You need to match how fast a device reacts to your equipment’s needs. Think about a server that stops working because of a power surge. This happened because the wrong electrical protection device was too slow. You can stop this problem by learning how Electrical Protection Devices work. Pick the right one for your equipment. SENTOP gives good solutions that experts use all over the world.
Key Takeaways
- Pick the right electrical protection device for your equipment. Think about how sensitive your equipment is and what it needs. This helps stop damage from electrical problems.
- Learn about the response time and I²t value of devices. Devices that act fast and have low I²t protect sensitive equipment better.
- Take care of your protection devices often. Look for damage or things that are worn out. This makes sure they work right when you need them.
- Fuses work faster than MCBs during short circuits. Use fuses for sensitive electronics. Use MCBs for regular circuit protection.
- Make sure you install protection devices the right way. Follow the instructions from the manufacturer. This helps you avoid mistakes that can cause failures.
- Use both fuses and MCBs together for better safety. This gives you quick action and lets you reset the system easily.
- Check if your devices have certifications like CE and UL. Certified devices follow safety rules and lower the chance of failure.
- Keep a log for your protection devices. Write down checks and repairs. This helps you see how they work and plan for future care.
Why Device Selection Matters
Milliseconds and Equipment Damage
A tiny delay can hurt sensitive equipment. Even a few milliseconds matter a lot. Devices like PLCs, VFDs, sensors, and industrial PCs can get damaged very quickly. Electrical faults can harm them in just microseconds or milliseconds. If you pick the wrong protection device, it may not react fast enough. This can cause expensive repairs or even break your equipment forever.
Here is a simple chart showing how fast electrical events can hurt your equipment:
| Event Type | Time Frame (milliseconds) | Voltage | Current |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESD | < 1 ms | > 500V | 1A to 10A |
| EOS | > 1 ms | < 100V | > 10A |
⚡ Tip: Always check how fast your Electrical Protection Devices can react. Fast devices help stop damage before it happens.
Even a short surge or spike can cause big problems. Sensitive equipment does not have much time to protect itself. If your device reacts too slowly, you could lose data or break important parts.
- Sensitive equipment can get damaged by electrical faults very quickly.
- PLCs, VFDs, sensors, and industrial PCs are at high risk.
Response Time and I²t Impact
When picking Electrical Protection Devices, look at response time and I²t. These two things decide how much energy hits your equipment during a fault. A fast device with low I²t will keep your equipment safer.
If you do not pick or take care of your protection devices, you can have problems. Your arc flash risk checks might not be right. This can make your equipment less reliable and cost more money. New devices like circuit breakers or fuses can make things safer. But they also add more places where things can go wrong. If you do not do regular maintenance, these devices might fail. This can cause equipment to break and stop working when you need it.
🛠️ Note: Test and maintain your Electrical Protection Devices often. This keeps your equipment safe and helps control costs.
Choosing the right device is more than just meeting the basics. You protect your equipment, avoid downtime, and keep things running well when you match device response time and I²t to your equipment’s needs.
Types of Electrical Protection Devices
There are many ways to protect sensitive equipment. The most common Electrical Protection Devices are fuses and miniature circuit breakers (MCBs). Each one works differently and reacts at different speeds. Knowing how they work helps you choose the right one.
Fuses: Fast and Current-Limiting
Fuses keep your equipment safe by stopping the circuit if too much current flows. They act very fast when there is a short circuit or high fault current.
Direct Thermal Action
A fuse has a thin metal wire inside. If too much current goes through, the wire gets hot and melts. This stops electricity almost right away. You cannot reset a fuse. You must put in a new one after it works.
Current Limitation
Fuses stop too much current from reaching your equipment during a fault. This helps keep sensitive parts safe. Fuses are faster than most other devices, especially in big short circuits.
