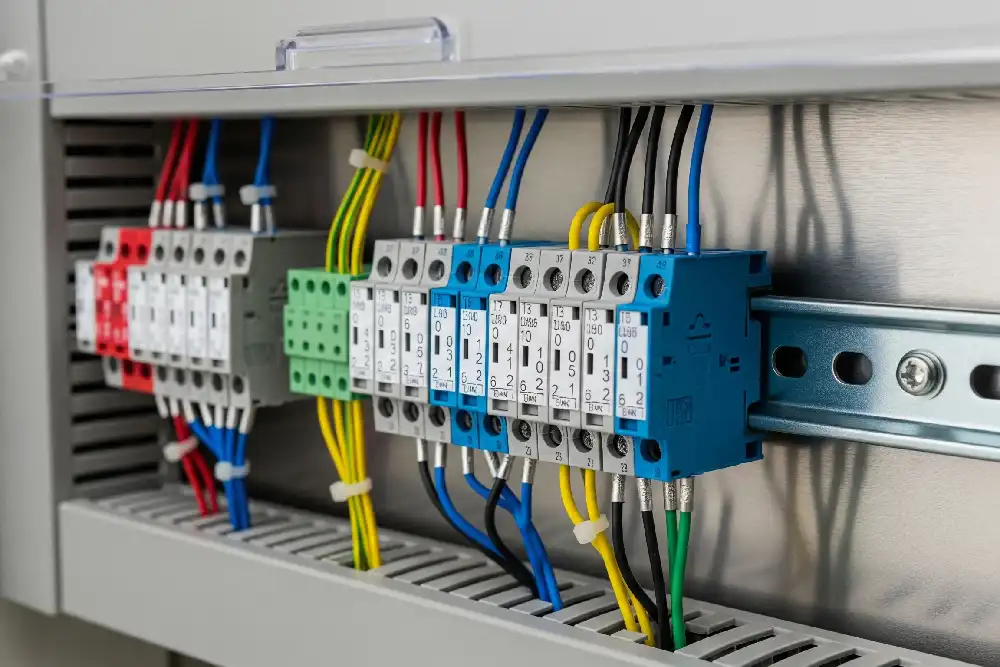
A din rail mount terminal block joins and holds wires in control panels. This device is important for keeping wires safe and tidy in many systems. It is used in factories and buildings. Many people want to know what makes these blocks work well and last long.
- Terminal blocks stop shocks and short circuits by gripping wires tightly.
- They keep wires neat, lower mistakes, and help you find and fix issues fast.
- Strong mounting and clear labels make things safer and help with easy repairs.
Key Takeaways
- DIN rail mount terminal blocks help keep wires safe and neat. They make it easy to connect wires in control panels. Modular design and snap-on mounting help workers install wiring fast. Workers can also change or fix wiring quickly. They do not need special tools for this. There are different ways to connect wires, like screw clamps and spring clamps. Push-in connections are also used. These fit many wire sizes and needs. Some blocks are special, like feed-through and earth blocks. Special function blocks help with safety and control. Picking the right block with good ratings is important. Clear labeling helps keep electrical systems safe and tidy.
What Is a DIN Rail Mount Terminal Block
Definition
A din rail mount terminal block connects and organizes wires in panels. Manufacturers make these blocks to fit on DIN rails. DIN rails are metal strips with set sizes. These sizes follow rules from groups like IEC 60715 and EN 50022. These rules help terminal blocks and other devices fit well together. This makes control panels safe and neat everywhere.
DIN rails hold terminal blocks and other devices in place. The most used type is the 35 mm × 7.5 mm top-hat rail. This size makes it easy to put in and swap parts. Terminal blocks work better with this system. It makes wiring and fixing things simpler. The set design also keeps electrical systems safe and steady.
DIN rail mount terminal blocks help workers build neat and safe wiring. They let people add, take out, or change wires easily. This does not hurt wires or equipment.
