuits or connecting devices, make sure the total power does not exceed the maximum carrying capacity of the circuit. Know each appliance’s power needs and prevent more than a few high-power devices from being plugged into the same circuit.
Use proper cables and sockets
Ensure to employ appropriate cables and sockets according to the power requirements. The improper wires or sockets cannot handle heavy current and, as a result, overloading may take place.
Check the circuit regularly
Inspect the home’s electrical circuits and appliances on a regular basis, particularly the wires’ health, sockets, and the appliances themselves. If wires are damaged, old, or the sockets loose, they should be replaced or repaired immediately.
The cost of repairing overloaded circuits
Depending on the severity of the problem, the nature of the fixing the overload circuit may vary from quick fixes to major electrical work overhauls.
If the easy fix can solve the problem of overload by mere resetting of the circuit breaker or by unplugging the device, the cost is very minimal – usually only in terms of time. But for problems that demand more effort like replacing the circuit breaker or re-wiring, the cost would be greater.
Replacing faulty or outdated circuit breakers typically costs between $100 and $300, depending on the type of circuit breaker and complexity of installation.
If your house requires rewiring or adding circuits to prevent future overloading, the cost can be between $500 and $2000 or more. This depends on the size of the house and number of new circuits required.
Common misconceptions about circuit overload
The difference between overload and short circuit:Short circuit and overload are normally mistaken by many. Short circuit is the flow of current acquiring an extremely low impedance path through a circuit, mostly when wires are in touch with one another, causing the current to shoot up. Overload occurs when the total power of equipment supplied by the circuit is too large, and the current exceeds the safety limit for a prolonged time.
Summarize
FAQ
What is circuit overload?
Circuit overload is the likelihood of the wires getting overheated, equipment getting damaged, or catching fire due to the current through the circuit being higher than its carrying capacity.
What are the common causes of circuit overload?
Common causes of circuit overload include excessive device loads, high power electrical, and aged wires.
What are the dangers of circuit overload?
The major dangers are fire risk, electrical damage, and unstable power supply.
How to prevent circuit overload?
By calculating the power of electrical appliances in a sensible way, the use of the right cables and sockets, and the regular examination of circuits, circuit overload can be easily prevented.
How to fix circuit overload?
The means to fix the problem of circuit overload are substituting circuit protection devices and providing independent circuits.
What is the difference between overload and short circuit?
Overload is caused by the current exceeding the circuit’s carrying capacity, while short circuit is a sudden increase in current in a path of low impedance.
Here are some information that you may have just been interested in:
Can we wait for a day if there is a problem with the circuit breaker?
5 reasons and solutions for circuit breaker tripping
What Causes Circuit Breaker Overheating and How to Prevent It