People use a molded case circuit breaker to keep circuits safe from too much current or in hard places. MCCBs can stop up to 200,000 amps, so they stop damage when something goes wrong. Places like hospitals and data centers use these breakers to keep power safe and steady.
- More people need electricity now, so we need breakers that fit each job.
- MCCBs have features for different current levels and uses, like in factories or offices. Picking the right breaker helps stop electrical problems and keeps things working well.
Key Takeaways
- Molded case circuit breakers keep electrical systems safe from too much current and short circuits. They are good for places like factories, hospitals, and renewable energy sites.
- MCCBs can be set to fit different machines and safety needs. This helps stop power loss and keeps equipment from breaking.
- These breakers are made strong to work in tough places like mines, ships, and outside. They can handle dust, water, and shaking.
- MCCBs can take more current than other breakers and fuses. They can be used again after they trip. They also give better safety and control.
- Picking the right MCCB depends on current, voltage, where it will be used, and safety rules. Always ask a licensed expert for big or hard projects.
When to Use a Molded Case Circuit Breaker
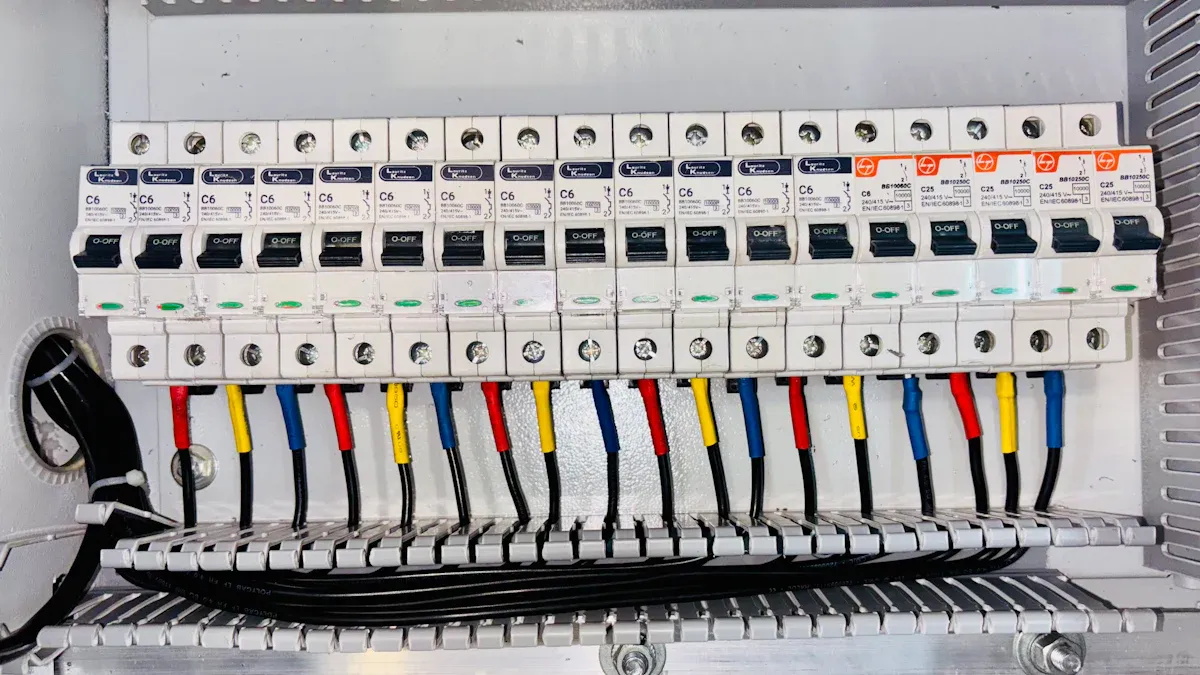

High Current Loads
Some electrical systems need help with high current. Factories and big buildings use lots of power. Renewable energy plants also use much electricity. These places use a molded case circuit breaker for heavy loads. This helps stop damage from short circuits or overloads. MCCBs can stop very high fault currents. They can handle up to 200,000 amps without breaking or burning.
