Imagine you work in a hospital where every second matters. You need power that always works. A standard ATS changes power sources when needed. But it cannot keep the power on during repairs. An automatic transfer switch with bypass isolation lets you fix or test the system. Patients’ equipment keeps running during this time. This design uses better safety features, remote watching, and smooth power changes. You get more trust in the power and less chance of losing it. This is important in places where power loss cannot happen.
Key Takeaways
- A standard ATS switches power to backup during outages. But you must turn off power for maintenance.
- A bypass isolation ATS lets you fix or test the system. You do not have to stop power. This keeps equipment running all the time.
- Bypass isolation ATS has extra safety features. These include mechanical locks and clear switch positions. They help stop power loss or accidents.
- Pick a bypass isolation ATS for places that need power always. These places are hospitals, data centers, and telecom networks.
- Regular testing and maintenance keep your ATS ready and reliable. This helps you avoid sudden power failures.
What Is an ATS
Basic Role
You use electricity for many things every day. If the power goes out, you want your lights and devices to keep working. An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) helps with this. The ATS is like a smart traffic cop for your power. It always checks your main power source. If the main power stops, the ATS quickly switches to a backup, like a generator.
Tip: An ATS keeps your equipment working without you doing anything.
Here are some important things an ATS does:
- Notices when the main power fails or gets too weak.
- Starts the backup generator or other power source by itself.
- Moves your power to the backup in just a few seconds.
- Watches both power sources for voltage and frequency.
- Switches back to the main power when it is safe again.
- Stops downtime and keeps your work going.
You do not have to worry about losing power or breaking your equipment. The ATS takes care of everything for you.
Power Source Switching
The ATS uses sensors and controls to check your main power. It looks for things like low voltage or power loss. When the ATS finds a problem, it acts fast. It disconnects your equipment from the bad power and connects it to the backup. This switch happens so fast you may not even notice.
- The ATS uses relays or sensors to watch voltage, frequency, and phase.
- If there is a problem, it starts the backup and gets ready to switch.
- The ATS checks that the backup is ready before moving the load.
- When the main power comes back, the ATS switches everything back safely.
You can relax knowing your important systems stay on, even if the power goes out. The ATS works by itself, so you do not have to worry about power problems.
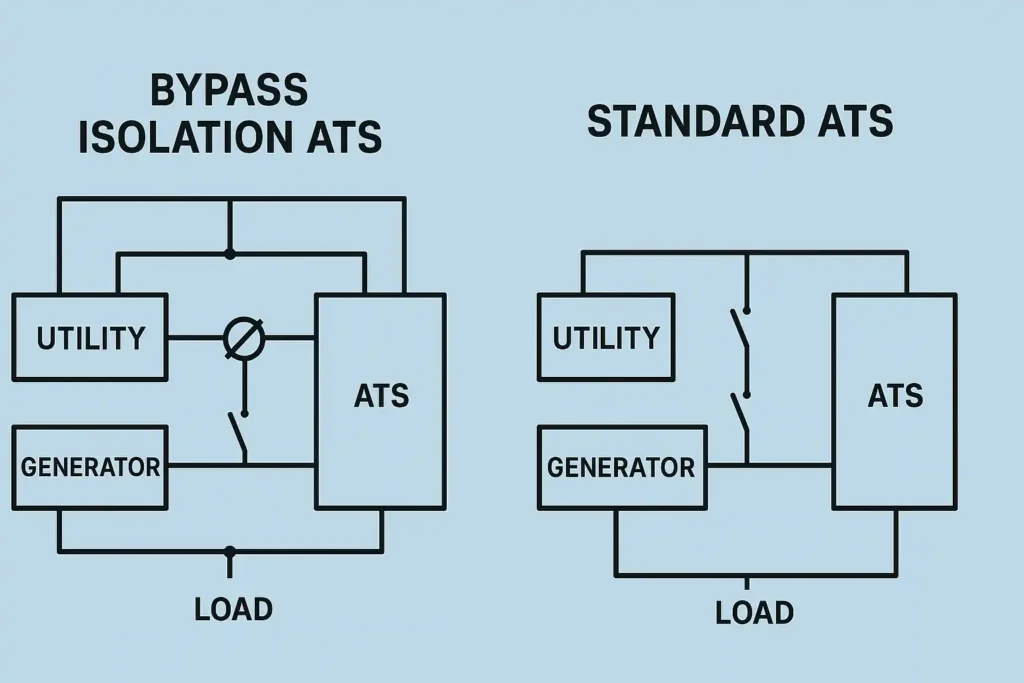
Standard ATS
How It Works
A standard Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) helps keep your power on. You do not have to do anything. The ATS does everything for you. Here is what happens step by step:
- The ATS always checks your main power.