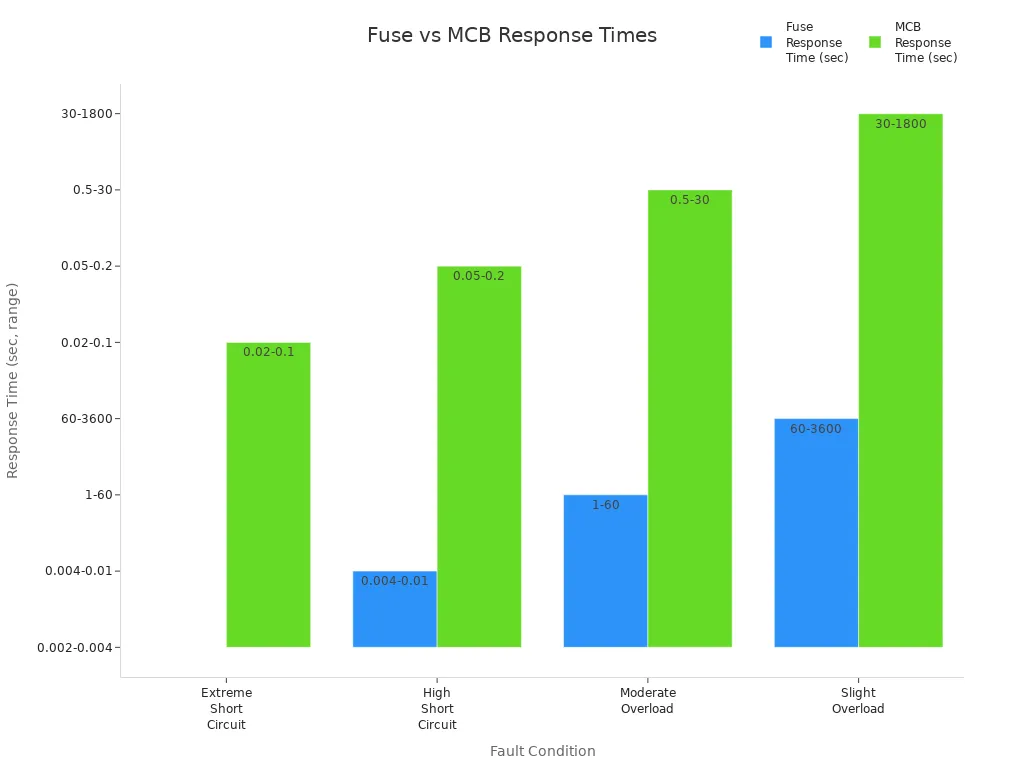
| Fault Condition | Fault Current | Fuse Response Time | MCB Response Time | Speed Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extreme Short Circuit | >10× rated | 0.002-0.004 sec | 0.02-0.1 sec | Fuse 5-25× faster |
| High Short Circuit | 5-10× rated | 0.004-0.01 sec | 0.05-0.2 sec | Fuse 5-20× faster |
| Moderate Overload | 2-3× rated | 1-60 sec | 0.5-30 sec | MCB 2× faster |
| Slight Overload | 1.5× rated | 60-3600 sec | 30-1800 sec | MCB 2× faster |
🕒 Tip: Fuses work much faster than MCBs in short circuits. This quick action can save your sensitive equipment from damage.
Degradation Factors
Fuses can get weaker over time from small surges or heat. Always check your fuses when you do regular maintenance.
MCBs: Adjustable and Convenient
MCBs protect circuits by turning off if there is too much current. You can turn them back on after they trip, which makes them easy to use.
Mechanical Operation
MCBs have a switch that breaks the circuit. If the current gets too high, the switch opens and stops the flow. This keeps your equipment safe from overloads and short circuits.
Dual Trip Mechanisms
Most MCBs have two ways to trip. One trips fast for short circuits. The other trips slower for overloads. This gives you more ways to protect your equipment.
Smart Options
Some new MCBs have smart features. You can watch and change settings for better control. This helps protect sensitive equipment even more.
Maintenance Needs
MCBs need to be tested often to make sure they work. Dust, wear, or broken parts can make them fail.