MCCBs are good for:
- Factories with motors, welding machines, and generators
- Solar farms and wind power stations
- Electric vehicle charging stations
The table below explains why MCCBs work for these jobs:
| Feature / Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Interrupting Rating | Can safely stop high fault currents without damage |
| Adjustable Trip Settings | Lets you set protection for each circuit |
| Voltage & Frequency Range | Works with many electrical systems |
| Overload Protection | Bimetallic strips protect against too much current |
| DC MCCB Applications | Used in solar systems for overcurrent and short circuit protection |
| Industrial Applications | Used for motors, welding machines, and generators |
| Specialized Features | Small size, manual reset, selectivity, and strong against the environment |
| Environmental Resistance | Molded case keeps out dust and water, making it last longer |
MCCBs can be set for 16 to 1600 amps. They work with voltages up to 690V. You can adjust trip settings to fit each machine or system. This makes it easy to use a molded case circuit breaker when power needs change or grow.
Critical Safety Needs
Some places cannot risk losing power or unsafe electricity. Hospitals, data centers, and trains need safe and steady power. These places use a molded case circuit breaker because it meets strict safety rules and reacts fast to problems.
MCCBs follow safety rules like UL 489 and UL 489I. These rules make sure breakers pass hard tests for fire, shock, and other dangers. MCCBs must keep working even if the environment changes or if there is a problem inside. This makes them a trusted choice for keeping people and equipment safe.
Note: MCCBs often protect transformers, motors, and capacitor banks in places like factories, farms, mines, and defense. They help with overload, short circuit, and undervoltage protection, and can switch lines and equipment.
Digital and IoT MCCBs add more safety. They let you watch systems from far away and fix problems fast. This helps keep things running and lowers the chance of accidents.
Demanding Environments
Some places are hard on electrical equipment. Dust, water, shaking, and temperature changes can hurt normal breakers. Many engineers pick a molded case circuit breaker for these places because it is strong and reliable.
MCCBs have a small, sealed body that keeps out dust and water. They can handle shaking and last for thousands of cycles, even in tough places. Top brands like Schneider Electric, Siemens, ABB, Eaton, and Legrand make MCCBs for high performance and long life.
- MCCBs protect equipment in:
- Ships and offshore platforms
- Mining sites
- Outdoor renewable energy places
- Factories with big machines
MCCBs have features like manual reset, selectivity, and modular designs. These make them easy to put in, fix, and use for different needs. Tests show MCCBs can handle thousands of ON/OFF cycles without breaking, proving they are reliable.
Tip: Always pick MCCBs from good brands to make sure they are safe and last long in tough places.
Key Features of MCCBs
Adjustable Tripping
MCCBs let you change the tripping settings. This means you can set the breaker for each circuit’s needs. It helps stop power from going out when it is not needed. It also keeps machines safe. Most MCCBs come with factory settings, but installers must check and change them. Safety rules like IEC 60364-6 and local codes say you must test and check often. If you set the breaker right, it only trips when needed. This protects against too much current, short circuits, and earth faults. You need to test and look at the MCCB often to keep it working well. Adjustable tripping makes power systems safe and lets you change things as needed.
Overload and Short Circuit Protection
MCCBs keep circuits safe from too much current and short circuits. They use two main ways to do this:
| Protection Type | How It Works | Standards Met |
|---|---|---|
| Overload Protection | A bimetallic strip gets hot and bends if there is too much current. This makes the breaker trip. | UL 489, IEC 60947-2 |
| Short Circuit Protection | An electromagnet moves fast when there is a big surge. It trips the breaker in a split second. | UL 489, IEC 60947-2 |
These features stop bad currents before they start fires or hurt things. MCCBs turn off power fast to keep people and equipment safe. In places like hospitals, MCCBs must meet special rules like IEC 60601-1 to protect sensitive tools. Picking the right MCCB and setting it up right helps stop shocks and broken equipment.
Manual and Automatic Operation
MCCBs can work by hand or by themselves. Workers can turn off circuits by hand to stay safe during repairs. This stops shocks and keeps workers safe. The automatic part uses thermal and magnetic pieces to trip the breaker if there is a problem. The thermal part helps with too much current. The magnetic part reacts to short circuits. You can change the trip settings to fit what you need. MCCBs can last through over a million uses, so they are very reliable.