- If the power stops or gets too weak, the ATS notices right away.
- The ATS tells your backup generator to turn on.
- The generator starts and gets ready to give power.
- The ATS switches your equipment from the main power to the generator.
- Your lights and machines keep working. You may not even notice a change.
- When the main power comes back and stays steady, the ATS switches your equipment back.
- The generator cools down and then turns off.
Note: This automatic process keeps your equipment safe and your building protected.
You can look at the main parts of a standard ATS in this table:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Input Port | Connects to main and backup power sources |
| Controller | Watches power and decides when to switch |
| Transfer Mechanism | Switches power using relays, contactors, or motor switches |
| Load Output Port | Connects to things like lights, servers, or machines |
| Signal Interface | Lets you watch and control the ATS from far away |
Key Features
Standard ATS units have many features to help keep your power safe and steady:
- Different ways to switch, like contactor or power frame, fit different needs.
- You can switch neutral wires, which is needed for some setups.
- Time delays stop false switching and help with generator timing.
- The ATS works with many power setups, like main and backup power.
- You can pick open or closed transition for safe or smooth power changes.
- Modes include manual, non-automatic, and automatic.
- Ratings like withstand closing current rating (WCR) help match your system.
- Testing and taking care of the ATS keeps it ready for emergencies.
Tip: Test your ATS often so it works when you need it.
A standard ATS helps you feel calm. You know your power will stay on, even if the main power fails.
Automatic Transfer Switch with Bypass Isolation
How It Works
You might wonder how power stays on during repairs. An automatic transfer switch with bypass isolation helps with this. This system uses a special setup. It has a draw-out transfer switch, an isolation part, and a manual bypass switch. You can move the power load to the bypass switch. Then you can safely check, fix, or even swap the main transfer switch. Your equipment keeps working the whole time.
Here is what happens step by step:
- The bypass switch takes over for the main transfer switch.
- The isolation part lets you disconnect the main switch for safety.
- You can test or fix the main switch while the bypass keeps power on.
- When you are done, you move the load back to the main switch.
This setup is great for places where power loss is not okay, like hospitals or data centers. You can feel calm knowing your important systems stay on, even when you do maintenance.
Bypass and Isolation Features
The automatic transfer switch with bypass isolation is special because it has more safety and control features. Here are some important things:
- Both the bypass and transfer switches have the same power ratings. This means you can move the load safely between them.
- Mechanical and electrical locks stop unsafe actions, like joining two power sources at once.
- The draw-out design lets you connect, test, or separate the switch with the door closed. This keeps you safe.
- You only need two handles to use bypass and isolation, so it is easy to use.
- Mechanical flags show you the position of each switch, so you always know what is happening.
- Strong cases and sealed relays keep out dust and dirt, which helps during repairs.
You should know that an automatic transfer switch with bypass isolation costs more and needs more space than a standard ATS. You need to plan for these extra needs, but you get power that stays on all the time. This makes it the best choice for places where power is very important.
Comparison
Operation
There are big differences in how these systems work. A standard ATS watches your main power. If the power fails, it starts the backup generator. Then it moves your load to the backup. Sometimes, this can cause a short power break. This only happens unless you use a closed transition. When the main power comes back and stays steady, the ATS switches back. You do not have to do anything. The system does all the work for you.
A bypass isolation ATS gives you more control. This system uses both automatic and manual switches. You can move the load to a bypass switch. You do not have to stop the power. This lets you test or fix the main transfer switch while things keep running. You get extra safety and backup. This setup is more complex and needs more space. It is very important for places like hospitals or data centers.
Some people think you can fix a standard ATS without turning off the power. That is not true. Only a bypass isolation ATS lets you do safe repairs while the power stays on.
Maintenance
You need to keep your power system working well. With a standard ATS, you must turn off the power to do service or tests. This can stop your equipment for a while. In some places, even a short power loss is a big problem.
