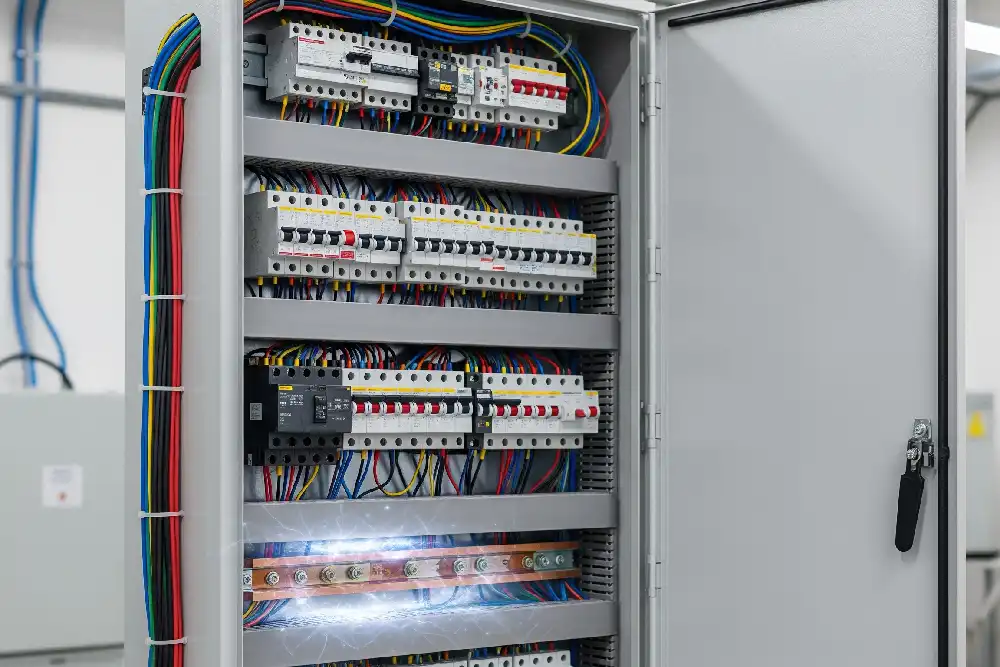
DB means Distribution Board in electrical terms. A Distribution Board controls how electricity moves. It splits power into different circuits. People call this device by many names in the electrical field:
- Panelboard
- Circuit breaker panel
- Breaker panel
- Electric panel
- Fuse box
- DB box
- Consumer unit
- Load center
Knowing the DB Electrical Full Name is important. It helps people stay safe. It also helps them handle electrical power well.
Key Takeaways
- DB means Distribution Board. It splits electrical power into smaller circuits in buildings.
- Distribution Boards keep circuits safe. They use breakers and fuses. These stop power if there is a problem. This helps prevent damage or fire.
- There are different kinds of DBs. Main boards work for whole buildings. Sub-boards are for smaller areas. Consumer units are for homes.
- Picking the right DB is important. You need to check power needs. You should count the number of circuits. Look for safety certifications. Make sure it uses good materials.
- Electricians must install DBs the right way. Regular checks keep DBs safe. This helps them work well for a long time.
DB Electrical Full Name and Meaning
What Does DB Stand For?
DB means Distribution Board in electrical terms. People see this short form in building plans and safety papers. The DB Electrical Full Name helps everyone know the main device that controls power in a building.
A Distribution Board is where electricity comes in and splits into different circuits for safe use.
Sometimes, people get confused because ‘dB’ is used in other ways. Groups like the IEC use ‘dB’ to mean DeciBel, which measures power or sound levels. A.H. Systems says ‘dB’ is the official short form for DeciBel. But when talking about wires and buildings, DB Electrical Full Name always means Distribution Board, not DeciBel.
- ‘dB’ means DeciBel in electronics and telecom.
- The IEC says ‘dB’ is a standard unit for measuring power.
- Suffixes like dBm or dBi show what is being measured, but ‘dB’ stays the same.
- In wiring, DB means Distribution Board, not DeciBel.
Distribution Board Definition
A Distribution Board is a box made of metal or plastic. It holds circuit breakers, fuses, and other safety parts. It gets power from the main supply and splits it into smaller circuits. Each circuit can power a different room or device. The DB Electrical Full Name shows its main job: to share power safely and well.
