The width of a DC circuit breaker changes with each model and use. Some common sizes are 13 mm for small breakers, 18 mm for regular mini circuit breakers, and up to 90 mm for big molded case types. The width decides how breakers fit in panels or on DIN rails. The right width helps keep the installation safe and stops crowding in electrical boxes.
- Example widths:
- 13 mm (mini)
- 18 mm (standard)
- 26 mm, 90 mm (large)
Picking the correct width of DC circuit breaker can help with fitting and safety.
Key Takeaways
- DC circuit breakers come in many widths. Some are as small as 6 mm. Others can be as big as 90 mm. The width changes how they fit in panels. It also affects how they fit on DIN rails.
- Picking the right breaker width is important. It helps with easy installation. It stops breakers from being too close together. It keeps the electrical system safe. It also makes sure everything works well.
- The breaker width should match the panel space. It should also follow rules like IEC 60898-1 for homes. For businesses, it should follow IEC 60947-2. This helps avoid problems with fitting and safety.
- If you need more current or voltage, use wider breakers. Think about how much power your system needs. This helps you pick the right breaker size.
- Always look at the product datasheet before you buy. Check the exact breaker width. This makes sure it will fit. It helps you avoid expensive installation mistakes.
Width of DC Circuit Breaker
Typical Sizes
Manufacturers design DC circuit breakers in many sizes. The width of DC circuit breaker models can range from very narrow to quite wide. Some single-pole breakers measure only 6 mm across. These slim designs save space in crowded panels. Standard miniature circuit breakers often use an 18 mm width for each pole. Larger molded case circuit breakers can reach widths of 90 mm or more.
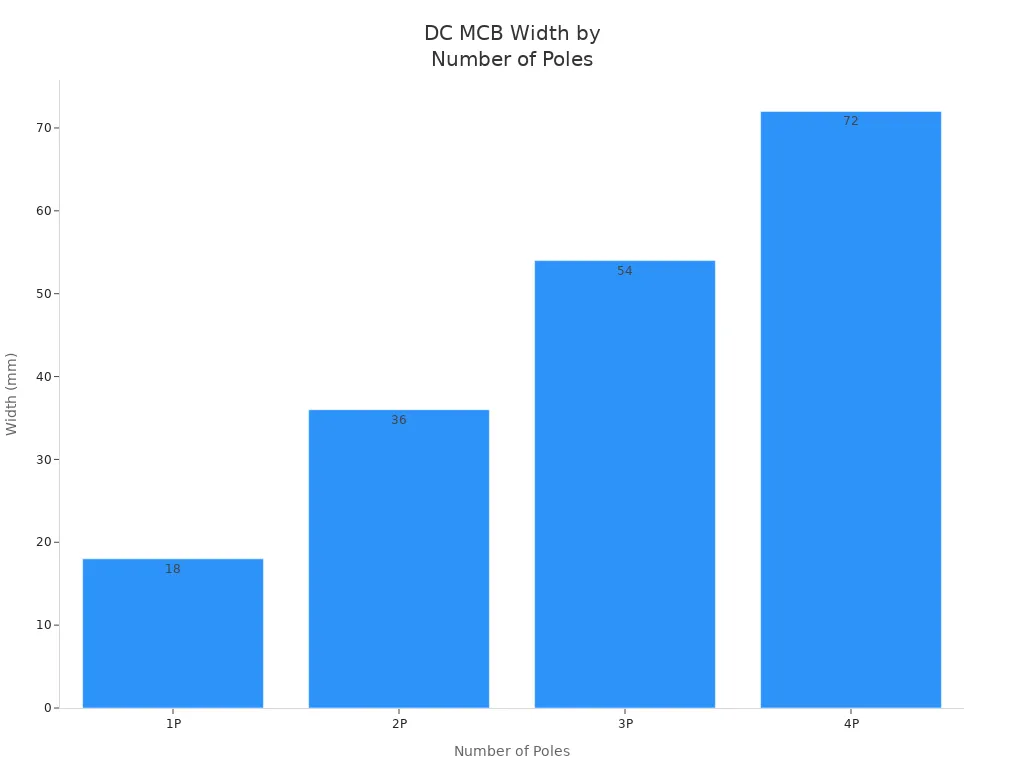
The number of poles affects the total width. For example, a one-pole breaker is 18 mm wide. A two-pole breaker doubles that to 36 mm. Three-pole and four-pole models measure 54 mm and 72 mm, respectively. This pattern helps installers plan how many breakers fit in a panel.