Primary Function
The main job of a din rail mount terminal block is to make safe connections between wires and devices. These blocks act like bridges for electricity. They help power move from one part to another. They also keep equipment safe from short circuits and surges.
| Function/Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical connection | Hold wires and equipment tightly together. |
| Protection | Stop short circuits and surges from happening. |
| Safe interface | Give a safe spot to connect parts. |
| Circuit completion | Join wires to finish circuits. |
| Application versatility | Used in many places like buildings, HVAC, and power supplies. |
| Connection types | Work with screw terminals, spring clamps, and ground terminals. |
| Installation and maintenance | Modular design makes putting in and fixing easy. |
Terminal blocks use screws or spring clamps to grip wires. This design makes connections better and saves time. It is faster than old ways like welding. The modular system lets people fix or change wires quickly. These features make din rail mount terminal blocks popular in many jobs.
DIN Rail Mount Terminal Block Features
Design
Engineers design DIN rail mount terminal blocks for easy installation and flexible use. These blocks fit on standard DIN rails, which come in two main sizes: 35 x 15 mm and 35 x 7.5 mm. The AVK Series, for example, uses these common rail sizes. These rails allow users to mount terminal blocks in control panels, cabinets, or racks. The mounting process uses snap or slide methods, so workers can quickly add or remove blocks without special tools.
The modular design stands out as a key feature. Users can place modules side by side in any order. This setup lets them build custom layouts for power supplies, PLCs, and other devices. Standard rail lengths and custom cuts help fit unique projects. Accessories like brackets and clips make installation even easier. The DIN rail itself does not carry current or signals, so users can mix different types of blocks for power, control, or signal needs.
Tip: Modular design makes upgrades and repairs simple. Workers can add, remove, or move blocks without rewiring the whole system.
Materials
Manufacturers use strong and reliable materials to build DIN rail mount terminal blocks. The conductive parts often use copper or brass. These metals provide excellent electrical conductivity and keep connections secure. Some blocks may also use aluminum for its resistance to vibration and temperature changes.
The housing, or outer shell, uses tough plastics like polyamide or thermoplastic. These materials protect against short circuits and keep the block stable in harsh environments. Polyamide and thermoplastic housings resist heat, chemicals, and impact. This combination of metals and plastics ensures the blocks last a long time and work well in industrial settings.
Connection Methods
DIN rail mount terminal blocks offer several connection methods. Each method affects how fast workers can install the blocks and how reliable the connections are.
| Connection Method | Description | Installation Speed | Reliability and Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Screw Clamp | Tightens wire with a screw. Good for large wires and high current. | Slower, needs screwdriver | Very secure if tightened well. Best for large wires. |
| Spring/Cage Clamp | Uses a spring to hold the wire. Needs a tool to open the clamp. | Faster than screw clamp | Reliable, resists vibration. Good for small wires. |
| Push-In Connection | Wire pushes in directly, no tools needed. | Fastest | Secure, best for compact spaces and high wire density. |
Push-in connections save the most time. Workers can insert wires without tools, which helps in tight spaces. Spring clamps work well in machines that vibrate, since the spring keeps the wire tight. Screw clamps give a strong hold for thick wires and high currents, but take longer to install.