Tip: MCCBs give you both manual control and automatic safety, so they are a good pick for tough jobs.
MCCBs vs. Other Breakers
MCCB vs. MCB
Molded case circuit breakers and miniature circuit breakers both keep circuits safe. But they are made for different jobs. MCCBs are best for places that need lots of power and strong safety. MCBs are good for small jobs, like homes or little offices.
| Feature | MCCB | MCB |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Current Ratings | 100 A to 2500 A | Up to 125 A |
| Short-Circuit Capacity | Up to 50 kA at 415 V | Around 16 kA |
| Application Range | Industrial, commercial, utility | Residential, small commercial |
| Trip Settings | Adjustable | Fixed |
MCCBs can handle much more current than MCBs. You can change the trip settings on an MCCB. This makes them better for big buildings, factories, and heavy machines. MCBs have fixed settings and lower limits. They protect things like lights and outlets in houses.
Tip: Pick MCCBs for high current or three-phase systems. Use MCBs for simple, low-power circuits.
MCCB vs. Fuses
Fuses and MCCBs both stop dangerous currents, but they work differently. A fuse melts a wire inside to break the circuit. An MCCB uses a switch that trips and can be reset.
| Device Type | Current Rating Range | Interrupting Capacity | Trip Settings | Reset Capability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuse | Fractions to thousands of Amps | Up to 300,000 A | None (single-use) | Must replace |
| MCCB | Up to 2,000+ A | Up to 200,000 A | Adjustable | Manual reset |
Fuses act fast and can stop very high currents. But when a fuse blows, you must put in a new one. MCCBs can be reset and used again, which saves time and work. MCCBs also let you set the protection more exactly.
Note: MCCBs are good for places where you need quick resets and flexible protection, like factories and data centers.
MCCB vs. Molded Case Switch
A molded case switch looks like an MCCB but works differently. It is just a manual on/off switch for circuits. MCCBs trip by themselves if there is too much current or a short circuit.
MCCBs keep people and equipment safe by stopping bad currents. Molded case switches only turn power on or off. They do not sense or stop faults.
- Use MCCBs when you need safety and automatic protection.
- Use molded case switches for simple power control without protection.
MCCBs give you both control and safety, so they are the best pick for tough and important jobs.
Molded case circuit breakers are best for places with lots of current, strict safety rules, or tough conditions. They can handle up to 1,000 volts AC and 1,200 volts DC. Their interrupt ratings start at 5,000 amps. Many industries use a molded case circuit breaker to keep things safe. The table below shows what makes MCCBs special:
| Feature | Benchmark / Statistic |
|---|---|
| Interrupting Capacity | Over 200,000 A |
| Voltage Range | Up to 1,500 V (DC for renewables) |
| Customization | Arc-flash, IoT, modular designs |
| Market Adoption | 65% in commercial, 45% in utilities |
Checklist for MCCB Use:
- Needs lots of current or high voltage
- Needs very safe power or no downtime
- Works in rough or changing places
For big or risky projects, always have a licensed expert check the system.
FAQ
What makes a molded case circuit breaker different from other breakers?
A molded case circuit breaker has a tough, sealed shell. It can handle more current than most other breakers. You can change the trip settings for different needs.
What should someone check before choosing an MCCB?
Someone should check the current rating and voltage. They also need to look at the environment. The type of load and safety rules matter too. These steps help pick the right MCCB for the job.
What happens if an MCCB trips?
If an MCCB trips, it stops electricity from flowing. This keeps people and equipment safe from harm. You can reset the breaker after fixing the issue.
What industries use MCCBs the most?
Industries like factories, energy, healthcare, and transport use MCCBs a lot. These places need strong protection for big machines and important systems.
The following information may be of interest to you
What You Need to Know About How Molded Case Circuit Breakers Work
Key factors to consider when choosing a molded case circuit breaker
MCB and MCCB Compared Which Circuit Breaker Is Right for You
Exploring the Components of Molded Case Circuit Breakers

Molded-case-circuit-breaker-125-ampere-4P.webp)

