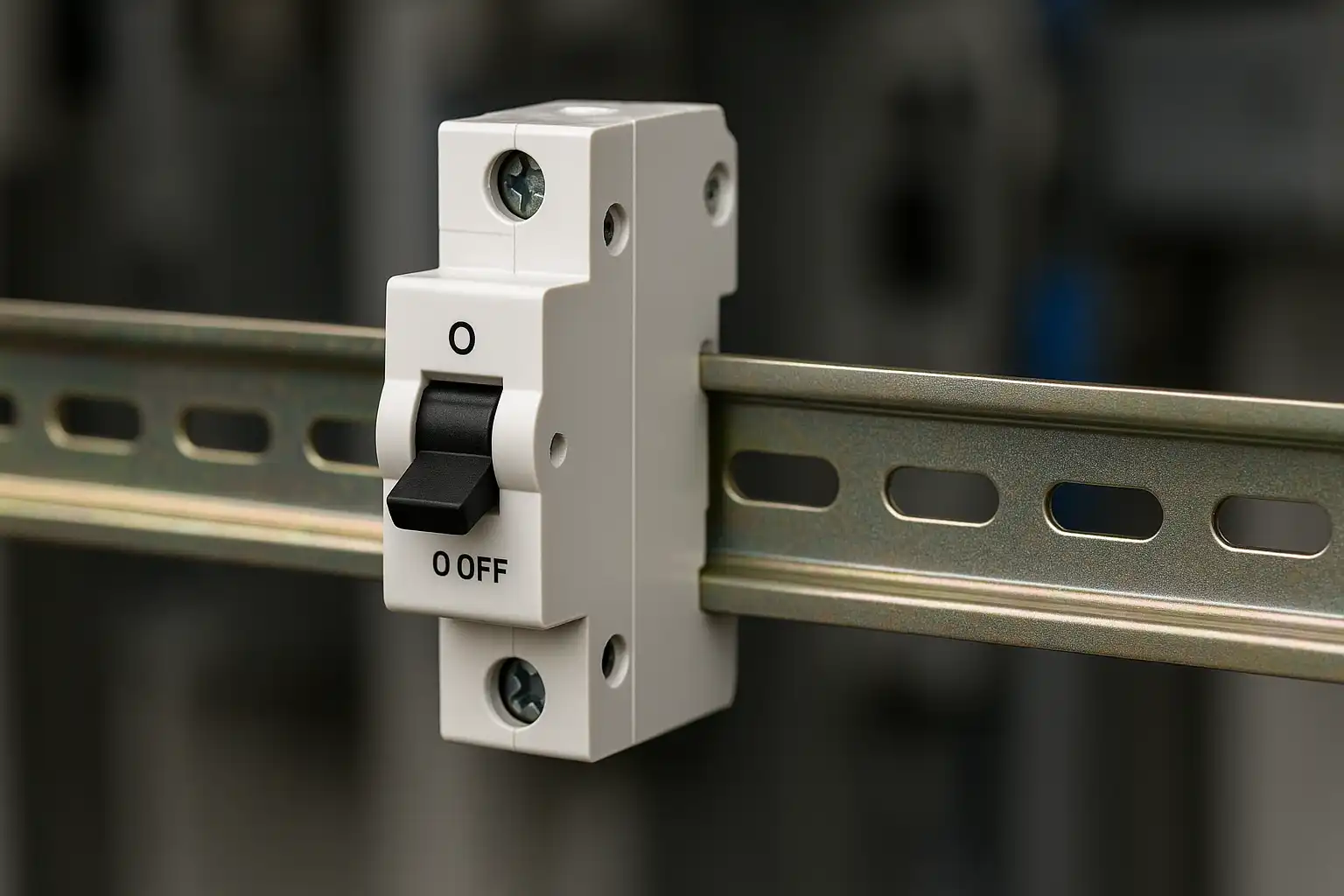
A DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker is a small device. It protects electrical circuits from getting damaged. It stops electricity if there is too much current or a short circuit. You can think of it as a safety switch you can reset. It helps stop electrical problems. People who work with electrical systems should know how it works. This helps keep people and equipment safe.
Key Takeaways
- A DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker keeps circuits safe. It stops too much current or short circuits fast and safely.