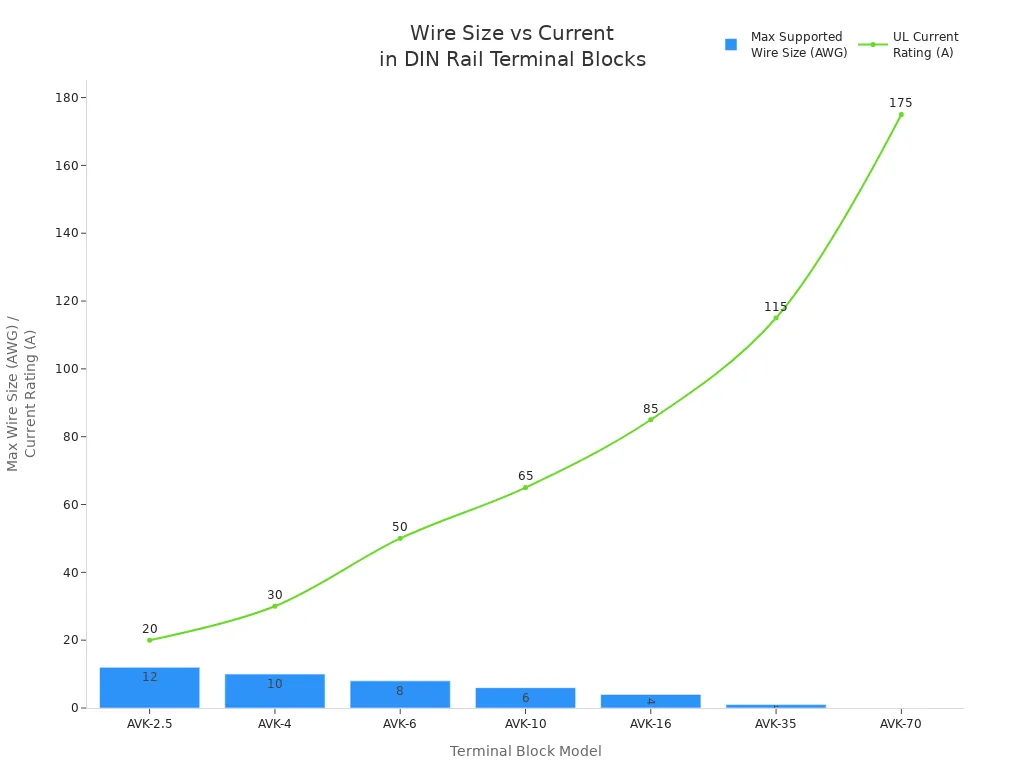
DIN rail mount terminal blocks support a wide range of wire sizes and current ratings. The table below shows some common models and their specifications:
| Model | Wire Size Range (AWG) | UL Current Rating (A) | Voltage Rating (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVK-2.5 | 26-12 | 20 | 600 |
| AVK-4 | 26-10 | 30 | 600 |
| AVK-6 | 26-8 | 50 | 600 |
| AVK-10 | 16-6 | 65 | 600 |
| AVK-16 | 12-4 | 85 | 600 |
| AVK-35 | 8-1 | 115 | 600 |
| AVK-70 | 6-2/0 | 175 | 600 |
Some terminal blocks, like those from the Same Sky series, support wire sizes of 1.5mm² or 2.5mm². These blocks have current ratings from 15 A to 20 A and voltage ratings up to 600 VDC. This range covers most needs in control panels and industrial systems.
Note: Always match the wire size and current rating to the terminal block model. This ensures safe and reliable connections.
Types and Configurations

Feed-Through
Feed-through terminal blocks let electricity move between two wires. Engineers use them to link input and output wires. The blocks are small and come in single, double, or multi-level designs. Workers put these blocks on DIN rails with screw clamps, spring clamps, or push-in connections. You do not need special tools to install them. Feed-through blocks are common in control panels and trains.
| Terminal Block Type | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Feed-Through | Connects two wires for wire-to-wire connection; single, dual, or multi-level; input and output contacts on opposite sides; commonly DIN rail mounted |
Multi-level feed-through blocks save space in tight spots. Some series, like Dinkle DP and WAGO 281, work with cables from 28 AWG to 6 AWG. These choices help workers wire things easily in small areas.
