You need to select the right Size of MCB when connecting solar panels. This helps protect your system from overloads and short circuits. Choosing the correct breaker keeps your solar setup safe and reliable. You can figure out the right size with a few simple steps. Anyone can do this with basic information about their solar system.
Key Takeaways
- Always pick a DC-rated MCB that matches or is higher than your solar system’s highest current and voltage. This keeps your system safe. – To find the right MCB size, multiply your solar panel’s highest current by 1.25 two times. Then round up to the next standard size. This helps stop the MCB from tripping too often. – Use single-pole MCBs for small systems. Use double-pole MCBs for bigger or grid-connected solar setups. This gives better protection. – Choose good quality, certified MCBs with safety marks like CE or TUV. This makes sure they work well and last a long time. – Think about cable size, temperature, and the environment when picking MCBs and cables. This helps stop overheating and voltage drops.
Size of MCB for Solar Panels
Recommended Ratings
To pick the right Size of MCB for your solar panels, use a simple rule. Find out the highest current your solar panels can make. Multiply this number by 1.25 to add a safety margin. Some experts say to multiply by 1.25 again for extra safety. The formula looks like this:
MCB Size = Maximum Panel Current × 1.25 × 1.25
Always round up to the next standard MCB size. This helps stop the MCB from tripping too often and keeps your system safe.
Tip: Always check the voltage rating on your MCB. The voltage rating should be the same as or higher than your solar system’s highest voltage. Most home solar systems need an MCB rated for at least 48V DC. Bigger systems might need up to 1,000V.
You also need to check the current rating. The MCB current rating should be as high as or higher than the most current your panels can make. This keeps your wires and equipment safe from too much current or short circuits.
Here are some important things to remember:
- Match the MCB current rating to your system’s highest current.
- Make sure the voltage rating is the same as or higher than your system’s voltage.
- Pick the right type of MCB (single-pole for small systems, double-pole for bigger or grid-connected systems).
- Look for certifications like TUV or CE for safety.
- Choose an MCB with enough breaking capacity to handle fault currents.
Common Sizes
Some MCB sizes are used more often in solar panel setups. For a normal home solar system (about 4kW), the most common Size of MCB is 16A. This size works well for many homes and does not trip too much.
Sometimes, manufacturers suggest higher ratings for certain inverter models. For example:
- ABB says to use a 20A MCB for their 3.6TL inverter and a 25A MCB for their 4.2TL inverter.
- SMA recommends up to 32A for their 3000TL to 5000TL inverter range.
You can see the usual ratings in the table below:
| Parameter | Typical Values / Range | Application Context |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 48V DC to 1,000V DC | Solar panel arrays (residential/commercial) |
| Rated Current | 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, up to 63A | Depends on system size and inverter model |
| Breaking Capacity | 6 kA to 10 kA | Residential and commercial solar systems |
For small systems, like a single 200W panel, you might use a 6A or 10A MCB. For a 4kW system, a 16A or 20A MCB is common. Bigger systems may need 25A, 32A, or even higher.
- MCBs for solar panels are usually low voltage (up to 1,000V).
- Always pick the Size of MCB based on your system’s highest current and voltage.
- Single-pole MCBs are good for small, simple systems. Double-pole MCBs give more safety for bigger or grid-connected systems.
Note: Always check your inverter and panel details before picking the Size of MCB. This makes sure your solar setup is protected the right way.
MCB Size Calculation
Step-by-Step Method
You can calculate the right Size of MCB for your solar panels by following a simple process. Start by finding the short circuit current (Isc) of your solar panel. You will see this value on the panel’s label or in the datasheet. This number shows the highest current your panel can produce.
Next, add a safety margin. The National Electrical Code (NEC) recommends multiplying the Isc by 1.25. This step protects your system from small changes in sunlight or temperature. For even more safety, multiply by 1.25 again. This gives you a total safety factor of 1.56.
Here is the formula you should use:
MCB Size = Isc × 1.25 × 1.25
After you get the result, round up to the next standard MCB size. For example, if your calculation gives you 14.5A, choose a 16A MCB. This step makes sure your breaker will not trip during normal use.
You also need to check the voltage rating. The MCB must match or exceed the highest voltage in your solar system. For most home systems, you need at least a 48V DC rating. Larger systems may need up to 1,000V DC.
Tip: Always check both the current and voltage ratings before you buy an MCB. This helps you avoid damage and keeps your system safe.