- These breakers clip onto a 35 mm DIN rail. This makes putting them in quick and simple. You can also upgrade or change them easily.
- They use heat and magnets to find overloads and short circuits. Then, they open the circuit to stop harm.
- You must wire them carefully and follow safety rules. This helps the system work well and stay safe.
- These breakers protect people and equipment in many places. They work in homes, offices, factories, and solar systems. They give strong and resettable protection.
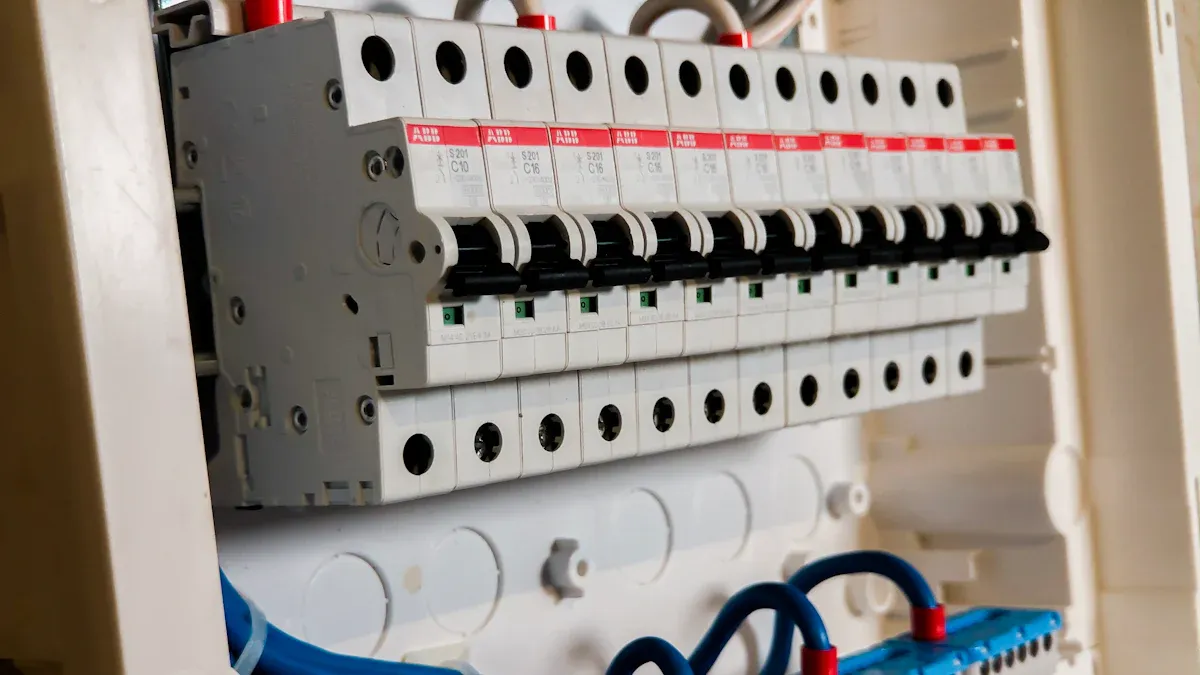
DIN Rail Mounted Miniature Circuit Breaker
Main Features
A DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker keeps circuits safe in many places. It snaps onto a 35 mm DIN rail. This rail helps you install it fast and safely in panels. The modular design lets you add or take out breakers easily. Each breaker sits next to others, so the system can change as needed.
Key features include:
- Current Ratings: These breakers come in many sizes. Some protect small circuits. Others work for bigger loads. Most range from 1 ampere to 63 amperes.
- Voltage Levels: Most breakers work with voltages in homes and businesses. Some are made for higher voltages in factories.
- Pole Configurations: You can pick single-pole, double-pole, or three-pole types. The choice depends on the circuit and how much protection you need.
- Compliance: Many breakers follow safety rules. UL489 and UL1077 are common in North America. These rules make sure the breaker is safe and works well.
Note: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) made the IEC 60715 rule. This rule sets the size and shape of DIN rails. It helps breakers from different brands fit and work together. RoHS compliance is also important. It means the breaker does not have harmful materials. This makes it safer for people and nature.