⚡ Note: Both fuses and MCBs must follow strict international rules, like IEC 60269 for fuses. SENTOP has many Electrical Protection Devices that meet these rules, so your projects stay safe and reliable.
SENTOP sells high-quality fuses, MCBs, and other protection devices. All products meet international rules like CE and UL. You can trust SENTOP for safe and reliable solutions at home, work, or in factories.
Selection Framework
Identify Protection Needs
Sensitivity and Damage Thresholds
You must know how sensitive your equipment is before picking a protection device. Every type of equipment has a voltage level that can cause harm. The table below shows common sensitivity classes:
| Class | Voltage Sensitivity Level |
|---|---|
| 0Z | Less than 50 volts |
| 0A | 50 volts to less than 125 volts |
| 0B | 125 volts to less than 250 volts |
If you know the Human Body Model (HBM) threshold, you can choose the right protection. Equipment with a low damage threshold needs a device that reacts fast and limits energy. You should also check resistance to ground and body voltage. These must stay under the damage threshold to keep equipment safe.
Process capability analysis helps you find the right electrostatic thresholds. This method checks your whole process and makes sure your protection devices fit your equipment’s needs.
Fault Current and Downtime
You need to know the possible fault current in your system. High fault currents can hurt sensitive equipment in just milliseconds. If you want to avoid long downtime, pick a device that reacts quickly and can handle the fault energy. Fast-acting fuses or MCBs with the right trip curve help you cut downtime and protect your investment.
Coordination
Your protection devices must work together. Coordination means only the device closest to the fault will trip. This keeps the rest of your system running. Good coordination helps you avoid extra shutdowns and keeps your equipment safe.
You should also think about environmental factors and regular maintenance. The table below lists important things for protecting sensitive equipment:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Conditions | Keep temperature and humidity at safe levels to protect components. |
| Protective Enclosures | Use IP-rated boxes to block dust and moisture. |
| Surge Protection | Install surge protectors and UPS to stop power spikes and outages. |
| Regular Maintenance | Inspect equipment often to catch problems early. |
🛡️ Tip: Always check both the sensitivity of your equipment and the environment where you install it. This helps you choose the best protection.
Compare Device Types
When to Use Fuses
Fuses are best when you need fast action. Use fuses for equipment that cannot handle high fault currents, like sensitive electronics or motors. Fuses are not reusable, but they limit current quickly and protect your equipment from sudden surges.
When to Use MCBs
MCBs are good for general circuit protection. You can reset them after a trip, which saves time. Pick MCBs with a B-curve for sensitive devices. These trip faster at lower currents and help protect delicate equipment.
Hybrid Strategies
You can use both fuses and MCBs together for extra safety. Fuses protect against fast, high-energy faults. MCBs handle overloads and let you reset the circuit. This combination gives you the best of both worlds.
Here is a table to help you compare fuses and MCBs:
| Feature | Fuse | MCB |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Fast-acting or slow-blow | Varies by trip curve (B, C, D) |
| Reusability | Not reusable | Reusable |
| Safety | Basic protection | Built-in safety mechanisms |
| Application Areas | Specific needs (e.g., motors) | General circuit protection |
| Suitability for Load | Fast-acting for sensitive | B-curve for sensitive devices |
- Fuses are best for special equipment like motors or electronics.
- MCBs protect main circuits and distribution lines.
- Using both together gives you maximum safety and reliability.
Review Technical Specs
Ratings and Curves
You need to check the ratings of your protection devices. Look at the maximum current (Imax) and the rated current (In). Imax shows how much energy the device can take in one event. In tells you how much it can handle over its life. Always match these ratings to your equipment.
Trip curves show how fast a device will react to different fault levels. For MCBs, B-curve types trip faster and suit sensitive loads. For fuses, check if you need fast-acting or slow-blow types.