Safety Margins
Safety margins protect your solar system from unexpected problems. These margins help your MCB handle extra current during hot days or when sunlight is very strong. The NEC and many experts support using these safety factors.
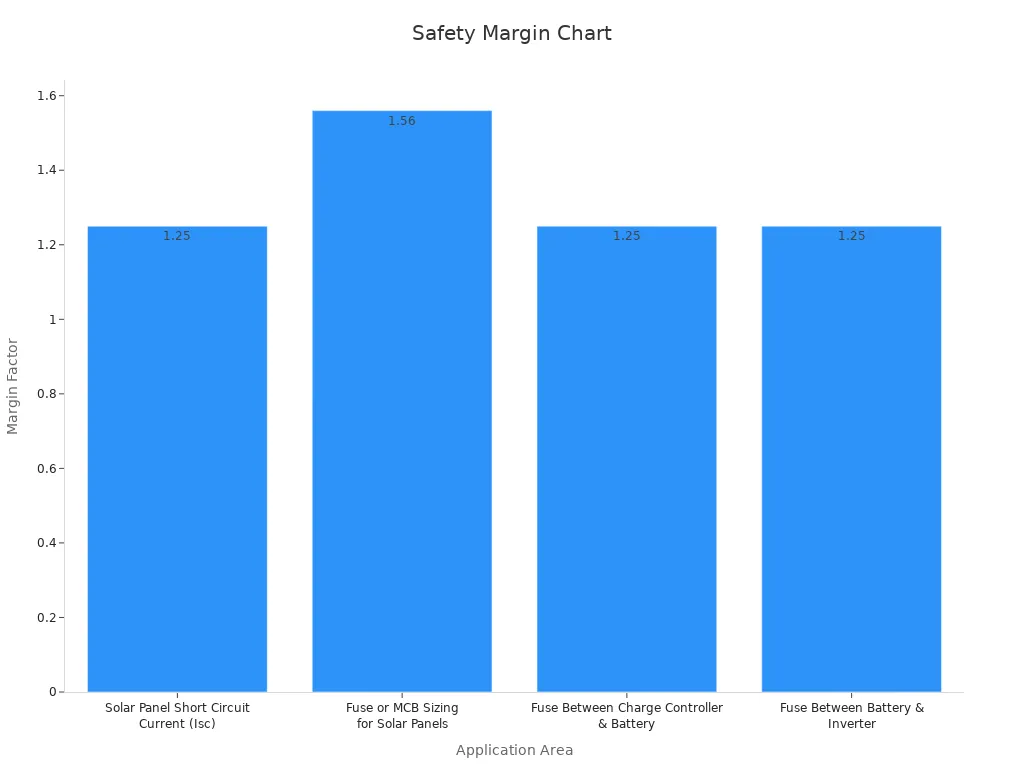
The table below shows the main safety margin factors for solar panel systems:
| Application Area | Safety Margin Factor | Explanation / Calculation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Panel Short Circuit Current (Isc) | 1.25 | NEC requires 1.25 times Isc as a base safety margin. |
| Fuse or MCB Sizing for Solar Panels | 1.56 (1.25 x 1.25) | Additional 1.25 factor applied to Isc margin, total 156% rating. |
| Fuse Between Charge Controller & Battery | 1.25 | Fuse rating = Charge Controller rated current x 1.25. |
| Fuse Between Battery & Inverter | 1.25 | Fuse rating = (Inverter Watts / Battery Voltage / Efficiency) x 1.25. |
You can also see these safety margin factors in the chart below:
Another important rule is the 120% rule for panel busbars. This rule says the total current from all sources, including solar panels, should not be more than 120% of the busbar rating. This keeps your system safe during high production times.
Note: Always use the correct Size of MCB and follow these safety margins. This will help you avoid fires, equipment damage, and power loss.
DC vs. AC MCBs
Key Differences
You might wonder if you can use any breaker for your solar panels. The answer is no. DC and AC MCBs have important differences. You need to know these differences to keep your solar system safe.
- Current Flow: DC current flows in one direction and does not cross zero. AC current changes direction and crosses zero many times each second. This makes DC harder to interrupt.
- Arc Handling: When you switch off a DC circuit, the current tries to keep flowing. This creates a strong arc. AC breakers can stop arcs easily because the current drops to zero. DC breakers need special parts to break the arc safely.