Components
A DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker has a few main parts. Each part helps keep the circuit safe.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Housing | Holds all parts together and keeps them safe |
| Toggle Switch | Lets you turn the breaker on or off |
| Terminal Clamps | Connect wires to the breaker |
| Trip Mechanism | Senses too much current and opens the circuit |
| Arc Chute | Puts out sparks when the breaker trips |
The housing is made of strong plastic. It keeps the inside parts safe and stops shocks. The toggle switch is on the front. You use it to reset the breaker after it trips. Terminal clamps hold the wires tight. The trip mechanism is the main part. It senses if the current gets too high. If this happens, it opens the circuit to stop electricity. The arc chute puts out sparks when the breaker trips.
Companies like Siemens, Schneider Electric, and ABB make many DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker types. These companies follow strict rules to keep their products safe and reliable. Governments and safety groups want these breakers to meet high standards. This helps protect people, equipment, and buildings from electrical problems.
How It Works
Overcurrent Protection
A DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker protects electrical circuits from too much current. It uses two main methods: thermal and magnetic. The thermal part reacts to slow, steady increases in current. The magnetic part responds to sudden spikes, like a short circuit.
The thermal mechanism uses a small metal strip called a bimetallic strip. When too much current flows, the strip heats up and bends. This bending action opens the circuit and stops the flow of electricity. The magnetic mechanism uses a coil. If a large surge of current passes through, the coil creates a strong magnetic field. This field moves a lever that quickly opens the circuit.
Manufacturers design these breakers with different trip curves. A trip curve shows how fast the breaker will react to different levels of current. For example, Trip Curve C is common in homes and offices. It trips quickly when the current is five to ten times higher than normal. This helps protect both people and equipment.
Tip: Always check the trip curve before choosing a breaker. The right curve keeps the system safe and avoids false trips.
Trip Mechanism
The trip mechanism is the heart of the breaker. It works in steps to keep the circuit safe.
- Normal Operation
The breaker stays closed. Electricity flows through the circuit. The bimetallic strip and magnetic coil stay at rest. - Overload Condition
Too many devices or a faulty appliance can cause an overload. The bimetallic strip heats up slowly. When it bends enough, it pushes a latch. The latch opens the contacts and stops the current. - Short Circuit Condition
A short circuit sends a huge surge of current through the breaker. The magnetic coil reacts instantly. It pulls a lever that snaps the contacts open. This action happens in less than a second. - Resetting the Breaker
After a trip, the user can flip the toggle switch to reset the breaker. The contacts close, and the circuit works again. If the problem is still there, the breaker will trip again.
| Condition | Response Time | Mechanism Used |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | Always On | None |
| Overload | Several Seconds | Thermal (Bimetallic) |
| Short Circuit | Instant | Magnetic Coil |
A DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker uses these steps to protect circuits every day. It keeps homes, offices, and factories safe from electrical dangers.
Installation
DIN Rail Mounting
Safety comes first when installing. Electricians turn off all power before starting. They use lockout-tagout steps to stay safe. They wear gloves and goggles to avoid getting hurt. Installers measure carefully with a tape and level. They drill holes to fit the DIN rail flat on the wall. DIN rails are usually 7.5 mm or 15 mm tall. This size matters for which breakers and parts will fit.
Here are the steps to mount:
- Line up the miniature circuit breaker with the DIN rail, top first.
- Push the breaker onto the rail until you hear a click.
- To take it off, push the bottom and lift the top a little.
For wiring, strip 11–13 mm of insulation from each wire. Use crimp-style lugs that fit the wire size. Tighten the wires with an electric screwdriver set to 2.0 N.m. You can feed wires from the top or bottom. Pick what fits best for space and repairs. Always follow the maker’s rules for load and mounting. This keeps the system safe and working right.
Tip: Always use the wiring diagram from the maker for correct setup.
You can use single-pole, double-pole, or multi-pole breakers. This makes it easy to add or remove breakers. The system is modular and simple to fix.