A bypass isolation ATS changes this. You can move the load to the bypass switch. This lets you separate the main transfer switch and work on it safely. Your equipment keeps running the whole time. This is very important in places like hospitals, airports, and factories. You can test or fix the switch as much as you need. You do not have to shut down your systems.
- Standard ATS: You lose power during maintenance.
- Bypass isolation ATS: You can do maintenance with no power loss.
Industry rules say you should use bypass isolation ATS in important places. They want systems that let you test and fix things safely. You do not have to stop the power. This keeps your building safe and working all the time.
Reliability
You want your power system to always work. Standard ATS units are good for many buildings, but they have limits. If you need to fix them, you must turn off the power. This can put your equipment at risk.
A bypass isolation ATS is more reliable. You get two ways for power to reach your equipment. If one part needs work, you can use the other. This backup means your equipment always has power. Industry rules now want this level of safety in places like hospitals and data centers. These systems also let you watch them from far away and have better safety features.
| Feature | Standard ATS | Bypass Isolation ATS |
|---|---|---|
| Power transfer | Automatic | Automatic + Manual Bypass |
| Maintenance | Needs power off | No power interruption |
| Redundancy | Limited | High |
| Reliability | Good | Excellent |
| Cost and space | Lower | Higher |
If you run an important place, pick a system that gives you the safety you need. A bypass isolation ATS helps you feel calm, even when you need to test or fix things.
Pros and Cons
Standard ATS
A standard ATS has many good points for most buildings. Here are some of the main benefits:
- The switch works by itself. You do not need to do anything.
- Power changes fast. Your lights and machines stay on in outages.
- The system helps keep you safe from shocks and surges.
- You can watch and control the system from far away.
- You can set when the generator starts or stops.
But there are also some downsides:
- It costs more than a manual switch. The technology is more advanced.
- Only trained electricians should install it. The setup is not simple.
- You need to check and care for it often. There are many electronic parts.
- Sometimes, it may switch by mistake during power surges or brownouts.
- You cannot use it with portable generators that do not have electric starters.
Tip: Always get a pro to install your ATS and check it often to keep it working well.
Bypass Isolation ATS
If you use an automatic transfer switch with bypass isolation, you get more features for important places. The table below shows the main good and bad points:
| Aspect | Fail-Safe Bypass ATS | Maintenance Bypass ATS |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Gives quick, sure bypass for emergency power. | Lets you do repairs without stopping power, if ATS is set right. |
| Operational Flexibility | You can use it anytime. This helps in emergencies and lowers mistakes. | You must move ATS by hand first if not set, so it is harder to use. |
| Safety & Reliability | Mechanical locks stop short circuits. The design is simple and works well. | Complex locks can make mistakes or problems more likely, especially if ATS is broken. |
| Load Interruption | There is a short power break during bypass. | Made to stop power breaks during repairs, but only if things are set right. |
| Limitations | You cannot avoid a quick power break. Not mainly for repairs without stopping power. | Bypass will not work if ATS is stuck or broken. Doing it by hand can be risky. |
| Best Use | Best for emergencies when you need power back fast and safe. | Best for repairs when you need power to stay on and ATS is working. |
Pick an automatic transfer switch with bypass isolation if you must keep power on during repairs or tests. This system is best for hospitals, data centers, and other places where power loss is not okay.
Use Cases
Standard ATS Applications
Standard automatic transfer switches are used in many places. These switches help keep power on when it is needed. They work well in buildings that need steady electricity but do not need special repair features. You can find them in:
- Data centers need servers to run all the time. This stops data from being lost.
- Factories and plants need machines to have steady power. This helps avoid stopping work.
- Hospitals and healthcare buildings need medical tools to keep working.
- Telecommunication systems need power for networks to work right.
- Offices and stores want lights, computers, and security to stay on.
- Homes use backup generators to keep important things on during blackouts.
Standard ATS units notice when power is lost and switch to backup. You do not have to do anything. This keeps your things safe and lets you keep working.
Tip: Test your ATS often so it works when you need it.
Bypass Isolation ATS Applications
A bypass isolation ATS is used where power loss cannot happen. This system lets you fix or test things without turning off the power. You see these switches in:
- Hospitals and clinics need life-support systems to always have power.
- Data centers and cloud hubs cannot have even a short power break.
