DIN rail circuit breakers help keep electrical systems safe at home and work. These devices protect against electrical problems. This helps stop damage and lowers risks. Their modular design lets people add or change parts easily. This makes upgrades and repairs simple. Many people pick DIN rail circuit breakers because they are easy to install. They also fit well in new panels. More people want these breakers each year. The global market is growing by about 5% every year. This is because of new technology and more need for safety.
Key Takeaways
- DIN rail circuit breakers stop too much electricity and short circuits. They help keep homes and factories safe. Their design lets you snap them on and off easily. This makes putting them in, fixing, or changing them simple. You need to pick the right breaker for your system. Match the current, voltage, and safety ratings to what you need now and later. Clean, test, and change old parts often. This helps breakers last 15 to 20 years and work well. Always look for the right certifications. Follow safety rules to keep your system safe and legal.
DIN Rail Circuit Breaker Basics

What Is a DIN Rail Circuit Breaker
A DIN rail circuit breaker is a safety device in electrical panels. It keeps circuits safe from too much current. People use these breakers at home and in factories. They are also used in control panels. The name “DIN rail” comes from the metal rail it sits on. This rail follows the EN 50022 standard. Most DIN rails are 35 mm wide and 7.5 mm high. Devices snap onto the rail, so they are easy to install.
Here is a table that lists the main details for DIN rail mounting:
| Specification Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Standard | EN 50022 (DIN 46277, BS 5584) |
| Rail Type | Top hat rail (TS35, TH35, Type O) |
| Rail Width | 35 mm |
| Rail Height | 7.5 mm (15 mm deep version also exists) |
| Mounting Method | Snap-on mounting |
| Module Width Unit (1M) | 18 mm |
| Device Width Examples | 1 module (18 mm), 2 modules (36 mm), 4 modules (72 mm) |
| Application | Low voltage switchgear and control gear, including circuit breakers |
DIN rail circuit breakers have different pole types. A single-pole breaker protects one circuit. Two-pole, three-pole, and four-pole breakers protect more circuits or three-phase systems. People use these breakers in control panels and automation systems. They are also used in branch circuits.
How It Works
A DIN rail circuit breaker keeps circuits safe from overcurrent, overload, and short circuits. It uses two trip mechanisms: thermal and magnetic.
- Thermal Trip Mechanism
The breaker has a bimetallic strip inside. If too much current flows for a long time, the strip gets hot and bends. This bending opens the contacts and stops the electricity. This helps protect against overloads that last a while. - Magnetic Trip Mechanism
The breaker also has a coil that makes a magnetic field. If a short circuit happens, the current rises very fast. The strong magnetic field pulls a lever and opens the contacts right away. This protects the circuit from sudden faults.
Tip: Thermal trips work slowly to avoid false alarms. Magnetic trips act fast to stop big faults.
Here is a table that compares the two trip mechanisms:
| Feature | Thermal Trip Mechanism | Magnetic Trip Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Bimetallic strip bends when heated by overcurrent | Electromagnetic coil trips instantly on high current |
| Response Time | Delayed; faster for bigger overloads | Instantaneous; reacts to short circuits |
| Protection Type | Prolonged moderate overloads | Sudden short circuits and heavy faults |
| Sensitivity | Sensitive to heat and ambient temperature | Sensitive to current magnitude |
| Operation | Strip bends and trips latch | Magnetic field pulls plunger to trip breaker |
| Purpose | Avoids nuisance trips, trips on sustained overloads | Fast disconnection to prevent damage |
| Time Delay | Yes | No intentional delay |
| Combined Use | Often combined for full protection | Often combined for full protection |
Most DIN rail circuit breakers use both trip types. This gives better protection for homes and industry. The breaker can handle slow overloads and fast short circuits. The actuator lever lets people reset the breaker after it trips. The lever also shows if the breaker is on or off.
DIN rail circuit breakers have different voltage ratings. People must pick the right rating for their system. These breakers help keep electrical systems safe and working well.
Key Features
Current Ratings
Current ratings show how much electrical current a circuit breaker can handle safely. DIN rail circuit breakers come in many current ratings to fit different needs. People can find models for both homes and factories. The ratings range from 0.5 amps up to 63 amps. This wide range helps protect small devices and large machines. The table below shows common ratings and other details:
| Poles | Voltage (AC/DC) | Frequency (Hz) | Rated Current Range (Amps) | Short Circuit Rating (Amps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,2,3 | Up to 415 VAC | 50/60/400 | 0.5 to 63 | Up to 10,000 |
| 1,2 | Up to 220 DC | N/A | 0.5 to 63 | Up to 10,000 |
| 1,2,3 | 240 VAC | 50/60 | 0.5 to 63 | 3,000 to 6,000 |
| 2,3 | 415 VAC | 50/60/400 | 0.5 to 50 | 3,000 to 6,000 |
Trip curves help match the breaker to the type of load. Type B works for homes and lights. Type C fits small motors. Type D and K suit heavy machines. Type Z protects sensitive equipment.