I²t and Temperature
I²t measures the energy that passes through during a fault. Lower I²t means less energy reaches your equipment. This is important for sensitive devices. Temperature also affects how fuses work. If the temperature goes up by 20°C, you may need to increase the fuse rating by 10-15%. If it drops by 20°C, decrease the rating by 10-15%.
| Temperature Change | Fuse Rating Adjustment |
|---|---|
| +20°C | Increase by 10-15% |
| -20°C | Decrease by 10-15% |
- I²t helps you see how much energy your equipment will face during a fault.
- Adjust fuse ratings for temperature changes to avoid nuisance trips.
Certification
Always pick devices that meet international standards. Look for certifications like CE and UL. These show that the device passed safety and performance tests. SENTOP offers Electrical Protection Devices that meet these standards, so you can trust their quality and reliability.
✅ Note: Certified devices give you peace of mind and help you meet legal requirements.
Application Recommendations
Semiconductor Protection
Semiconductor equipment needs protection from voltage spikes and surges. MOVs and TVS diodes are good for this job. These devices react fast to sudden voltage changes. They help keep chips and circuits safe.
Here is a table that shows how MOVs and TVS diodes work with different pulses:
| Device Type | Pulse Type | Clamping Effect | Peak Voltage Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOV | Narrow | None | Significant |
| MOV | Wide | Obvious | Significant |
| TVS | Narrow | None | Significant |
| TVS | Wide | Obvious | Significant |
Both MOVs and TVS diodes lower peak voltages. Wide pulses get more clamping, so protection is better. Use these devices in control panels, PLCs, and sensor circuits.
💡 Tip: SENTOP has surge protection devices with MOV and TVS technology. These products meet world standards and help keep semiconductor equipment safe.
Motor Circuits
Motors need special protection because they face many risks. They can have overloads, short circuits, and high starting currents. Pick protection devices that match what motors need.
Here is a table that lists important things for motor circuit protection:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Overload Protection | Stops motors from running too long at high current. |
| Short-Circuit Protection | Cuts power fast during a short circuit. |
| Thermal Trip Feature | Trips when the motor gets too hot. |
| Instantaneous Trip Feature | Responds quickly to sudden current spikes. |
| Bi-metallic Strip Relay | Handles high starting currents and protects against overloads with a time delay. |
| Ambient Temperature Compensation | Keeps relay performance steady, even if the room gets hot or cold. |
| Adjustable Trip Settings | Lets you set trip points to match your motor’s normal running current. |
Use MCBs with thermal and magnetic trip features for most motors. For big motors, add overload relays and temperature sensors. SENTOP sells MCBs and overload relays with settings you can change. These products help protect motors in factories, workshops, and HVAC systems.
⚙️ Note: Always match the protection device to your motor’s size and type. This helps stop false trips and keeps equipment working.
Transformer Circuits
Transformers need different protection based on their size and use. Small transformers often use fuses. Bigger ones use circuit breakers and relays. Oil-filled transformers need extra safety devices.
Here is a table that shows common protective devices for transformer circuits:
| Protective Device | Function | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Fuses | Melt and break the circuit if current gets too high. | Small distribution transformers. |
| Circuit Breakers | Interrupt fault current automatically. | Medium and large power transformers. |
| Protective Relays | Detect abnormal current or voltage and send trip signals. | Transmission and substation transformers. |
| Buchholz Relay | Detects gas or oil flow from internal faults. | Oil-immersed transformers (>500 kVA). |
| Surge Arresters | Divert lightning or switching surges to ground. | All transformers, especially HV/EHV. |
| Temperature Sensors | Monitor winding and oil temperature. | Distribution and power transformers. |
| Pressure Relief Devices | Release excess pressure to prevent tank rupture. | Oil-filled transformers. |
Use fuses for small transformers. Use circuit breakers with relays for bigger ones. Add surge arresters and temperature sensors for more safety. SENTOP has fuses, circuit breakers, and surge protection devices for these needs. These products help keep transformer circuits safe and reliable.
🛡️ Tip: Always check your transformer’s size and type before picking protection. This helps you choose the right device for the job.
Distribution Panels
Distribution panels need strong protection for sensitive equipment. These panels give power to many devices. If one thing goes wrong, it can cause big trouble. Surge protection is very important for these panels. Surge protectors stop high voltage spikes from hurting your equipment.
