The rated value of molded case circuit breaker indicates the maximum current, voltage, and breaking capacity it can safely manage. Understanding the rated value of molded case circuit breaker is essential for selecting the appropriate breaker for each application, ensuring safety and reliability. For instance, standards like IEC 60947-2 require the service breaking capacity (Ics) to be at least 75% of the ultimate breaking capacity (Icu) in most situations. In critical facilities, the Ics must equal the Icu. Regularly verifying and setting the rated value of molded case circuit breaker helps prevent unexpected trips and maintains safety by adhering to these regulations.
Key Takeaways
- Rated current tells us the most current an MCCB can handle without turning off. It helps you choose the right breaker for each circuit.
- Rated voltage should be the same as or higher than the system voltage. This makes sure the breaker can stop problems safely and not get damaged.
- Breaking capacity shows the biggest fault current the breaker can stop safely. Always pick a breaker with a higher breaking capacity than the system’s fault current.
- Insulation and impulse voltage ratings keep the breaker safe from power surges. These ratings help the breaker last longer when there are high-voltage spikes.
- Always look at the breaker’s label and datasheet to check the rated values before you install it. Pick breakers that match the system’s needs and follow safety rules.
Rated value of molded case circuit breaker
Rated Current
Rated current is the most current an MCCB can carry all the time without tripping. This number helps you pick the right breaker for the job. MCCBs have settings that let you change the rated current. This means you can protect different circuits better. The rated frame current (Inm) is the highest trip current you can set. MCCBs work in many places, from small shops to big factories.
The rated value of molded case circuit breaker for current usually goes from 10 A to 2,500 A. This lets engineers choose breakers for both small and large currents.
The table below shows common rated current ranges by standard:
| Standard | Rated Current Range (A) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 60947-2 | Up to 2,500 | Adjustable trip settings for various uses |
| UL 489 | Up to 1,200 | Common in North American installations |
MCCBs have different trip types like B, C, D, K, and Z. These types fit different jobs, from homes to factories. Picking the right rated current keeps wires and equipment safe from too much current or short circuits.
Rated Voltage
Rated voltage is the highest voltage the MCCB can safely stop and separate. This includes the rated working voltage (Ue) and the rated insulation voltage (Ui). Ue is the voltage the breaker handles during normal use. Ui is the highest voltage it can take during tests.
The rated value of molded case circuit breaker for voltage should be the same as or higher than the system voltage for safety.
MCCBs can handle many voltages, as shown below:
| Standard | Rated Voltage (V) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 60947-2 | Up to 1,500 DC | Good for DC jobs, like solar power |
| UL 489 | Up to 800 AC | Used a lot for AC power |
| UL 489B | Up to 1,500 DC | Used in DC setups, like renewable energy |
| ANSI NEMA AB 3 | Up to 1,000 AC | Works for most business and factory uses |
MCCBs must have voltage ratings that are at least as high as the highest voltage in the circuit. This makes sure the breaker can stop faults without sparks or insulation problems.
Breaking Capacity
Breaking capacity is the most fault current the MCCB can safely stop. There are two main numbers: rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity (Icu) and rated service short-circuit breaking capacity (Ics). Icu is the most current the breaker can stop once without harm. Ics is the current it can stop many times and still work.
The rated value of molded case circuit breaker for breaking capacity is very important for safety. It must be higher than the biggest fault current in the system.
The table below shows breaking capacity rules:
| Standard | Breaker Type | Breaking Capacity Limits | Key Ratings and Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEC 60947-2 | MCCB / ACB | 25kA and above (industrial) | Needs Icu and Ics, plus thermal ratings |
| IEC 60898-1 | MCB | 6kA–10kA (domestic) | Focuses on Icn (like Icu) |
| UL / NEC (US) | Commercial Panels (>400A) | Minimum 22kA Icu | Keeps commercial setups safe |
MCCBs use smart protection like electronic trip units and thermal-magnetic parts. These help find and stop faults fast. Picking the right breaking capacity keeps equipment safe and follows safety rules.
Insulation and Impulse Voltage
Insulation and impulse voltage ratings keep the MCCB safe from power surges and help it last longer. The rated insulation voltage (Ui) shows how strong the insulation is. Ui is usually higher than the working voltage for extra safety. The rated impulse withstand voltage (Uimp) shows how well the breaker can handle sudden surges, like lightning or switching.
The rated value of molded case circuit breaker for insulation and impulse voltage makes sure the device can take high-voltage spikes without failing.