Accessories
Accessories help the system work better and safer. All accessories must meet rules like IEC 60715, CE, TUV, and ISO. These rules make sure parts fit, are safe, and work well. The 35 mm DIN rail keeps things steady and stops shaking. This helps breakers and accessories last longer. RoHS rules mean no dangerous stuff is used. This keeps people and nature safe.
| Specification Aspect | Details / Values |
|---|---|
| Rated Current | 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A |
| Rated Operating Voltage (VDC) | 12V, 24V, 48V, 300V, 600V, 900V, 1200V |
| Rated Insulation Voltage Ui | 1250 VDC |
| Rated Impact Voltage Uimp | 6 kV |
| Ultimate Breaking Capacity Icu | 6 kA |
| Run Breaking Capacity Ics | 100% of Icu |
| Mechanical Endurance | Actual average: 20,000 operations; Standard: 8,500 operations |
| Electrical Endurance | Actual average: 2,500 operations; Standard: 1,500 operations |
| Wiring Capacity | For In ≤ 32A: 1.5 |
| Ambient Temperature Range | -20°C to +70°C |
| Altitude | Up to 2000 meters |
| Relative Humidity | Up to 95% |
| Pollution Level | Levels 2 and 3 |
| Installation Environment | No obvious shock and vibration |
| Installation Category | Class II, Class III |
| Installation Method | Standard DIN rail mounting |
| Dimensions (W x H x D in mm) | Width options: 18, 36, 54, 72; Height: 98; Depth: 71 |
| Weight (kg) | 0.12 to 0.48 depending on size |
Some extra features are a two-stage spring buckle for a tight fit, side heat strips for better airflow, and a shell that does not burn easily. Modular designs can use up to four poles. Many accessories have a window to show if contacts are open or closed.
Benefits
Safety
A miniature circuit breaker on a DIN rail keeps people safe. It also protects equipment from harm. The breaker stops electricity if it senses danger. This fast action helps stop fires and keeps wires safe. The strong plastic housing blocks electric shocks. Users can reset the breaker with the toggle switch after fixing problems. Many breakers follow strict safety standards. These rules make sure the device works well in homes, offices, and factories.
Note: Regular checks help keep the system safe. Electricians should test breakers to make sure they trip at the right time.
The modular design makes replacement easy. If one breaker fails, a technician can swap it out. They do not need to touch other parts. This feature cuts downtime and keeps things running smoothly.
Applications
People use these breakers in many places. In homes, they protect lights and outlets. In offices, they guard computers and other devices. Factories use them to keep machines safe. The modular system fits well in power panels. It also works in automation systems where machines need steady power. Solar power systems use these breakers as disconnects. This setup makes it easy to turn off parts for repairs.
- Common Uses:
- Residential circuit protection
- Commercial building panels
- Industrial automation
- Solar energy disconnects
- Control cabinets
A DIN rail system saves space in crowded panels. Installers can add or remove breakers as needs change. This flexibility helps with upgrades and repairs. The design supports both single-pole and multi-pole setups, so it fits many types of circuits.
A DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker keeps circuits safe by stopping bad currents. Electricians put these in homes, offices, and factories to protect people and things. They act fast and you can turn them back on after fixing the problem. Many control panels and solar systems use them for steady power. If you are making a new electrical system, you should think about using this breaker for more safety and simple upgrades.
FAQ
What does “DIN rail mounted” mean?
A DIN rail mounted device attaches to a metal rail called a DIN rail. This rail holds electrical devices in place inside control panels. The design allows for quick installation and easy removal.
Can you reset a miniature circuit breaker after it trips?
Yes. After fixing the problem, a person can flip the toggle switch to reset the breaker. The circuit will work again if the issue no longer exists.
How do you know if a breaker fits your panel?
Check the panel’s DIN rail size and the breaker’s width. Most panels use a 35 mm DIN rail. The breaker’s label shows its size and type. Always match these details before installation.
What is the difference between a fuse and a miniature circuit breaker?
A fuse melts and must be replaced after it trips. A miniature circuit breaker can be reset and used again. Both protect circuits, but breakers offer easier maintenance.
Where do people use DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breakers?
People use these breakers in homes, offices, factories, and solar systems. They protect lights, outlets, machines, and control panels. The modular design fits many
types of electrical setups.
The following information may be of interest to you
Leading Manufacturers of Miniature Circuit Breakers in 2025
Top 2 Pole Miniature Circuit Breakers for Home Use in 2025
Which type of MCB is most suitable for building wiring
What is a C-type MCB and can it be installed at home?