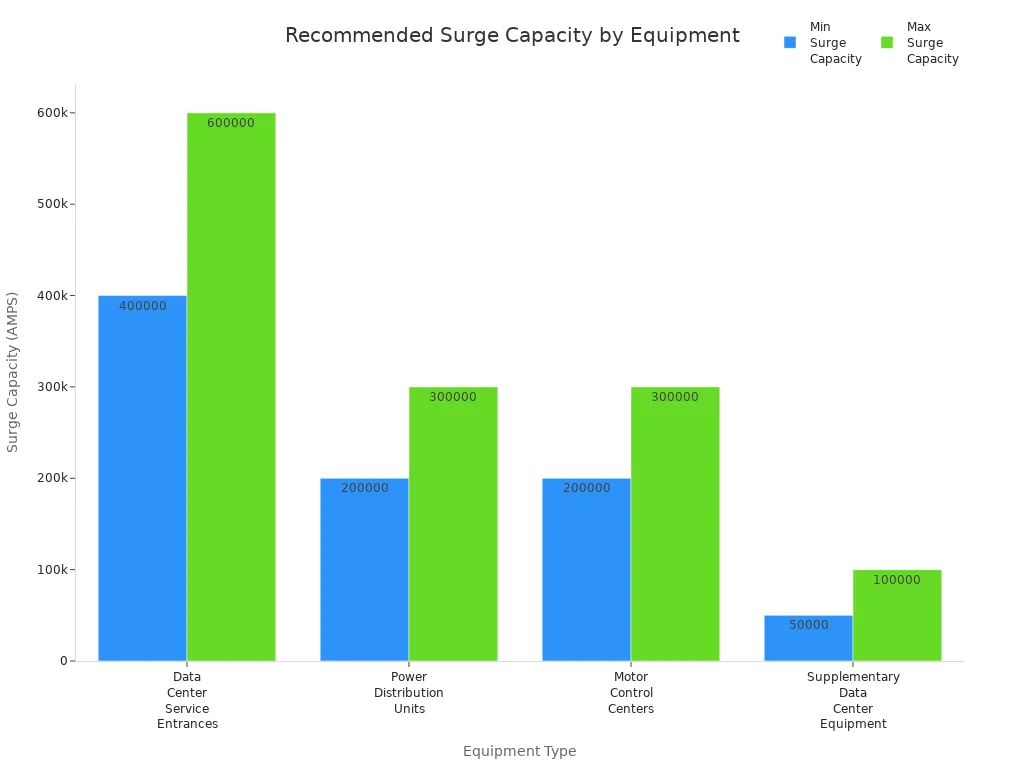
Pick a surge protector with the right surge capacity for your equipment. The table below shows how much surge capacity different equipment needs:
| Equipment Type | Recommended Surge Capacity (AMPS) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Data Center Service Entrances | 400,000 to 600,000 | Handles large power needs and keeps critical systems running. |
| Power Distribution Units | 200,000 to 300,000 | Use side-mounted surge protectors with dry relay contacts. |
| Automatic Transfer Switches | N/A | Protect every power connection point for best results. |
| Motor Control Centers | 200,000 to 300,000 | Redundant systems give you more mounting options. |
| Supplementary Data Center Equipment | 50,000 to 100,000 | Choose ratings based on how critical the equipment is. |
The chart below shows how surge capacity needs change for each type of equipment:
When you pick protection devices for distribution panels, check if they meet international standards. SENTOP sells surge protectors, circuit breakers, and distribution boxes that follow CE and UL rules. These devices help keep your equipment safe and your work going.
Here are some tips to protect your distribution panels:
- Use surge protectors with the right capacity for your equipment.
- Install circuit breakers that match your panel’s load and fault current.
- Choose distribution boxes with high IP ratings to block dust and moisture.
- Test your protection devices often to make sure they work when needed.
