You might ask what the full name of mccb electrical is. MCCB means Molded Case Circuit Breaker. An MCCB helps protect electrical circuits from getting too much power or short circuits. The molded case is made from strong materials that do not let electricity pass through. This keeps you safe from getting shocked. The mccb electrical full name tells us this breaker works in low-voltage systems. It can stop electricity by itself if it finds a problem. People use an MCCB to keep equipment and wires safe in homes, schools, and factories.
Key Takeaways
- MCCB means Molded Case Circuit Breaker. It is a device that keeps electrical circuits safe from too much power or short circuits. The molded case gives strong insulation. It helps stop electric shocks. It also keeps dust and water away from the inside parts. MCCBs use heat and magnets to trip and stop electricity fast. This happens if there is too much power or a short circuit. This keeps people and equipment safe. MCCBs have different current ratings. They are good for factories, big buildings, and heavy machines. These places need protection that can be changed. MCCBs can handle more current than MCBs and other breakers. They have settings you can adjust. They give better protection for complicated electrical systems.
MCCB Electrical Full Name
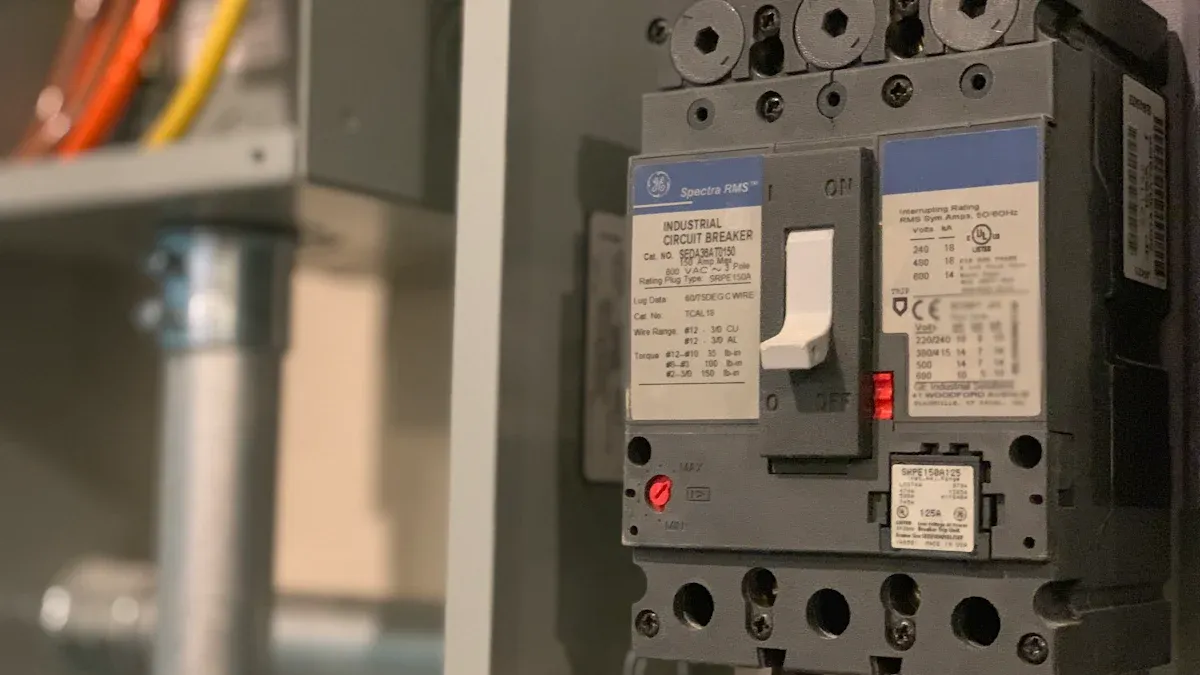
MCCB Full Form
You may see the term MCCB in many electrical diagrams and manuals. The mccb full form is Molded Case Circuit Breaker. This abbreviation is recognized worldwide, including by international standards like IEC 60947-2 and UL 489. When you read about the mccb electrical full name, you know it stands for a device that protects circuits from too much current or short circuits. The mccb full form helps you quickly identify its purpose in electrical systems.
Tip: Always remember that the mccb full form—Molded Case Circuit Breaker—tells you both the type of device and its main job: to keep your electrical circuits safe.
You will find the mccb electrical full name used in many technical documents. It is important to know this full form because it helps you choose the right circuit breakers for your needs. The mccb full form also appears on product labels and in safety codes.
Molded Case Circuit Breaker Meaning
The phrase “molded case circuit breaker” describes both the construction and the function of the device. You can break it down into two main parts:
- Molded Case: This means the breaker has a strong, insulated shell. The molded case keeps all the working parts safe from dust, moisture, and accidental contact. It also stops electricity from leaking out, which protects you and your equipment.