Earth Terminal
Earth terminal blocks keep electrical systems safe by linking wires to the ground. They look like feed-through blocks but do a different job. Makers use green and yellow colors for earth terminals. This color rule helps workers spot grounding points fast. The AVK series and Phoenix Contact blocks use these colors to follow safety rules.
| Terminal Block Type | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Earth (Ground) | Visually similar to feed-through but connects wiring directly to ground or DIN rail; typically green/yellow color-coded; used for grounding purposes |
Earth terminals must follow safety rules. They need low contact resistance and must not get too hot. They also need strong insulation. These things stop overheating and keep ground connections steady.
| Resistance Property | Safety Requirement / Purpose | Limit / Standard Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Low Contact Resistance | Minimizes voltage drop and temperature rise to ensure stable, safe earth connection | ≤ 6.4 mV or ≤ 1.5× initial measured value for PE terminal |
| Temperature Rise | Prevents overheating that could damage terminal or cause hazards | Temperature rise ≤ 45 K; voltage drop within limits |
| Short-time Withstand Current | Ensures terminal block can handle fault currents without damage until protective device acts | No damage; voltage drop remains within specified limits |
| Clearance and Creepage Distances | Prevents flashover or insulation breakdown between conductive parts and to mounting support | Compliance with normative minimum distances |
| Dielectric Strength | Ensures insulation material withstands rated voltages without flashover or breakdown | No flashover or breakdown |
| Short Circuit Current Rating (SCCR) | Confirms terminal block safety under short circuit conditions | Minimum SCCR 10 kA for terminal blocks |
Special Function
Special function terminal blocks give extra protection and control. Some blocks have fuses inside to stop too much current. Others have LED lights to show if a fuse is working. These blocks are good for sensitive devices like sensors and relays. Workers use screw or spring clamps to hold wires in place.
| Terminal Block Type | Features and Applications |
|---|---|
| Special Function Terminal | May include integrated fuses for overcurrent protection; LED indicators for fuse status; suitable for sensitive equipment like sensors and relays |
Makers offer special function blocks in single, double, or triple levels. Dinkle DP Series and MISUMI BTSE Series fit cables from 26 AWG to 6 AWG. WAGO 281 and 2002 Series are slim and use screwless connections for quick setup.
A din rail mount terminal block can hold many types and setups. This makes it easy for workers to build safe and neat electrical systems.
Functions and Applications
Signal Transmission
A din rail mount terminal block helps send signals between devices. The metal parts inside connect wires and keep signals strong. The plastic housing covers the wires and stops current from leaking. Workers use these blocks in control cabinets. They link controllers, PLCs, and I/O modules. The blocks fit many wire sizes and types. Their tight connections keep signals clear and steady. This helps machines work well and lets workers find problems fast.
Power Distribution
DIN rail mount terminal blocks help share power in industrial panels. These blocks take power from one source and send it to many devices. They can handle high current and voltage, like 250 A and 600 V. The modular design lets workers add or remove blocks easily. Some blocks use spring pressure connections to hold wires tight. This design makes wiring faster and needs fewer tools. Safety covers protect workers from shocks. The blocks fit many wire sizes, so they work for small and big machines.
Tip: Terminal blocks keep wiring neat and make changes easy.
Control Systems
Control systems need good wiring to work well. DIN rail mount terminal blocks organize wires for sensors and controllers. These blocks protect against short circuits and surges. The plastic housing covers each wire. Some blocks have fuses that break the circuit if needed. Earth terminal blocks send extra charge safely to the ground. Workers use these blocks in many places:
- Industrial automation: Connect sensors, actuators, and PLCs.
- Power distribution: Send power to different machines.
- Building wiring: Link lights, alarms, and security systems.
- Smart homes: Connect devices for easy control.
Terminal blocks make wiring safer and easier in all these systems.
Advantages and Usage
Installation
Engineers like DIN rail mount terminal blocks because they are fast to install. Workers can snap blocks onto the rail quickly. They do not need screws or special tools. Snap-on feet and push-in jumpers make it even faster. Some products, like WAGO and Kasuga Electric Works, use screwless wiring. This lets workers connect wires quickly and safely. Spring terminal blocks, such as the JUT3-2.5/3, use a spring that pulls back. This makes installation easy and helps stop wires from coming loose. Modular designs and snap-on clips help workers finish jobs faster. These features save time and effort, especially for big projects.
Tip: Snap-in mounting and screwless wiring make work easier and safer. They help workers avoid mistakes and finish jobs faster.