A Distribution Board keeps people and things safe by stopping electricity if there is a problem. It also helps control and fix different parts of the electrical system. Electricians and building owners use the DB Electrical Full Name to find the main power point in homes, offices, and factories.
Alternative Names
Distribution Boards have many other names in different places. The DB Electrical Full Name can change by country or region. The table below lists some common names:
| Region/Country | Alternative Names for Distribution Boards |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Consumer unit (used in homes) |
| North America | Panelboard, Breaker panel, Electrical panel, Load center |
| General/Other | Enclosure box, Box panel, Distribution cabinet, Meter box, Control box, Electric cabinet, Lighting box, Fuse box |
People may also hear names like DB box, fuse box, or electric panel. These all mean the same kind of device. Knowing the DB Electrical Full Name and other names helps people talk clearly about electrical systems anywhere.
Functions and Importance
Power Distribution Role
A distribution board is the main place for power in buildings. It gets electricity from the main supply. Then it sends power to different circuits. Each circuit gives power to certain things, like lights or outlets. This makes it simple to control power in each area.
Distribution boards help people watch how much energy is used. They also show where you can save power.
The board lets people reach safety devices fast. You can reset breakers or change fuses when needed. There are different types of boards, like main boards and sub-boards. Each type helps handle power in its own way. In homes, the board controls lights, outlets, HVAC, and more.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Main Function | Distributes power to circuits |
| Typical Circuits | Lighting, outlets, HVAC, appliances |
| Control | Isolates circuits for maintenance |
Circuit Protection
Distribution boards keep circuits safe from harm. They use things like circuit breakers and fuses. These stop power if there is too much current. Circuit breakers turn off power if it gets too high. Fuses break the circuit if there is too much current, but you must replace them after.
- Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) stop power during short circuits or overloads.
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs) find leaks and stop electric shocks.
- Residual Current Breakers with Overcurrent Protection (RCBOs) protect from leaks and too much current.
Busbars inside the board send power to each circuit. The main switch lets you turn off the whole board fast in an emergency.
Safety in Electrical Systems
Safety is a very important job for every distribution board. Boards must follow strict rules like IEC, UL, and NEMA. They have things like insulation, covers, and labels to stop accidents.
Only trained electricians should install boards to follow safety rules and lower risks.
Distribution boards use boxes to cover live parts and stop accidents. Surge protection keeps electronics safe from voltage spikes. Ground and neutral bars give safe places for wires, lowering shock risk. Checking and fixing boards often keeps them safe for a long time.
| Safety Feature | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Circuit Breakers/Fuses | Prevent fires and equipment damage |
| Enclosure | Protects from accidental contact |
| Surge Protection | Shields devices from voltage spikes |
| Labels | Aid safe maintenance and troubleshooting |
Types of Distribution Boards
Main Distribution Board
A Main Distribution Board is the main place for power in big buildings. It gets electricity from the main supply. Then it splits the power into smaller circuits. Large buildings like offices and factories use these boards. They help handle lots of electricity. The board has main breakers, bus bars, and surge protectors. These parts help control power and stop overloads. They also let you turn off power fast in an emergency. Many new boards let you check them from far away for safety.
The Main Distribution Board gives safe and steady power to every part of a building.
| Feature/Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Main Breaker | Turns off all power and stops overloads. |
| Bus Bars | Sends power to smaller circuits. |
| Circuit Breakers | Keep each circuit safe from too much power. |
| Safety Features | Has surge protectors and devices that find problems. |
Sub Distribution Board
A Sub Distribution Board gets power from the main board. It sends power to certain places, like floors or work areas. Tall buildings use these boards for each floor. This makes wiring safer and more reliable. If one circuit has a problem, only that spot loses power. Sub boards stop too much power from going to one area.
- Sub boards give control and safety to each area.
- They help spread out the power load.
Sub Distribution Boards make fixing and checking power systems easier in big buildings.
Consumer Unit
A consumer unit is the main power point in homes and small offices. It has things like MCBs, RCDs, and SPDs. The main switch controls all the power from the meter. MCBs keep circuits safe from too much power. RCDs stop shocks by finding faults. RCBOs do both jobs for extra safety.
- Consumer units keep homes safe from power problems.