- Circuit Breaker: This part of the name tells you that the device can stop the flow of electricity if something goes wrong. The breaker uses special parts inside, like bimetallic strips and magnetic coils, to sense when the current is too high. When this happens, the breaker “trips” and cuts off the power.
You will see molded case circuit breakers used in places where you need strong protection, such as factories, schools, and large buildings. These circuit breakers follow strict rules set by groups like IEC and UL. For example, IEC 60947-2 covers molded case circuit breakers for use up to 1000 V AC or 1500 V DC. UL 489 sets the rules for how these breakers must work in North America.
- Common Misconceptions:
- Some people think all circuit breakers are the same, but molded case circuit breakers have special features for higher currents and tougher environments.
- Others believe that using a bigger breaker is always safer. In fact, picking the wrong size or type can cause problems, such as not tripping when needed.
You should always check the mccb electrical full name and the mccb full form when selecting a breaker. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your electrical system safe.
MCCB Functions and Features
Overload and Short-Circuit Protection
An mccb helps keep your electrical system safe. It protects against too much current and sudden faults. If the current stays high for a long time, the mccb senses it. Inside, a thermal part gets hot when the current is above the safe level. When this happens, the breaker trips and stops electricity from flowing. This keeps wires from getting too hot and lowers fire risk.
The mccb also protects against short circuit. If there is a sudden surge, the breaker acts fast. It uses a magnetic trip to spot the spike. The breaker disconnects the circuit in just milliseconds. This quick action keeps your equipment and wires safe from harm.
Here are the main things an mccb does:
- Stops overheating and fire by protecting against overloading.
- Prevents damage to equipment by stopping short circuit.
- Lets you adjust trip settings for different loads and motors.
- Protects motors and welding machines from arc flash and high voltage.
Note: An mccb can trip if the voltage drops too low. This helps protect your devices from unsafe conditions.
Manual Switching
You can use an mccb as a manual switch. This means you can turn circuits on or off when needed. It helps you do maintenance or handle emergencies safely. The mccb lets you isolate parts of your system. This makes it safer to work on equipment. You can also control loads and manage power in your building.
Molded Case Construction
The molded case is what makes this device special. The case is made from strong materials like glass polyester or thermoset resin. It covers all the parts and keeps them safe from dust and moisture. The shell also stops accidental contact. The molded case gives extra insulation. This helps prevent electric shocks and keeps the breaker working in tough places.
| Feature | Benefit for You |
|---|---|
| Molded insulating case | Stops electric shock and keeps dust out |
| Arc extinguishing system | Reduces fire risk during faults |
| Strong frame material | Adds durability and heat resistance |
You can trust mccb circuit breakers to protect against overloading and short circuit. The molded case design keeps you and your equipment safe.
How MCCB Works
Thermal and Magnetic Tripping
MCCB circuit breakers have two ways to trip. The first way is thermal tripping. A bimetallic strip heats up if too much current flows for a long time. The strip bends because the metals grow at different speeds. When it bends enough, it pushes a trip bar. This stops electricity from moving in the circuit. This protects wires and equipment from getting too hot.
The second way is magnetic tripping. This happens when a very high current appears quickly, like in a short circuit. The big current makes a strong magnetic field in an electromagnet. The field pulls an armature fast. This trips the breaker almost right away. You get quick protection from dangerous faults.
Tip: MCCB circuit breakers use both thermal and magnetic tripping. This gives you good protection from slow overloads and sudden short circuits.
Here is a table that shows how each way works:
| Mechanism Type | Working Principle | Key Components | Operation Condition | Trip Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Trip | Bimetallic strip heats and bends when too much current flows for a long time. The trip happens after a delay. | Bimetallic strip, trip bar | Overload (too much current for a while) | Strip bends, moves trip bar, breaker trips after delay |
| Magnetic Trip | Electromagnet gets strong when a big current flows fast. It pulls an armature and trips the breaker right away. | Electromagnet, armature, trip bar | Short circuit (very high current) | Armature moves, turns trip bar, breaker trips instantly |
Circuit Protection Mechanism
MCCB circuit breakers help keep your electrical system safe. The thermal part heats up and trips after a short wait if there is too much current. The magnetic part trips almost right away if there is a short circuit. Both parts work together to give strong protection in many cases.
When you use MCCB, it can stop very large fault currents safely. This means the breaker will not get damaged when stopping big problems. MCCB is used in places that need both overload and short-circuit protection, like factories and big buildings.
- You get protection from slow overloads.
- You get fast action for short circuits.
- You keep your equipment and wires safe.
Note: Using both thermal and magnetic tripping in MCCB circuit breakers makes them a good choice for factories and commercial buildings.