- Telecom networks must keep calls and messages working all the time.
- Big factories and heavy industries lose money if machines stop.
- Power grids with wind or solar need to handle changes and stay stable.
The table below shows where each switch works best:
| Application Area | Standard ATS | Automatic transfer switch with bypass isolation |
|---|---|---|
| Homes | ✅ | ❌ |
| Hospitals | ✅ | ✅ |
| Data Centers | ✅ | ✅ |
| Factories | ✅ | ✅ |
| Telecom Networks | ✅ | ✅ |
| Renewable Energy Grids | ❌ | ✅ |
Note: Pick a bypass isolation ATS for places where you cannot risk losing power, even for a short time.
Choosing the Right ATS
Key Factors
When you choose an ATS, you need to think about what your building or business needs most. Some places can handle a short power break. Others, like hospitals or data centers, cannot risk any downtime. You should look at these key factors:
- Backup Power Criticality: Decide if your work needs power all the time. If you cannot have any power loss, you need a system that switches fast and keeps running during repairs.
- Maintenance and Testing: Think about how often you need to check or fix your switch. If you want to do this without turning off the power, you need a bypass isolation feature.
- Type of Power Sources: Look at what kinds of power you use, like utility, generator, or UPS. Some switches work better with certain setups.
- Transfer Time: Some jobs need power to switch very quickly. Make sure your ATS can meet this need.
- Environmental Conditions: Check if your building has high heat, dust, or moisture. These things can change what kind of ATS you need.
- Budget: Bypass isolation ATS costs more and takes up more space. Standard ATS is less expensive but may not fit critical needs.
Here is a table to help you compare:
| Factor | What to Consider |
|---|---|
| Backup Power Criticality | Is continuous power a must? |
| Maintenance/Testing | Do you need to service without power loss? |
| Power Sources | What types of power will you use? |
| Transfer Time | How fast must the switch happen? |
| Environmental Conditions | Will heat, dust, or moisture affect the switch? |
| Budget | How much can you spend? |
Practical Tips
You can make a better choice by following these tips:
- Set up regular checks and tests for your ATS. This keeps it ready for emergencies.
- Train your team to spot problems early and know how to fix them.
- Use experts for inspections. They can find hidden issues before they cause trouble.
- Keep your ATS clean and dry. Protect it from dust and water.
- Store spare parts and have a plan for emergencies.
- Write down all maintenance and repairs. Follow the maker’s instructions.
- Plan for upgrades as your needs grow or change.
Tip: Always match your ATS to your most important needs. If you run a hospital or data center, you may need an automatic transfer switch with bypass isolation. For less critical places, a standard ATS may be enough.
You have learned that a standard ATS switches power by itself. A bypass isolation ATS lets you fix things without turning off the power. Picking the right ATS helps keep your equipment safe. It also helps your work keep going. Some places, like hospitals or data centers, always need power.
Checklist for choosing your ATS:
- Decide if your work must have power all the time
- See if you need to fix things without stopping power
- Check if the ATS works with your power sources
- Find features like quick switching and safety locks
- Plan to check and take care of your ATS often
Choose the ATS that fits your most important needs. This will help keep your systems safe and working well.
FAQ
What is the main benefit of a bypass isolation ATS?
You can do maintenance or testing without turning off your power. This keeps your equipment running and safe. Hospitals and data centers often need this feature.
Does a bypass isolation ATS cost more than a standard ATS?
Yes, you will pay more for a bypass isolation ATS. It has extra parts and safety features. You also need more space for installation.
Can you upgrade a standard ATS to a bypass isolation ATS?
You cannot easily upgrade a standard ATS to a bypass isolation ATS. The systems have different designs. You need to plan and install a bypass isolation ATS from the start.
Where should you use a standard ATS?
You can use a standard ATS in homes, small offices, or places where a short power break is not a big problem. It works well for most basic backup needs.
How often should you test your ATS?
You should test your ATS at least once every month. Regular testing helps you find problems early. This keeps your backup power system ready for emergencies.
The following information may be of interest to you
What to Know Before You Purchase an Automatic Transfer Switch
Automatic transfer switch for solar energy to the grid brings peace of mind fast
The Best Automatic Transfer Switch for Solar Energy in 2025

Automatic-transfer-switch-products.webp)
Latest-automatic-transfer-switch.webp)