Interrupting Capacity
Interrupting capacity tells how much fault current a breaker can stop safely. DIN rail circuit breakers often have interrupting capacities up to 6,000 amps. Some models reach 10,000 amps for tough jobs. This feature keeps people and equipment safe during big faults. The chart below compares interrupting capacities for different breaker types:
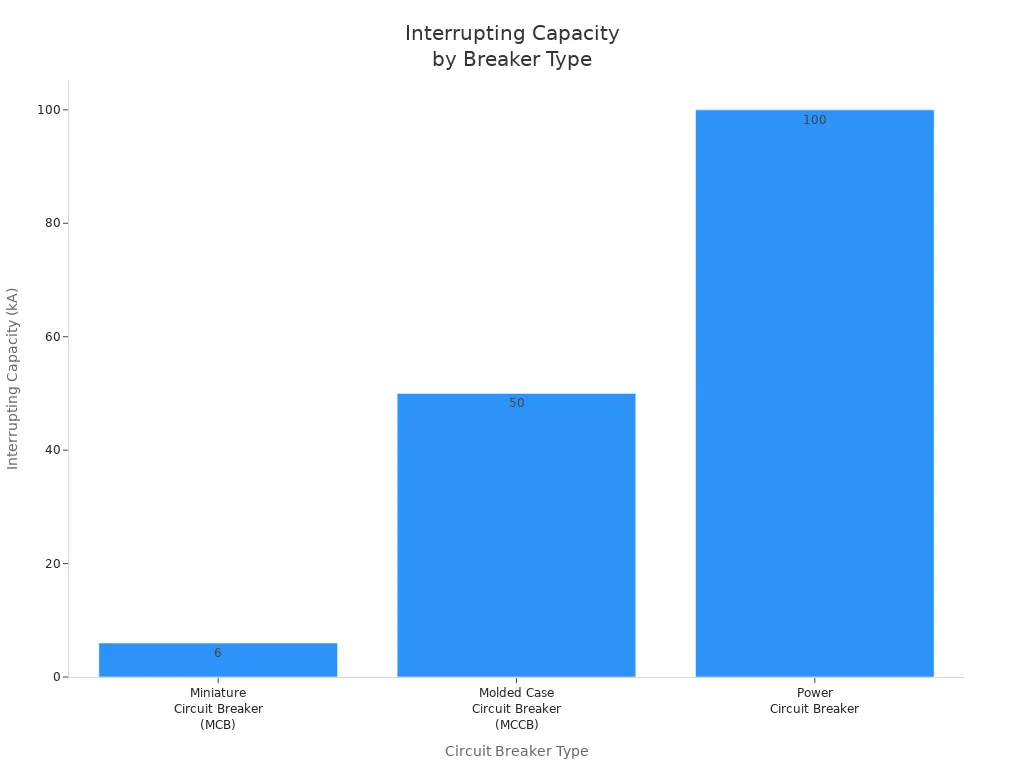
Miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) work well for homes and small businesses. Molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) handle bigger loads in factories. Power circuit breakers protect large systems in substations.
Certifications
Certifications show that a DIN rail circuit breaker meets safety rules. The most important ones are UL 489 and UL 1077. These come from Underwriters Laboratories. UL 489 is for main circuit protection. It needs strict testing and high safety. UL 1077 is for extra protection inside equipment. It has less strict tests.
- UL 489 is needed for main panels and branch circuits in North America.
- UL 1077 is used for extra safety inside machines or devices.
- Both certifications help people choose the right breaker for their needs.
Many DIN rail circuit breakers also have other marks, like TUV or CSA. These show the breaker is safe for use in many countries. The modular design lets people add or change breakers easily. This helps with upgrades and repairs.
Note: Always check for the right certification before choosing a breaker for your system.
Choosing a DIN Rail Circuit Breaker
Assessing Needs
People need to know what their electrical system needs first. They should check if they use lights, heaters, or motors. Each one uses a different amount of current. Add up the current for all devices to stop overloads. It is smart to add a safety margin of 125% for things that run all the time. This gives extra safety. People must also look at the voltage, like 220V or 440V. The breaker’s short-circuit rating should be higher than the biggest fault current. Hot or wet places can change how well the breaker works. Some places need special breakers for tough conditions. Always follow local safety rules to keep the system safe and legal.
Tip: Think about adding more devices later. Pick a breaker with a higher rating to be ready for future needs.