Types and Applications of MCCB
Current Ratings
There are many types of MCCBs with different current ratings. These ratings tell you how much current the breaker can handle. If the current gets too high, the MCCB will trip. You can use MCCBs for small circuits or big machines. Some common current ratings are:
- 0A to 75A
- 75A to 250A
- 250A to 800A
- Above 800A
Some MCCBs have even higher ratings, like 500A, 1,500A, 2,500A, or more than 4,500A. This means you can pick the right MCCB for your job. You might need one for a small shop or a large factory. MCCBs have higher current ratings than miniature circuit breakers (MCBs). MCBs usually go up to 125A. MCCBs can go up to 2,500A or more. This makes them good for heavy-duty work.
Tip: Always look at the current rating before picking an MCCB. This helps keep your equipment safe from damage.
Here is a table that shows the differences between MCBs and MCCBs:
| Feature | Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) | Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) |
|---|---|---|
| Current Rating | Up to 125A | 15A to 2,500A |
| Interrupting Capacity | Up to 10,000A | Up to 200,000A |
| Trip Settings | Fixed | Adjustable |
| Application | Homes, small offices | Factories, large buildings |
Industrial and Commercial Use
You can find MCCBs in many places. They protect circuits in factories, schools, and big buildings. MCCBs handle large electrical loads and stop overloads and faults. You can use them in wind energy, solar power, and building safety. These breakers help machines work well and stop accidents.
MCCBs are also used in commercial places. You might see them in malls, hospitals, or office towers. Their strong build and adjustable settings make them great for places with changing needs. MCCBs are important for keeping big equipment safe and power systems working.
- MCCBs protect circuits from overloads and short circuits.
- You can trust MCCBs to work well in tough places.
- MCCBs can handle bigger loads than other breakers, so they are good for factories.
⚡ MCCBs are a smart pick when you need strong protection for big machines and complex systems.
MCCB vs. MCB and Other Breakers
MCCB vs. MCB
Circuit breakers are used in homes and factories. The two main types are MCCB and MCB. MCBs are good for small jobs, like lights and outlets at home. MCCBs are better for big jobs, like running machines in factories. They are different in size, how much current they handle, and their features.
Here is a table that shows how MCCB and MCB are different:
| Feature | Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) | Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Current | Up to 125A, suitable for low current applications | 100A to 2500A, suitable for high current applications |
| Size | Smaller, compact design | Larger, rugged molded case structure |
| Application Areas | Residential and small commercial use | Industrial and large commercial use |
| Trip Mechanism | Thermal magnetic trip (bimetal strip + magnetic coil) | Electronic trip mechanism with adjustable settings |
| Protection Functions | Overload and short circuit protection | Overload, short circuit, ground fault, and communication features |
| Installation Method | Mounted on distribution box rails | Installed inside distribution cabinets |
| Durability | Designed for less harsh environments | More durable, withstands harsh environments |
| Cost | Lower cost, simpler design | Higher cost, more complex and durable |
| Maintenance | Simple, easy to reset and replace | Requires regular inspection and maintenance of electronic trip units |
You use MCBs for homes and small stores. MCCBs are best for places with big machines or lots of power. MCCBs let you change trip settings to protect special equipment. MCBs have fixed settings and are good for simple circuits.
Tip: Pick MCCB for big motors or large buildings. Use MCB for lights and outlets at home.
MCCBs are also used where extra safety is needed, like ground fault protection. MCBs do not have these extra features.
MCCB vs. Other Circuit Breakers
You might wonder how MCCB is different from other breakers. Some other types are air circuit breakers, rcd, rccb, earth leakage circuit breaker, and residual circuit breaker. Each one has a special job.
- MCCBs can handle high currents, up to 3200A. They break the circuit fast if there is a problem. You use them in factories and big buildings.
- Air circuit breakers (ACBs) work with even bigger currents, up to 6300A. You find them in main panels in large plants. ACBs have more protection features.
- RCD and RCCB keep people safe from electric shock. They sense if electricity leaks to the ground and trip the circuit. You use them in homes, schools, and hospitals.
- Earth leakage circuit breaker and residual circuit breaker also stop power if they find leakage. These breakers help prevent shocks and fires.
Here is a list of what each breaker does:
- MCCB: Stops overload, short circuit, and ground fault in big systems.
- MCB: Protects simple circuits from overload and short circuit.
- ACB: Handles very high currents and gives more protection in factories.
- RCD, RCCB, earth leakage circuit breaker, residual circuit breaker: Keep people safe from shock by sensing leakage.