- Design Features: DC MCBs use arc extinguishing chambers and stronger materials. These features help them handle high DC voltages, sometimes up to 1,000V. Some DC breakers, like the CHINT Ex9BP series, also have visual indicators and can work with wires in any direction.
- Standards and Ratings: DC MCBs follow strict standards like IEC/EN 60947-2. They offer high breaking capacity, often up to 6kA, and support a wide range of current loads from 10A to 63A.
Note: The growth of solar power and electric vehicles means more systems use DC. This makes DC-rated MCBs even more important for safety.
Why DC-Rated is Essential
You must use DC-rated MCBs for solar panels. Using an AC breaker in a DC circuit can cause serious problems.
- DC current does not stop or reverse. AC breakers may not trip or may trip too soon, leaving your system unprotected.
- AC breakers do not have the right parts to stop DC arcs. This can lead to fire or damage.
- DC MCBs have special designs to handle the strong arcs in solar systems. They protect your home and equipment.
- DC breakers meet safety rules and work well with high voltages found in solar arrays.
- You can use DC MCBs in many places, like rooftop solar, off-grid homes, and even large solar farms.
⚠️ Always choose a DC-rated MCB for your solar panels. This simple step keeps your system safe and reliable.
Other Selection Factors
Cable Size
Picking the right cable size is very important. The cable size helps control how much electricity can move safely. If the cable is too thin, it can get too hot. This can even start a fire. For example, a 2.5 mm² cable can carry 18 to 24 amps. If you use more current, the cable gets hot and wastes energy. Long or thin cables can also cause voltage drop. If you use a 2.5 mm² cable for 10 amps over 20 meters, you lose over 3% of your power. This means your solar system will not work as well.
Most homes use 4 mm² cables for systems under 3kW. Bigger systems or longer cables need 6 mm² cables. Here is a simple guide:
| Cable Size | Current Capacity (Amps) | Recommended System Capacity | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4mm² | 40-50A | Small residential (<3kW) | Good for short runs |
| 6mm² | 60-70A | Larger (5kW+) or long runs | Best for longer distance |
Tip: Always check the cable length and current before you choose. Thicker cables help stop voltage drop and keep your system safe.
Temperature & Environment
The outside temperature can change how your MCB works. When it is hot, the MCB might trip faster than you think. In tests, experts saw that MCBs react quicker when it is warm. This is because the inside parts heat up faster. If your solar system is outside, sunlight and heat can affect the cables and the MCB. You should pick cables and breakers that can handle sun and high heat. This helps your system last longer and stay safe.
Product Quality
You should always pick good quality, certified products for your solar system. Good MCBs have marks like ISO 9001, CE, and RoHS. These marks show the product passed tough safety and quality tests. Some brands also test their MCBs for weather and electric safety. Here is a table of common certifications:
| Certification Type | Details |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system |
| CE | European safety standard |
| RoHS | Limits hazardous substances |
Choosing certified products makes sure your Size of MCB and other parts will protect your home and work well for a long time.
You can pick the right Size of MCB for your solar panels by using some easy steps. Always use DC-rated breakers and figure out the size with a safety margin. Keep these tips in mind to stay safe:
- Find out your system’s highest current and voltage.
- Add 25% more to your current number for safety.
- Use breakers that are certified and good quality.
- Think about future upgrades and your local weather.
If you are not sure, ask an expert for help.
FAQ
What happens if you use the wrong size MCB for solar panels?
If you use the wrong size MCB, your system may not work safely. A small MCB trips too often. A large MCB may not protect your wires or equipment from damage.
What is the difference between DC and AC MCBs?
DC MCBs break direct current safely. AC MCBs work with alternating current. You must use a DC MCB for solar panels because it handles the strong arcs that DC power creates.
What should you check before buying an MCB for solar panels?
You should check the current rating, voltage rating, and certification. Make sure the MCB matches your system’s needs. Look for marks like CE or TUV for safety.
What size MCB do you need for a 4kW solar system?
Most 4kW home solar systems use a 16A or 20A MCB. Always check your panel and inverter details before you choose the final size.
What is the 120% rule in solar panel installations?
The 120% rule means the total current from all sources should not go over 120% of the panel busbar’s rating. This keeps your system safe during high power
production.
The following information may be of interest to you
How to calculate the capacity of a circuit breaker
The difference between miniature circuit breakers and fuses
What Is a Thermal Magnetic MCB and How Does It Work
What Type of Breaker Works Best for a 1.5 Ton AC Unit
What size of wire is needed for a 30 ampere circuit breaker