MCCBs are tested with special wave shapes, like 1.2/50 µs, to check their surge strength. A common Uimp value is 8kV. These ratings follow IEC 60947-2 and UL 489 rules, which need tough tests for safety.
Key Points:
- Rated insulation voltage (Ui) sets the needed space between parts.
- Rated impulse withstand voltage (Uimp) shows the biggest surge the breaker can take.
- Both are needed for safe use where voltage changes or surges happen.
Picking the right insulation and impulse voltage ratings helps stop insulation failure and keeps the MCCB safe in all situations.
Reading Rated Values
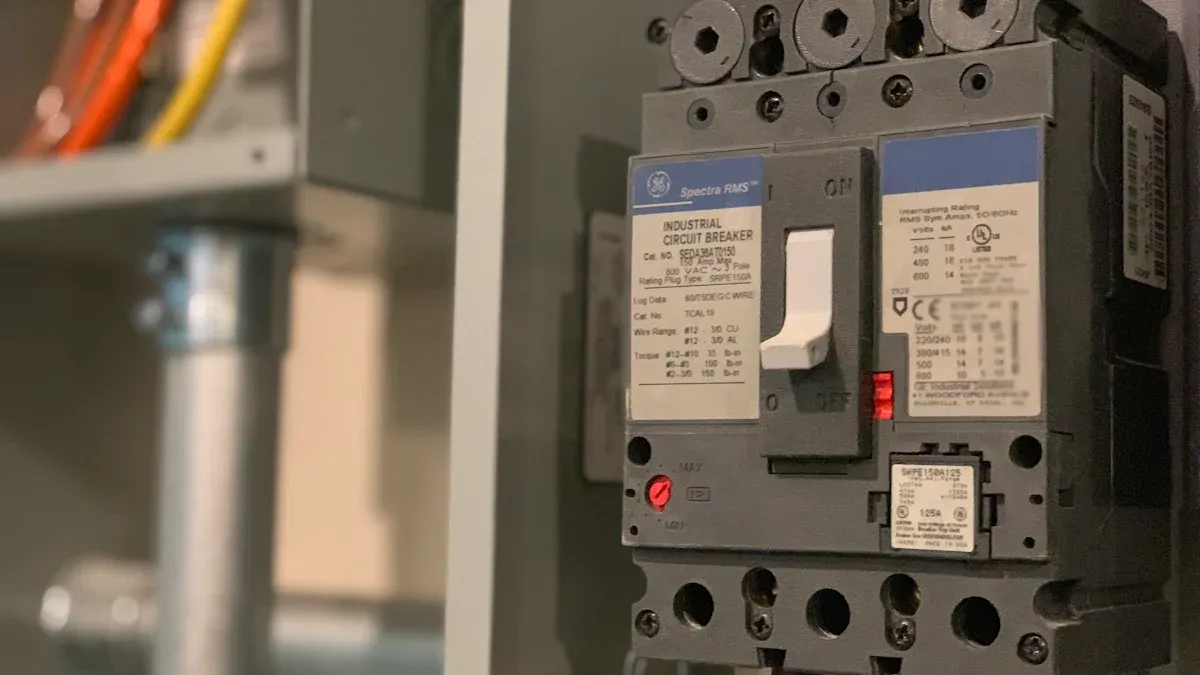
Breaker Label Information
Makers put important facts right on the molded case circuit breaker. These labels help people see if the breaker is the right one. Labels show the rated current, voltage, and breaking capacity. They also list the breaker’s type, listing status, and top short-circuit current. Some labels say which panelboards work with the breaker. They may list maker names and catalog numbers. People can find out how many poles the breaker has and its electrical ratings. Labels show the highest voltage or short-circuit current allowed. They may also tell about ambient temperature ratings and wire insulation needs. These markings help keep the breaker safe to use and make sure it fits the system.
Tip: Always check the label before you put in or change a breaker. This makes sure it is right for your system.
Datasheet Interpretation
Datasheets give more details about the rated value of molded case circuit breaker. They have technical facts that are not on the label. People can find the rated frame current, rated current, insulation voltage, and working voltage. Datasheets also show the ultimate and operating short-circuit breaking capacities. Some datasheets tell about arcing distance, which helps stop faults when current is high. Extra things like auxiliary contacts or shunt releases are listed too. These facts help people pick the best breaker for safety and control.