💡 Tip: Always check the surge capacity and certification before you buy protection devices. SENTOP gives you good solutions for every kind of distribution panel.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Wrong Device Choice
Some people think any protection device will work. This is not true for sensitive equipment. Many people make mistakes when picking electrical protection devices. You must match the device to your equipment’s needs. If you pick a device with too little protection, your electronics can get damaged. Some people choose devices just because they are cheap. This can lead to bad quality and safety problems. Others forget to think about where and how they put the device. Where you install the device changes how well it works.
Here are mistakes you should not make:
- Picking a device that does not protect your electronics enough.
- Not thinking about where and how you install the device.
- Choosing a device only because it is cheap, which can be unsafe.
⚠️ Tip: Always check what your equipment needs and where you will install the device. Do not pick a device just because it costs less. Good protection saves money over time.
If you do not check the protection level, you might pay for repairs. Bad installation can make the device work less well and cost more. Cheap devices can break early, so you need to replace them more often.
Ignoring Coordination
Your protection devices must work together. If you do not make them work together, you can have bigger problems. When devices do not coordinate, you might have surprise downtime. This can make things confusing and cause mistakes. Sometimes, people who do not know enough try to fix things. This can make accidents more likely. If you skip safety checks, you might miss problems. Fixing things too fast can leave problems that cause more trouble later.
- Surprise downtime can confuse people and make things unsafe.
- People who are not trained may make mistakes when fixing things.
- Skipping safety checks means some problems stay hidden.
- Fixing things too quickly can cause new problems.
🛡️ Note: Make sure your protection devices work together. This keeps your system safe and helps stop downtime.
Overlooking I²t
I²t shows how much energy goes through a device during a fault. If you do not check I²t, you might pick a device that is too slow or too fast. This can cause false trips or big damage. You must match the I²t value to your equipment’s needs.
| I²t Value Comparison | Consequence |
|---|---|
| I²t_Fuse < I²t_SPD(Imax) | False trip, leaving your system unprotected |
| I²t_Fuse too high | Slow response to short-circuit, big damage |
If your fuse has a lower I²t than your surge protector, it might trip too much. This leaves your system without protection. If the fuse’s I²t is too high, it might not react fast enough. Your equipment could get badly damaged.
💡 Tip: Always check I²t values when you pick protection devices. The right I²t keeps your equipment safe and stops false trips.
You can avoid these mistakes by learning about your equipment and protection devices. Take time to look at technical details and how you will install the device. Good choices keep your equipment safe and your system working well.
Neglecting Maintenance
Some people think their job is finished after installing a protection device. This is not true. Every protection device needs regular care to work right. If you skip maintenance, your sensitive equipment could get damaged.
Dust, dirt, and water can get inside circuit breakers and fuses. These things can make the device fail when you need it most. The moving parts in MCBs can wear out over time. Fuses can get weaker after many small surges. If you do not check these devices, you might miss problems until it is too late.
Here are some signs your protection devices need checking:
- The device trips more often than before.
- You see burn marks or color changes.
- The device feels hot when you touch it.
- You hear buzzing or clicking noises.
- The device will not reset or work smoothly.
🔍 Tip: Always look at your protection devices during regular checks. Watch for dust, rust, or loose wires.
You should follow a simple plan for maintenance. This helps you find problems early and keeps your equipment safe. Here is a basic checklist you can use:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Check for dust, dirt, and damage |
| Tighten Connections | Every 3 months | Make sure all screws are secure |
| Test Operation | Every 6 months | Trip and reset the device |
| Replace Worn Parts | As needed | Change out old or damaged parts |
| Clean Contacts | Every 6 months | Remove dust and corrosion |
If you use SENTOP protection devices, you get strong materials and good design. But you still need to check them often. Good care helps you avoid sudden failures and costly downtime.
You should also keep notes about all maintenance work. Write down the date, what you checked, and any problems you found. These notes help you see patterns and plan future checks.
🛠️ Note: Never ignore warning signs. If a device looks or sounds wrong, change it right away.
