Key points
- A fuse holder is a hardware device for repairing and mounting fuses, granting the fuse the facility to blow timely on an overloading current or short circuiting, switching off the circuit and protecting electrical equipment from break down.
- The fuse holder works in harmony with the fuse, and when the current is beyond the rated value of the equipment, the fuse melts to cut off the flow of current, safeguarding electrical equipment from damage and even safety accidents such as fires.
- In selecting a fuse holder, the right specifications and material need to be determined based on the rated current, operating temperature, and application environment of the electrical equipment to ensure effectiveness of protection.
What is a fuse holder
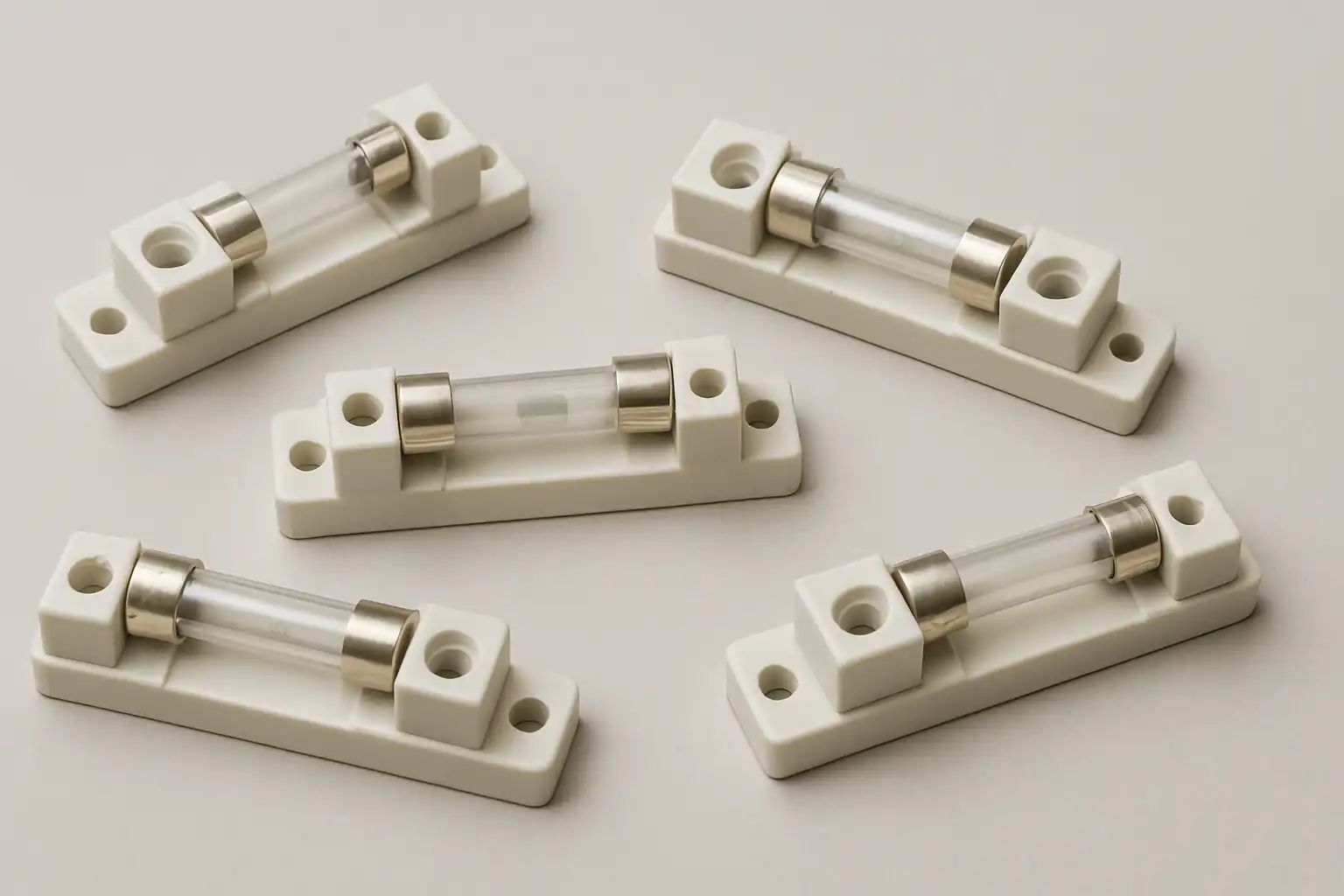
In theory, a fuse holder, also known as a “fuse tube” or “door”, is an insulated tube that contains replaceable fuse components. When the contained fuse is blown (“blown”), the circuit will be disconnected, and the fuse holder will fall off from the upper contact and hang on the hinge at the lower end.
