What is ELCB and how does ELCB work?
What is ELCB?
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) is an electrical protection device used to detect leakage faults in circuits and automatically cut off power. It is one of the important safety devices in early electrical systems to prevent electric shock, equipment damage, or fire risks caused by leakage by monitoring abnormal changes in current or voltage.
How does ELCB work? How does ELCB work?
When ELCB detects leakage current through the ground wire, it triggers the circuit breaker operation using the internal current sensor. After the current leaks through the ground wire and exceeds the set threshold, the ELCB breaks the circuit and cuts off the power supply to avoid personnel from receiving an electric shock injury.
What are the types of ELCB
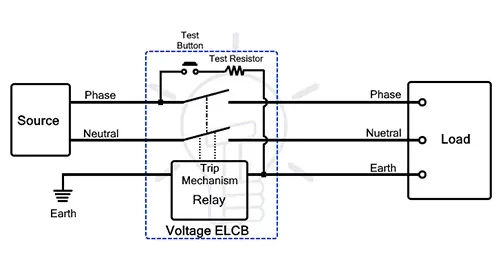
- Voltage operated ELCB
- When the device experiences leakage, the leakage current flows back to the ground through the ground wire, causing the ground wire voltage to rise. When ELCB detects that the ground voltage exceeds the safety threshold, it quickly disconnects the circuit.
- Current operated ELCB
- Compare the current balance between the phase line and neutral line. Under normal circumstances, the two currents are equal; If there is leakage and the current difference exceeds the threshold, the ELCB will immediately trip.
What is RCCB and how does RCCB work?
What is RCCB
RCCB or Residual Current Circuit Breaker is an electrical protective equipment which identifies leakage current in a circuit and cuts off power supply very quickly. The main goal of RCCB is to prevent electric shock accidents as well as electric fires because of leakage.
It verifies whether there is leakage or not by measuring the difference between the current (i.e. residual current) of the phase line (live line) and the neutral line. When the value of difference is above the set threshold, the RCCB trips in milliseconds to ensure personal and equipment protection
How does RCCB work? The working principle of RCCB
Application of Kirchhoff’s Current Law
- In a normal circuit, the phase line current (flowing into the load) is equal to the neutral line current (flowing out of the load). If there is a leakage (such as electric shock to the human body or insulation failure of equipment), some of the current will be lost through other paths (such as the human body or ground wire), resulting in a difference in current between the phase and neutral lines (residual current). RCCB detects this difference through its built-in zero sequence current transformer (CT)
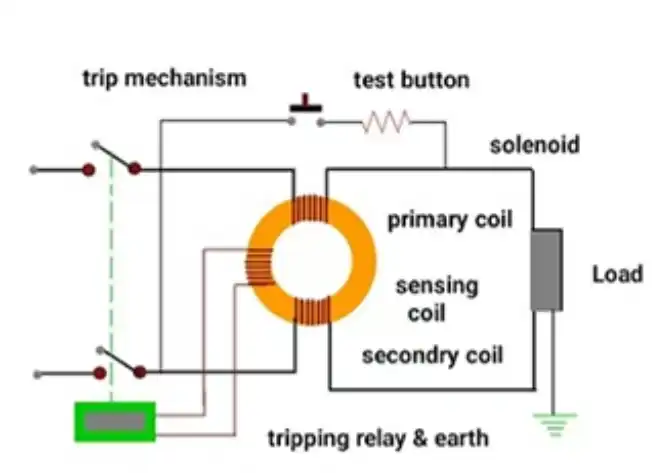
Trigger mechanism
- When the residual current exceeds the preset threshold (usually 10mA, 30mA, or 100mA), the magnetic field induced by the transformer will drive the trip relay to operate and cut off the power supply of the circuit.
- Trip time is usually ≤ 0.1 seconds (high-speed type) or ≤ 2 seconds (delay type) to ensure fast response
Test function
- RCCB is equipped with a test button, which simulates leakage current (such as current through a resistor bypass) when pressed, to verify whether the device is working properly. If the test does not trip, the equipment needs to be replaced
The structural composition of RCCB
- Current Transformer (CT): The principal component that gauges the phase line and neutral line difference.
- Release relay: electromagnetic or permanent magnet type, which drives a mechanical switch to open the circuit when it receives a signal.
- Contact system: employed for the conduction and disconnection of the circuit.