Flexibility
DIN rail mount terminal blocks are very flexible for changing systems. Modular designs let engineers add, move, or swap units easily. Click-on and click-off mounting makes changes simple. Workers can leave space for upgrades later. Spring clamp terminals are good for wires that need to be moved often. They stop problems like screws getting loose. Multi-hole blocks let workers add or move wires without trouble. These features keep wiring neat and help with complex circuits in busy places.
- Modular designs help systems grow fast.
- Clamps make it easy to disconnect wires for repairs.
- Many shapes and sizes fit different wires.
- Neat wiring helps control big systems.
Reliability
DIN rail mount terminal blocks work well in tough places. Spring connections, like in WAGO’s TOPJOB S series, stop wires from shaking loose. These connections do not need much care. Makers use strong metals like copper alloys and stainless steel. These metals do not rust and are very strong. Spring-cage clamps keep wires tight, even if things shake or get hot. Products meet rules like IEC 60947 and UL ratings. This means they are safe and last a long time. Careful making and testing make sure they work well in hard jobs.
Selection Tips
Picking the right terminal block keeps things safe and working well. Engineers should follow these tips:
- Make sure the DIN rail fits and wires can bend.
- Pick single, dual, or triple-level blocks for your needs.
- Choose the right way to hold wires for your job.
- Check for UL or IEC safety marks.
- Pick blocks with higher current and voltage ratings than needed.
- Match wire size and type to the block.
- Think about how wires go in and what type of module you need.
- Use colors to help find and fix problems.
- Buy from good brands to get safe and strong blocks.
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Current Rating | Pick blocks that can handle 1.5 times the current you expect. |
| Voltage Rating | Make sure the block’s voltage rating is higher than your system. |
| Pole Count | Choose the number of circuits you need. |
| Pitch | Think about the space between poles for safety. |
| Wire Size/Type | Match the block to your wire’s size and type. |
| Wire-Entry Orientation | Pick the best direction for wires based on your setup. |
| Wire-Securing Method | Choose screw, push button, or push-in as needed. |
| Module Type | Decide if you want modules that lock together or single pieces. |
| Safety Ratings | Look for UL and IEC marks. |
| Color Coding | Use colors to make repairs and checks easier. |
Safety tips: Use spring pressure connections, prepare wires right, mark blocks clearly, and test everything after installing.
DIN rail terminal blocks are important in today’s electrical systems. They keep wires safe and neat. Workers can install them quickly. These blocks have a modular design. They do not shake loose when machines vibrate. Clear labels help workers fix things fast.
- Standard mounting and smart features make work safer and faster.
- Flexible choices fit small spaces and tricky setups.
To stay safe, pick blocks with the right ratings. Make sure wires are the right size. Check and care for the blocks often. Good habits stop problems and help systems last longer.
Tip: Neat wiring and good parts make every project better.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a DIN rail mount terminal block?
A DIN rail mount terminal block joins wires in control panels. It keeps wires safe and tidy. This makes it easier to fix problems. It also helps stop electrical issues.
Can DIN rail terminal blocks handle high current?
Yes, many DIN rail terminal blocks can carry high current. Some types can handle up to 620 amps. Always check the current rating before you use one. Make sure it matches your system.
How do you choose the right terminal block for your project?
Tip: Look at the wire size, current, and voltage ratings. Pick a block that fits your DIN rail. Make sure it meets safety rules. Color codes and modular designs help with setup and changes.
Are DIN rail terminal blocks reusable?
Engineers can use DIN rail terminal blocks again if they are not broken. Take out the wires and check the block for damage. If it looks good, put it on another rail. Always check for wear before using it again.
What accessories work with DIN rail terminal blocks?
Common accessories are end covers, jumpers, marking tags, and test plugs. These parts help keep wires neat and easy to find. They also help connect circuits and label wires for quick fixes.
See also
What is a DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker and how does it work
What Is a Terminal Block and How Does It Work
What should you know about DIN rail circuit breakers for home and industry
What You Should Know About Terminal Blocks and Their Other Names
How many wires can be connected to one terminal block