In fact, a fuse holder is a device used for installing and fixing fuses, which is usually connected to the electrical circuit system of electrical equipment. When the current exceeds the rated value of the fuse, the fuse will be blown, thereby cutting off the current and protecting electrical equipment from damage. The function of the fuse holder is to provide a reliable connection platform, ensuring that the fuse can function when needed.
What is a fuse
A fuse is an electrical safety device used to provide overcurrent protection for circuits. Its basic components are metal wires or metal strips. When excessive current flows, the metal wires or strips will melt, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device
The relationship between fuses and fuse holders
A fuse is an electrical safety device that can open the current in case of an overload according to the specifications of the designed current. The fuse holder is a housing for the installation of fuses, whereby the position of the fuse in the circuit is safe and easy to replace. The two are utilized together to collectively serve the purpose of electrical device protection.

The working principle of the fuse holder and how does it work?
The core function of a fuse holder is to achieve intelligent control of current through thermal effects. Its working principle can be divided into the following steps:
- Current conduction: When current passes through the conductor in the fuse holder, the conductor generates heat due to resistance. Under normal current, heat can be dissipated quickly through heat dissipation design in order to maintain temperature stability
- Overload trigger: The moment the current exceeds the rated value, the temperature of the conductor rapidly increases. When the temperature reaches the melting point, the fuse melts, breaking the circuit instantly to prevent the current from causing any further damage to the equipment
- Fault isolation: Once the fuse has blown, the fuse holder physically separates the fault area to prevent fire or damage to the equipment.
How to choose the appropriate fuse holder
- Consider the rated current of the equipment
In choosing a fuse holder, the rated current of the electrical device is most important. Different electrical devices carry different currents, and therefore the appropriate fuse holder and fuse rating should be chosen. A fuse holder that is too small will melt over and over again, but one that is too large will not adequately protect the equipment.
- Types of fuse holders
According to different application situations, there are different types of fuse holders to choose from. For example, common fuse holders are glass tube fuse holders, ceramic fuse holders, socket fuse holders, etc. There are matching applicable situations and benefits for every type of fuse holder.
- Temperature resistance and material selection
Resistance of temperature and resilience of material by the fuse holder are also critical factors for its selection. Great care should be taken that the material of the fuse holder must be extremely temperature-resistant to prevent damage or risks to safety by thermal heat. Different materials like high-temperature-resistant plastic, ceramics, etc., are in use.
Application scenarios of fuse holder
- Household Electric Appliances:
Microwave ovens, air conditioners, and other equipment use fuse holders to prevent motor overload or circuit short circuits, thus avoiding the risk of fire.
- Automotive Electric System
The front cabin fuse box centrally manages the entire vehicle’s electrical circuits, such as headlights, speakers, etc., with clear markings for quick replacement
- Industrial equipment:
In high current load scenarios (such as transformers and robots), the fuse holder needs to be equipped with an intelligent temperature control system to monitor and cut off abnormal currents in real time
conclusion
The fuse holder is a key part of electrical equipment protection. On home appliances, industrial equipment, or motor vehicles for transportation, the fuse holder can provide safe overload and short-circuit protection for the equipment to operate normally. Correct fuse holder selection and routine maintenance are the foundations for the long-term steady operation of electrical equipment.
FAQ
In what way does a fuse holder differ from a fuse?
A fuse is a current protection device that melts to open an electric circuit. A fuse holder is a device used to support and hold fuses in a way so that the fuses can function correctly when they are defective.
How to choose a suitable fuse holder for electrical devices?
In making a selection of a fuse holder, the rated current of the equipment, the operating voltage, and the operating temperature need to be taken into account. Ensure that the current ratings of the fuse holder are compatible with the equipment, and adopt appropriate materials to sustain high operating temperatures.
What is the service life of the fuse holder?
A fuse holder’s life is longer in general but may vary depending on the application environment. Regular replacement and checking of fuse holders and fuses can effectively extend electric equipment’s service life.
How many types of fuse holders are available?
Glass tube fuse holders, ceramic fuse holders, and socket type fuse holders are the most widely used fuse holders. All of them are appropriate for different electrical equipment and operating conditions.
Here are some information that you may have just been interested in:
Solar photovoltaic connector inline fuse holder (with fuse)
What are fuses in electrical systems?
What trip circuit breakers and blown fuses indicate