Regular care is not just about safety. It also helps your equipment last longer and work better. When you take care of your protection devices, you protect your investment and keep things running smoothly.
Advanced Protection Strategies
Current Limitation
You can keep sensitive equipment safe by limiting current during faults. Fast current limitation stops dangerous surges before they reach devices. A Surge Stopper circuit is one advanced way to do this. It uses a current limit loop to control voltage when there is too much current. This keeps voltage steady and stops high spikes from hurting electronics. The Surge Stopper lets the MOSFET work safely, so equipment stays safe even if there is a short circuit.
It is also important to set up an ESD protected area. You can use anti-static floors, grounding systems, and ESD-safe workstations. These steps help stop electrostatic discharge, which can hurt electronics and cost money. Using both strategies makes your equipment’s environment safer.
⚡ Tip: Always use current-limiting devices and ESD protection where you have sensitive electronics. This lowers the risk of sudden failures.
Selective Coordination
Selective coordination helps your electrical system stay reliable. If a fault happens, only the closest device will trip. The rest of your system keeps working. You do not have to shut down big areas for small problems. Selective coordination is very important in places with sensitive loads, like hospitals, data centers, or factories.
You can get selective coordination by picking protection devices with the right trip curves and settings. This method isolates faults to the smallest area possible. Your sensitive equipment stays safe, and you have less downtime.
🛡️ Note: Selective coordination keeps your system running well. It protects equipment and helps you avoid costly stops.
Smart Devices
Smart protection devices give you more control and information. These devices use advanced technology to watch, react, and report on electrical events. You can use them to protect many types of sensitive equipment. The table below shows how smart devices help in different situations:
| Application Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Computing Equipment | Protects computers, laptops, and servers from surges that can slow or damage them. |
| Audio and Visual Equipment | Safeguards sound systems and TVs from surges that affect quality. |
| Networking Gear | Keeps modems, routers, and switches safe to prevent lost connections. |
| Smart Home Devices | Protects smart lights, thermostats, and cameras from damaging surges. |
| Medical Equipment | Essential for life-saving devices to prevent dangerous surges. |
| Industrial Control Systems | Protects PLCs and sensors from surges that can stop production. |
| Telecommunications Equipment | Safeguards phones and faxes from surges that can damage systems. |
When you pick smart protection devices, follow these steps: First, find out what equipment you have and what surge protection it needs. Next, check the joule rating to see if it matches your device’s sensitivity. Then, look at the clamping voltage for fast response to surges.
Smart devices often have surge battery backup. This feature is important for critical devices, like medical computers. It keeps equipment running during power outages and protects against overvoltage. You keep your data safe and your important devices working.
💡 Tip: Use smart protection devices for the best safety and control. They help you watch your system and react quickly to problems.
Installation and Maintenance

Proper Installation
You must put electrical protection devices in the right way to keep your sensitive equipment safe. Safety is the most important thing. Always do these steps:
- Find the Right Spot. Put the device at the main board or near your sensitive equipment.
- Turn Off the Power. Switch off the main breaker so you do not get shocked.
- Wear PPE. Use gloves that do not let electricity through and wear safety glasses.
- Make Sure You Can See Well. Work where it is bright so you do not make mistakes.
- Attach the Device. Fix the surge protector or breaker to a DIN rail or panel.
- Get the Cables Ready. Take off the plastic from the ends of the wires.
- Connect the Wires. Use the wiring diagram to make the right connections.
- Check the Connections Again. Make sure every wire is tight and will not come loose.
- Turn the Power Back On and Test. Switch the power on and see if the device works right.
- Ask an Expert if Needed. If you are not sure, call a licensed electrician for help.
⚠️ Tip: Always read the instructions from the maker before you start. Safety comes first. Doing the steps the right way helps stop accidents and keeps your system working well.
Routine Testing
Testing your protection devices often helps you find problems early. You should test them on a regular plan. Here are some checks you should do:
- Voltage Relays: Do a test to check the relay’s supply voltage.
- Creep or Pickup Test: Change the relay’s settings and watch for the right pickup voltage.