- Test circuit: has test buttons and analog resistors for functional testing
What are the types of RCCB
According to the circuit structure requirements, the number of poles of RCCB can be divided into:
2-pole (1P+N): Suitable for single-phase circuits, only controlling the live and neutral wires
3 poles (3P): used for three-phase circuits, without neutral line protection
4-pole (4P): A three-phase four wire system that can simultaneously protect both the live and neutral wires of the three phases
There are three types of rated residual operating currents: 30mA, 100mA, and 300mA, with different rated ampere capacities.
Classify by the type of residual current detected
- Features: Can only detect standard sine wave AC leakage (50Hz or 60Hz)
- Application: Suitable for pure AC circuits, such as ordinary household lighting and socket circuits.
Type A RCCB
- Features: On the basis of AC type, it has added the ability to detect pulsating DC leakage (such as the current after half wave rectification)
- Application: Suitable for devices with rectifier circuits (such as variable frequency air conditioners, LED drivers).
F-type RCCB
- Features: Supports high-frequency residual current detection (10Hz~1000Hz), suitable for circuits containing frequency converters or high-frequency equipment
- Application: High frequency scenarios such as industrial equipment and photovoltaic inverters.
Type B RCCB
- Features: Comprehensive detection of AC/DC leakage, including smooth DC and high-frequency current, is the most widely covered type
- Application: Distributed photovoltaic systems, electric vehicle charging stations, and other scenarios that require comprehensive protection.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M7_W9LjtDNw
The main differences between ELCB and RCCB
It is crucial to understand the core differences between residual current circuit breakers and residual current circuit breakers when comparing them. Although both are designed for electrical safety, they have significant differences in functionality and usage.
1.Working principle
ELCB: Trigger protection by monitoring changes in ground voltage. When equipment leakage causes abnormal increase in ground voltage (such as exceeding 50V), ELCB will cut off the circuit
RCCB: Determine leakage by comparing the current difference (i.e. residual current) between the phase wire (live wire) and neutral wire. When the difference value exceeds the threshold (such as 30mA), the RCCB immediately trips
2.Sensitivity and usage
RCCB is more sensitive to minor electrical leakage, ensuring that even low-level faults can be detected and dealt with in a timely manner. This makes RCCB very effective in preventing electrical fires and electric shocks.
ELCB is mainly used for older devices and is less sensitive to small leakage compared to RCCB. Due to the higher efficiency of RCCB, ELCB is gradually being replaced by RCCB in most modern systems.
3.Dependency on ground wire
ELCB: Dependent on the ground wire, a reliable ground wire must be connected in order to function properly. If the ground wire breaks or is poorly grounded, the ELCB will completely fail
RCCB: No need for grounding wire, even if the grounding wire is missing or damaged, it can still effectively detect leakage
4.Structural differences
ELCB
Core components: Voltage detection coil+mechanical release device
Trigger condition: Abnormal increase in ground voltage
RCCB
Core components: Current Transformer (CT)+Electronic Amplification Circuit+Tripping Device
Trigger condition: residual current exceeds threshold
5.Installation and maintenance of RCCB ELCB circuit breaker
Due to the need for fewer wires in the system, in newer electrical systems, The installation and maintenance of RCCB are easier and cheaper.
The installation of ELCB is more complex as it requires the installation of grounding wires and is more common in older infrastructure.
RCCB vs ELCB Comparison Table
Aspect RCCB ELCB
Function Detects residual current and trips the circuit to prevent electric shock. Detects earth faults and trips the circuit to prevent electrical hazards.
Detection Type AC:Exchange residual current
A:AC+pulsating DC
B:AC+pulsating DC+smooth DC
F:Residual current of frequency converter/electronic equipmentVoltage-operated: Detects voltage drop in earth line.
Applications AC:Standard residential circuit
A: Pulse DC appliances (such as washing machines)
B:Industrial equipment, solar energy systems
F:Data center, precision electronic equipmentOlder buildings, systems with basic earth fault protection needs.
Sensitivity High (especially for A/B/F types) Lower, suitable for basic fault detection.
Response Time Fast (milliseconds) Slower
Grounding Requirement Operates without grounding. Requires reliable grounding for accurate detection.
Operating Principle Compares live and neutral currents; trips on imbalance. Monitors voltage difference between earth and neutral lines.
Maintenance Low maintenance, high reliability. Higher maintenance (requires grounding checks).
Installation New systems (residential/industrial/renewable energy). Retrofitted in older systems.