| Number of Poles | Width (mm) |
|---|---|
| 1P | 18 |
| 2P | 36 |
| 3P | 54 |
| 4P | 72 |
Some brands offer even narrower options. A single-pole PTCB breaker measures just 6 mm. This design works well for tight spaces and small current needs. Multi-pole breakers allow adjustable current for each channel, but their widths vary by model.
Tip: Always check the product datasheet for exact width before buying a DC circuit breaker.
Width Measurement
Manufacturers specify the width of DC circuit breaker in millimeters or inches. Most datasheets list the width per pole. For example, a miniature circuit breaker might show 18 mm for each pole. If a breaker has more than one pole, multiply the width by the number of poles to get the total.
Installers use these measurements to plan panel layouts. A panel with 10 single-pole breakers needs 180 mm of space. If the breakers are multi-pole, the total width increases. Molded case circuit breakers often have wider bodies because they handle higher currents. These breakers may measure 90 mm or more.
Some DC circuit breakers mount on DIN rails. The width must match the rail spacing. Others use chassis mounting, which requires more room. The width of DC circuit breaker affects how many units fit in a row and how much space remains for wiring.
Manufacturers also design breakers to meet standards. For example, IEC 60947-2 sets rules for molded case circuit breakers. These standards help ensure safe and reliable installations.
Note: The width of DC circuit breaker can influence the choice of enclosure and the overall safety of the system.
Importance of Width
Installation
The width of DC circuit breaker plays a big role during installation. Installers must match the breaker width to the space in the panel or on the DIN rail. If the breaker is too wide, it may not fit into the standard panel or DIN rail box. Some large breakers can take up the space of four regular breakers. This can make mounting difficult and may require a bigger or deeper panel box. Sometimes, installers use special adapters to fit breakers with different widths. When the breaker does not fit well, it can lead to loose mounting or poor alignment. This makes the installation harder and can affect how safe and reliable the system is.
Compatibility
Compatibility means the breaker must work with the other parts in the system. The width affects how many breakers fit in a row and how much space remains for wires and other devices. DIN rails have standard sizes, so the breaker width must match these standards. If the breaker is too wide or too narrow, it may not line up with the other equipment. This can cause problems with wiring and may even stop the panel door from closing. Installers often check the datasheet to make sure the breaker will fit with the rest of the system.
Safety
Choosing the right width of DC circuit breaker helps keep the system safe. If the breaker is too wide or too narrow for the application, several risks can appear:
- Overheating and fire hazard if the breaker allows too much current.
- Nuisance tripping if the breaker is too small, which can stop equipment from working.
- Failure to stop short circuits, which can damage equipment or cause explosions.
- Problems in three-phase systems, like overheating or relay faults.
- Higher maintenance costs due to frequent malfunctions.
- Unwanted tripping of other breakers, which can cause more faults.
Tip: Always select a breaker with the correct width and rating for the job. This helps prevent safety issues and keeps the system running smoothly.
Choosing the Right Width

Selection Factors
Picking the right width of DC circuit breaker depends on many things. Each job, like solar power or battery systems, has its own needs. DC circuit breakers keep solar panels and batteries safe from too much current. The kind of breaker is important. Thermal, magnetic, and hybrid breakers work in different ways. The highest current and voltage ratings matter a lot for size. Interrupting capacity and trip features also help decide which breaker to use.
Installers check the system voltage and how much current is expected. Lower voltage DC circuits need more current for the same power. This means the breaker might need to be wider to handle it. The type of job changes what is needed. Homes use small breakers for less current. Businesses and factories need bigger breakers for more current.
| Factor | Influence on DC Circuit Breaker Width/Rating |
|---|---|
| Current Rating | Higher current at lower voltage (DC) requires larger protective devices. |
| Voltage Level | Lower voltage DC circuits need higher current, affecting breaker size. |
| Application Type | Residential, commercial, and industrial systems need different breaker sizes. |
| Wire Insulation & Ampacity | Wire type and temperature rating affect breaker sizing. |
| Breaker Physical Size (Width) | Larger width often means higher current rating and breaking capacity. |
Installers also think about wire insulation and how much current the wire can take. The breaker must stop the wire from getting too hot. The width of DC circuit breaker usually gets bigger with higher current and harder jobs.