MCCBs cost more than MCBs and other simple breakers. The price changes with the brand and features. Look at the chart below to see price ranges:
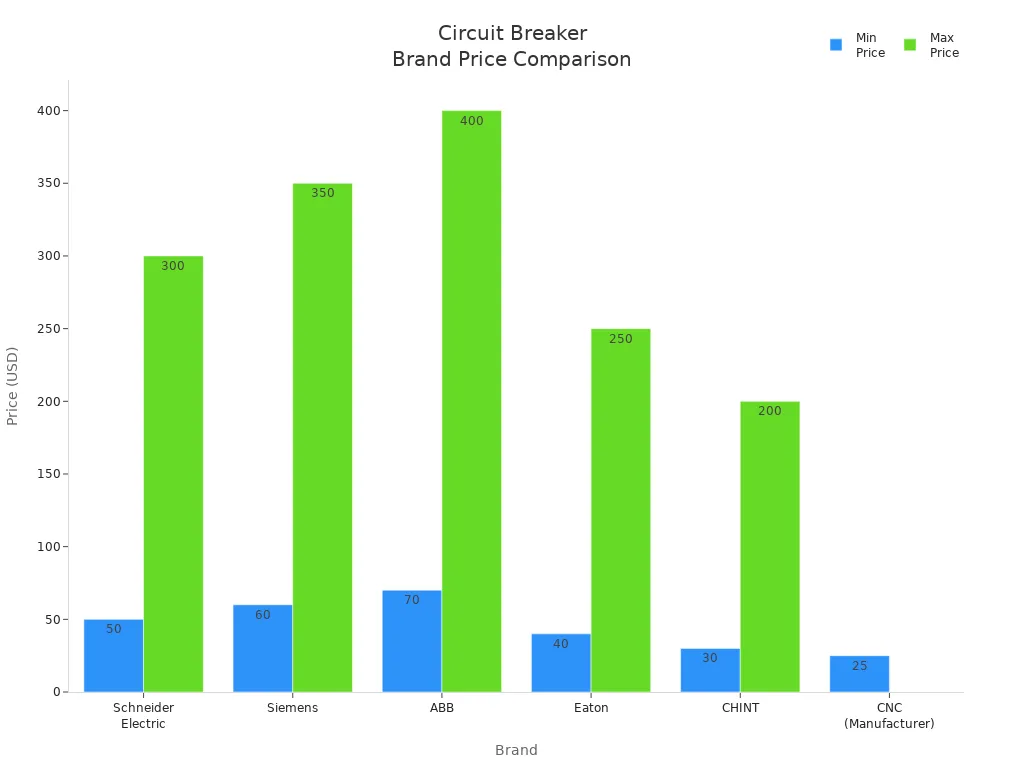
Pick MCCB if you need strong protection for big machines or want to adjust settings. For easy jobs or personal safety, use MCB, rcd, rccb, earth leakage circuit breaker, or residual circuit breaker.
- Molded Case Circuit Breaker is a device that keeps circuits safe from too much current, short circuits, and ground faults.
- It comes in a tough case that does not let electricity escape. Inside, special parts can find problems and quickly stop the power.
- This breaker helps protect people and equipment at home, in schools, and in factories.
- Pick this breaker if you need to handle lots of power, want to change settings, or need extra safety for big or tricky systems.
Always make sure the breaker fits your system to get the best safety.
If you are looking for high-quality and reasonably priced molded case circuit breakers, please feel free to contact the ONESTOP team, and we will provide you with the best customized solution
FAQ
What is the difference between MCCB and rcd?
You use MCCB to protect circuits from overload and short circuit. You use rcd to protect people from electric shock. MCCB stops high current. rcd detects leakage current and trips the circuit to keep you safe.
What does rcd stand for in electrical safety?
You see rcd in many safety guides. rcd means Residual Current Device. You use rcd to sense when electricity leaks to the ground. rcd trips the circuit to prevent shock or fire.
What is the main function of rccb?
You use rccb to protect against earth leakage. rccb stands for Residual Current Circuit Breaker. rccb detects small leaks in current and disconnects the power. You keep people safe from electric shock with rccb.
What types of rcd can you find in homes?
You find several types of rcd in homes. Some rcd protect single sockets. Some rcd cover whole circuits. You use rcd with different ratings for different appliances. rcd helps keep your family safe.
What makes rcd different from rccb?
You use rcd for general protection against leakage. rccb is a type of rcd with extra features. rccb can disconnect power quickly when it detects leakage. You get better safety with rccb in places with high risk.
See also
What Is the Full Name of MCB in Electrical Systems
How to Tell When a Distribution Board Is Overloaded
Exploring the Components of Molded Case Circuit Breakers
MCB and MCCB Compared Which Circuit Breaker Is Right for You
What Situations Call for the Use of a Molded Case Circuit Breaker