Cost Lower for basic types; higher for advanced types (B/F). Relatively higher (especially maintenance).
Standards Complies with IEC 61008/61009. Complies with IEC 61008/61009.
Key Difference Focuses on current leakage protection; adaptable to complex scenarios. Relies on grounding integrity; suitable for basic protection.
Choosing the appropriate RCCB or ELCB: A Practical Guide
Choosing the appropriate RCCB or ELCB for your electrical system is crucial for ensuring safety and reliability. The following practical guidelines can help you make the right choices:
Load size and rated current: RCCB and ELCB
The current ratings of ELCB and RCCB may be the same, but RCCB is more sensitive and widely used in today’s safety standards.
For a regular household 32A circuit, you need an RCCB or ELCB with a rated current of at least 40A to conduct normal current within a safe range.
In the working area of heavy machinery powered by 100A circuits, 125A rated ELCB or RCCB switches are required to carry high loads and reduce tripping.
Current Rating: RCCB and ELCB
For RCCB or ELCB to work normally, the system voltage must be equal to its rated value, which is the main reason for the disadvantage of ELCB, and RCCB has a wide range of applications and is widely used in modern high-voltage systems. For example;
An RCCB of 400V and 100mA characteristics can be used to protect this machine from electrical faults.
However, if in a 400V system, the ELCBs residual current circuit breaker must be rated to 400V in order to achieve the same protection, but RCCB is generally more favored compared to ELCB due to RCCB’s ability to excellently detect faults in modern day appliances.
Brand and Budget: RCCB and ELCB
RCCB: Renowned brands offer RCCBs in various price ranges to ensure that you can find the model that suits your budget and performance needs.
ELCB: Although ELCB may be more affordable, choosing a reliable brand is still important for ensuring long-term performance and safety.
RCCB and ELCB are standard electric protection devices used mainly to prevent leakage accidents on electrical machinery. Following are some recommended suppliers and brands for reference. Price varies depending on brand, specification, and purchase quantity.
ONESTO
ONESTO’s RCCB and ELCB series are widely used in the international market with guaranteed product quality. They are widely used in household and commercial applications and have high cost-effectiveness.
Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric offers multiple models of RCCB and ELCB, which are reliable and widely used in industrial and commercial fields. The price budget is relatively high
Siemens
Siemens’ RCCB and ELCB have a high market share, and their product designs are safe and reliable, meeting international standards.
ABB
The RCCB and ELCB provided by ABB are suitable for various environments, especially in the industrial and construction fields, and are commonly used for the protection of high-power equipment.
Installation and maintenance safety measures: RCCB and ELCB
Reasons why RCCB is superior to ELCB
Understanding the advantages of RCCB over ELCB is crucial for making informed decisions when considering electrical safety equipment. Here are the reasons why RCCB may be the best choice to meet your needs:
Security and protection: Raise your security and protection level
- RCCB detects the imbalance even very tiny and give superb protection. Compared to ELCB, RCCB is better at preventing electric shock and fire.
- ELCB is efficient, but not very sensitive to small leaks, so it is more suitable for old devices with specific ground fault protection.
Adapt better to recent systems
- RCCB is designed to fit smoothly into contemporary electrical systems, making it a good solution for new installations and upgrades. Due to many differences, ELCB is typically more suitable for older configuration and is often requires more settings if used in newer setups.
- In the case of an upgrade for an old manufacturing plant, it may require extra modifications (ex: add a grounding cable to match the new ELCB), hence for new installations, RCCB would undoubtedly be a more logical choice.
Reduce maintenance and long-term costs
- Due to the adoption of advanced technology and design, RCCB typically requires less maintenance. Compared to ELCB, RCCB is able to handle minor leakage, thereby reducing trip frequency and potential maintenance needs.
- For example, regularly check the grounding connection, regularly test the voltage sensitivity of ELCB, and recalibrate to maintain accuracy. RCCB is easier to maintain, requiring simpler and less frequent testing and visual inspections.
Improve efficiency and performance
- RCCB can improve the efficiency of detecting and isolating faults, ensuring the safety and operation of your electrical system.
- ELCB may not provide the same level of performance as RCCB, especially in environments where high sensitivity and fast response are crucial.
Here are some information that you may have just been interested in:
What Are Residual Current Circuit Breakers and How Do They Work
What Is the Amperage Requirement for Ground Fault Protection Systems
How to choose a residual current circuit breaker manufacturer