Standards
Standards help people pick the right DC circuit breaker for each place. Homes use IEC 60898-1. This rule says the biggest current is 125 amps and is for houses. These breakers are small and fit on DIN rails. Businesses and factories use IEC 60947-2. This rule is for molded case and air circuit breakers up to 6300 amps. These breakers are bigger and can handle more power.
| Application Type | Breaker Type | Amp Ratings | Physical Size / Frame Size | Typical Use Case / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) | 15 to 60 amps | Compact, DIN-rail mounted, supports up to 125A | Used in homes for lighting, outlets, appliances |
| Commercial | Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) | 100 to 225 amps | Larger frame size than MCBs | Used in small factories, offices, retail stores |
| Industrial | Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) and Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) | 400 to 6000+ amps | Largest frame sizes, suitable for high current and voltage | Used in heavy industry, manufacturing plants, data centers |
Manufacturers give details for each breaker. Installers should follow these tips and local rules. DC circuit breakers must be made for DC. AC breakers do not safely stop DC current because DC does not cross zero. This can make dangerous sparks.
Practical Tips
Installers can use a checklist to pick the right width of DC circuit breaker:
- Find out the highest current and voltage for the job.
- Pick the breaker type (thermal, magnetic, or hybrid) for the system.
- Use the maker’s tips for size and where to put it.
- Put the breaker close to the battery’s positive side to lower fire risk.
- Size the breaker using math, like 1.25 times the charge controller’s output.
- Think about things like heat and airflow.
- Make sure the breaker fits the panel or DIN rail and has the right number of poles.
- Follow local rules and standards (IEC 60898-1 for homes, IEC 60947-2 for businesses and factories).
- Pick DC-only breakers for DC jobs.
- Plan to check and care for the breaker often to keep it safe.
Tip: Always look at the datasheet for the width of DC circuit breaker before you install it. This helps you avoid fitting problems and keeps things safe.
Knowing the width of DC circuit breakers helps keep things safe. It also makes sure everything fits together right. Some people choose the wrong breaker type, not just the wrong size. This can cause problems in the system. Now, many companies make smaller and smarter breakers. These new breakers can even be watched from far away. It is still important to read datasheets and product details before buying.
Good planning and smart choices stop fitting mistakes. They also help keep your system safe. Use the tips and examples here to pick the right breaker for your project.
FAQ
What does the width of a DC circuit breaker mean?
The width shows how much space the breaker takes up in a panel or on a DIN rail. Manufacturers measure this in millimeters or inches. Installers use this number to plan the layout and make sure everything fits.
What types of DC circuit breakers have different widths?
Miniature circuit breakers, molded case breakers, and multi-pole breakers all have different widths. Miniature types often measure 13 mm or 18 mm per pole. Molded case breakers can reach 90 mm or more.
Tip: Always check the datasheet for the exact width before installation.
What happens if the breaker is too wide for the panel?
A breaker that is too wide will not fit in the panel. Installers may need a larger enclosure or must rearrange other devices. This can delay the project and increase costs.
What standards help decide the correct width?
Installers follow standards like IEC 60898-1 for homes and IEC 60947-2 for businesses. These rules set the size and safety requirements for DC circuit breakers.
| Standard | Typical Use |
|---|---|
| IEC 60898-1 | Residential |
| IEC 60947-2 | Commercial/Industrial |
What should installers do before choosing a DC circuit breaker width?
Installers should read the product datasheet, measure the panel space, and match the breaker width to the job. They must also follow local codes and safety rules.
See also
What are the standard sizes of circuit breakers
1A-25A 1000Vdc 10x38mm mm Din rail fuse
What is a DIN rail mounted miniature circuit breaker and how does it work
What should you know about DIN rail circuit breakers for home and industry
Understanding DC Miniature Circuit Breakers for Beginners

KC3-H-2-Pole-Breaker-Mini.webp)