- Only trained people should install them to follow safety rules.
New consumer units keep homes safe and make repairs easy.
DB Box
A DB box gives power to certain spots, often for short times or outside. Building sites, outdoor parties, and small work areas use DB boxes. These boxes are small and easy to move. They have covers to keep out dust, water, and bumps. DB boxes are not fixed like other boards. They use strong covers and weather-safe parts to stay safe.
| Feature | Distribution Board | Distribution Box |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Handles power for many circuits with breakers. | Gives power to one spot and keeps wires safe. |
| Size & Mobility | Big and stays in one place. | Small, easy to move, good for short-term use. |
| Use Cases | Used in homes, offices, and factories. | Used for short jobs at building sites or events. |
DB boxes are a good choice when you need power for a short time or in different places.
Practical Aspects
Selection Criteria
When you pick a distribution board, you must think about a few things. The board needs to handle all the power your building uses. Electricians add up the wattage of every device and appliance. This helps them make sure the board is safe for the job. The number of circuits depends on what you need to power. If you want to add more things later, pick a board with extra space. This is good if you want solar panels or a car charger in the future.
Safety is very important. The board must follow local rules like NEC or IEC. Look for marks like UL or CE to know it is safe.
A good board is made from materials that do not burn easily. It also keeps out dust and water. Good grounding and bonding help stop electric shocks. Boards should be easy to reach and not near water or danger. The table below shows what to check when picking a board:
| Criteria | What to Check |
|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Matches total wattage |
| Number of Circuits | Sufficient for current and future use |
| Safety Certifications | UL, CE, IEC marks |
| Material Quality | Flame-retardant, corrosion-resistant |
| Location | Dry, accessible, protected |
| Grounding/Bonding | Proper provisions |
Installation Tips
Putting in a distribution board the right way keeps everyone safe. Electricians pick a dry spot with good air flow. They put the board at about 1.5 meters high. Wires must be the right size and connected tightly. Each circuit gets its own breaker or fuse for safety.
Boards must meet rules like NEC or IEC. Using certified parts and clear labels helps keep things safe.
Some mistakes are putting too much power on one circuit or not grounding well. Bad labels can also cause problems. Electricians check the load, use the right tools, and label each circuit. Never put boards near water unless they are protected. Only trained people should do hard installs.
Maintenance
Checking the board often keeps it working well and safe. Electricians look for damage, loose wires, or hot spots. They tighten screws and busbars to stop sparks. Cleaning dust helps stop heat from building up.
Maintenance means testing breakers, changing bad parts, and making sure air can move.
Boards must stay dry and not get rusty. In wet places, electricians seal gaps and use special materials. Tests can find hidden problems. Keeping records helps track fixes and upgrades. At home, people check boards once a year. In big buildings, checks happen more often. Only trained workers should do this work to keep things safe.
DB means Distribution Board. It is very important in every electrical system. Knowing the DB Electrical Full Name helps people see how power moves safely. Distribution boards stop circuits from getting too much power or having problems. They use main breakers, RCDs, and clear labels to keep everyone safe. Checking the board often and using covers stops dust or water from causing harm. People who work with electrical systems should always follow these safety steps.
FAQ
What is the main job of a distribution board?
A distribution board splits electrical power into smaller circuits. It helps control and protect each circuit in a building. This keeps people and equipment safe from electrical problems.
What does a circuit breaker do in a DB?
A circuit breaker stops the flow of electricity if there is too much current. This prevents fires and damage to devices. It acts as a safety switch inside the distribution board.
What should people check before choosing a DB?
People should check the load capacity, number of circuits, safety certifications, and material quality. The board must fit the building’s needs and follow local safety rules.
What is the difference between a main DB and a sub DB?
A main DB controls power for the whole building. A sub DB handles power for a smaller area, like one floor or section. Both help manage and protect electrical circuits.
What happens if a DB is not maintained?
If a DB is not maintained, wires can become loose or damaged. This may cause overheating, power loss, or even fires. Regular checks keep the system safe and working well.
See also
How a Distribution Board Works and Why It Matters
The difference between single-phase and three-phase DB boxes
How to Tell When a Distribution Board Is Overloaded
How to choose the size of the distribution board
Distribution Box Industry Comparison of Types and Uses