Here is a table that shows common rated parameters in datasheets:
| Rated Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Rated Frame Current (Inm) | The most current the MCCB frame can take; sets frame size and top trip range. |
| Rated Current (In) | The current where the MCCB trips to stop overload; can be set up to the frame current. |
| Rated Insulation Voltage (Ui) | The most voltage the breaker can take in tests; higher than working voltage for safety. |
| Rated Working Voltage (Ue) | The voltage for normal use, usually the same as the system voltage. |
| Rated Impulse Withstand Voltage (Uimp) | The highest sudden voltage the breaker can take (like from lightning). |
| Operating Short Circuit Breaking Capacity (Ics) | The most fault current the MCCB can stop and still work after. |
| Ultimate Short Circuit Breaking Capacity (Icu) | The most fault current the MCCB can stop; going over this may break it. |
Symbols and Abbreviations
Breaker labels and datasheets use many symbols and short forms. These help people know the rated value of molded case circuit breaker fast. Common short forms are:
- Inm: Rated frame current
- In: Rated current
- Ui: Rated insulation voltage
- Ue: Rated working voltage
- Uimp: Rated impulse withstand voltage
- Icu: Ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity
- Ics: Operating short-circuit breaking capacity
Other symbols may show how many poles the breaker has or its trip type. Some show special things like auxiliary contacts. People should look at the datasheet or maker’s guide for all symbols. Knowing these markings helps people pick the right breaker and follow safety rules.
Breaker Selection
Application Matching
Picking the right molded case circuit breaker starts with knowing the job. Engineers first check the system voltage. They make sure the MCCB’s working voltage matches the system. They look at how much current the system uses. Adjustable trip settings help set the right protection. The frame size must match the system’s current needs. The number of poles, like 2P, 3P, or 4P, depends on how many wires need to be stopped. For special jobs, like welding or solar power, engineers pick MCCBs with special trip settings. They use thermal-magnetic trip units for overload and short-circuit protection. Regular checks, like using test kits and thermal cameras, help keep breakers safe.
Tip: Always pick a breaker with a breaking capacity higher than the biggest fault current in the system.
Calculation Methods
Engineers use rules like IEC 60947-2 and IEEE 1584-2018 to find the right breaker size. They collect facts like transformer size, cable length, and load horsepower. Software tools help with short-circuit and arc flash studies. The steps are simple:
- Find the biggest load current.
- Multiply by a safety factor, often 1.25, to get the lowest breaker rating.
- Figure out the possible fault current at the spot.
- Pick a breaker with a breaking capacity above this number.
- Make sure the rated insulation voltage fits the system.
Good data and regular updates keep these steps correct.
Common Mistakes
| Common Mistake | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Wrong trip setting | Breaker does not trip at safe levels | Fire or injury risk |
| Ignoring temperature effects | Trip current changes with temperature | Bad protection in cold or hot weather |
| Overlooking transient overloads | Short surges may not trip breaker | Unsafe operation |
| Assuming all brands perform the same | Breakers are not all the same | Unreliable protection |
| Skipping maintenance | Missed faults or damage | Higher failure risk |
Note: Always check the breaker’s label, test how it works, and think about the environment to avoid these mistakes.
Picking the correct molded case circuit breaker keeps people and equipment safe. Engineers must look at the rated current, voltage, and breaking capacity. They should read datasheets and use standards like IEC 60947-2 or UL 489.
- Safety is the most important thing to think about.
- Following the rules helps stop accidents from happening.
Checking all the technical details carefully helps stop expensive errors and keeps everything working safely.
FAQ
What does “rated current” mean on an MCCB?
Rated current shows the highest current the breaker can carry without tripping. This value helps users pick the right breaker for their system. Always match the rated current to the circuit’s needs.
How can someone find the rated values on a molded case circuit breaker?
Manufacturers print rated values on the breaker’s label. Users can also check the datasheet for more details. Look for numbers like In (current), Ue (voltage), and Icu (breaking capacity).
Why is breaking capacity important when choosing an MCCB?
Breaking capacity tells how much fault current the breaker can safely stop. If the system’s fault current is higher than the breaker’s rating, the breaker may fail. Always choose a breaker with a higher breaking capacity than the system’s possible fault current.
Can one MCCB work for both AC and DC circuits?
Some MCCBs can handle both AC and DC, but not all. Users should check the label or datasheet for voltage ratings. The breaker must list both AC and DC ratings to use it safely in both types of circuits.
The following information may be of interest to you
Key factors to consider when choosing a molded case circuit breaker
What You Need to Know About How Molded Case Circuit Breakers Work
What Situations Call for the Use of a Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Your Circuit Breaker Panel