Selection Steps
There are a few steps to pick the right DIN rail circuit breaker:
- Add up all the electrical loads. Keep the load at or below 80% of what the breaker can handle.
- Check the rules in your area to make sure the breaker is allowed.
- Find a spot in the panel that matches the needed amps and volts.
- Pick the right breaker type and number of poles for your circuit.
- Turn off the main power and use a tester to make sure it is safe.
- Snap the breaker onto the DIN rail and connect it to the busbar.
- Attach the wires tightly to the breaker and ground busbar.
- Turn the power back on and test if the breaker works.
- Label the breaker so you know what it controls.
You can use terminal blocks, relays, and mounting kits to help with wiring. These parts keep the panel neat and make changes easier later.
Home vs. Industry
Homes and factories need different things. In homes, people use single-pole or double-pole breakers for lights and outlets. These breakers stop overloads and short circuits in small circuits. Factories may need three-pole or four-pole breakers for big machines or three-phase power. Industrial breakers must handle more current and bigger faults. They also need to fit in bigger boxes and connect to busbars. The right size, like the 35mm DIN rail, helps them fit. Steel or aluminum is picked for strength or the environment. Factories often use contactors and PLCs in panels for more control and automation.
Installation and Applications

Installation Tips
Putting circuit breakers in panels keeps people and things safe. Before starting, check the panel for rust or damage. Always turn off the power and use a tester to make sure. Follow the maker’s steps, like how tight to make screws and where wires go. Pick the right size and type of breaker for the job. Make sure all wires are tight and use the right thickness. Use tools with covers to stop shocks. After snapping the breaker onto the DIN rail, test it by making a fake problem and see if it trips. Label everything clearly and update your notes for later.
Tip: Never work on panels with power on. Do not put too much load on a breaker. If you are not sure, ask an electrician for help.
Maintenance
Taking care of circuit breakers helps them last longer. Look at them often to find dust, rust, or loose parts. Clean them to stop dirt from making them too hot. Check if the moving parts work well. Test if the breaker trips when it should. Oil the moving parts so they do not wear out fast. Change any broken or old parts right away. Keep panels dry and cool to stop water and dust from hurting them. Make a plan to check and clean them on time. Most circuit breakers work for 15 to 20 years if you take care of them.
- Check and clean breakers often.
- Test if they work right.
- Change old or broken parts fast.
- Keep panels dry and clean.
Common Uses
Circuit breakers stop too much current and short circuits. In homes, they protect wires for lights and plugs. In factories, they help control panels and big machines like motors. DIN rails can hold breakers, relays, terminal blocks, and power supplies. This makes it easy to change or add new parts. Companies like Schneider Electric, Siemens, Eaton, and ABB make many kinds of breakers. Some have smart features and save energy.
| Brand | Distinguishing Features |
|---|---|
| Schneider Electric | Smart tech, energy efficiency, global presence |
| Siemens AG | Advanced protection, innovation, strong distribution |
| Eaton Corporation | Wide range, sustainability, customer focus |
| ABB | Key player, broad product line |
DIN rail circuit breakers help keep electrical systems safe and working well.
- They stop too much current, short circuits, and earth faults. This helps stop fires and keeps equipment safe.
- Their small size and simple setup work for homes and factories.
- New features and standard parts make them easy to use and fix.
Knowing these things helps people pick the right breaker and keep things running.
FAQ
What makes a DIN rail circuit breaker different from a regular breaker?
A DIN rail circuit breaker snaps onto a standard metal rail. This design allows easy installation and removal. Regular breakers often bolt into place. DIN rail breakers fit well in modular panels for homes and industry.
What should someone check before installing a DIN rail circuit breaker?
They should check the voltage and current ratings. The breaker must match the system. They also need to inspect the panel for damage. Using the correct size and type keeps the system safe.
What types of loads can DIN rail circuit breakers protect?
DIN rail circuit breakers protect lights, outlets, motors, and control panels. They work for both small home circuits and large industrial machines. The right breaker type depends on the load’s size and use.
What certifications should a DIN rail circuit breaker have?
A DIN rail circuit breaker should have UL 489 or UL 1077 certification. These marks show the breaker meets safety standards. Some breakers also have TUV or CSA marks for use in other countries.
What maintenance does a DIN rail circuit breaker need?
They need regular checks for dust, rust, and loose parts. Cleaning and testing help prevent problems. Replacing worn or damaged parts keeps the breaker working well. A simple schedule helps extend the breaker’s life.
The following information may be of interest to you
What is a DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker and how does it work
How to Install Circuit Breakers on DIN Rails Step by Step
Top 2 Pole Miniature Circuit Breakers for Home Use in 2025
Manual transfer switch Din rail 63A
Step by Step Guide to Installing Miniature Circuit Breakers