- Trip Time Test: Time how long it takes for the relay to trip and see if it matches what is expected.
- Differential Relays: Check the lowest pickup and the slope of the differential curve.
- Fuses: Test if the fuse works by checking if electricity can go through. Use a tester or multimeter. If the number is low, the fuse is good.
- MCBs: Trip and reset the breaker to make sure it works smoothly.
🛠️ Note: Write down all your test results. This helps you see patterns and plan when to do more checks.
Addressing Degradation
Protection devices can get weaker or stop working well over time. Heat, dust, and small surges can make this happen. You need to look for signs that your devices need care:
- Devices trip more than they used to.
- You see burn marks or color changes.
- The device feels hot when you touch it.
- You hear buzzing or clicking sounds.
- The device will not reset or work right.
Make a plan to check for these problems. Clean off dust and dirt from your devices. Tighten any loose wires or screws. Change out any parts that are old or broken right away.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Look for dust, dirt, and damage |
| Tighten Connections | Every 3 months | Make sure all screws are tight |
| Test Operation | Every 6 months | Trip and reset the device |
| Replace Worn Parts | As needed | Change out old or broken parts |
💡 Tip: Taking good care of your protection devices helps them last longer and keeps you from losing time and money.
Device Selection Checklist
Quick Steps
You can protect your sensitive equipment by using a simple checklist. Follow these steps to help you pick the right device:
- Identify Equipment Sensitivity
Make a list of devices that need protection. Check if they can be hurt by voltage spikes or current surges. - Determine Fault Current and Voltage
Find the highest current and voltage your system could get during a fault. This helps you choose the right device. - Choose the Right Device Type
Decide if you need a fuse, MCB, or both. Fuses are best for fast protection. MCBs are good if you want to reset the circuit easily. - Check Device Ratings
Look at breaking capacity, trip curve, and voltage rating. Make sure these numbers match what your equipment needs. - Review Certification
Pick devices with certifications like CE or UL. These show the device meets safety rules. - Plan for Proper Installation
Follow the maker’s instructions. Use the right size and make tight connections. This helps stop failures. - Schedule Regular Maintenance
Make a plan to test and check your devices often. Change any parts that are worn or broken right away.
💡 Tip: Keep a list of all your protection devices. Write down the type, rating, and last time you checked them. This helps you see how they work and plan future checks.
Key Takeaways
You can keep your sensitive equipment safe by following some simple rules. Here are the most important things to remember:
- Match Device Characteristics
Always pick a device that fits your system. Check breaking capacity, trip curve, and voltage rating. The right match keeps your equipment safe if something goes wrong. - Proper Installation
Put in devices the way the maker says. Use the right size and make sure all wires are tight. Good installation stops many problems. - Regular Maintenance
Test and check your devices often. Look for signs of damage or wear. Change parts when needed to keep your protection strong.
| Step | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Match Characteristics | Stops equipment damage during faults |
| Install Properly | Lowers the chance of device failure |
| Maintain Regularly | Keeps your equipment safe and working well |
✅ Remember: Picking the right device, installing it the right way, and checking it often gives you the best protection for your sensitive equipment. SENTOP has certified solutions to help you reach these goals.
Picking the right electrical protection device helps keep your equipment safe. You need to match the device’s features to what your equipment needs. Always follow simple steps when you choose a device. Try not to make mistakes that can hurt your equipment. Look at the technical details before you pick.
- Check what your equipment needs.
- Look at different device choices.
- Make a plan to check and fix devices often.
💡 SENTOP gives you safe and trusted options. Choose carefully to protect your equipment and keep everything working well.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a fuse and an MCB?
A fuse melts and breaks the circuit when too much current flows. You must replace it after it works. An MCB trips like a switch. You can reset it and use it again.
How often should I check my protection devices?
You should check your devices every month. Look for dust, damage, or loose wires. Test operation every six months. Write down each check in a logbook.
Can I use both a fuse and an MCB together?
Yes, you can use both. A fuse reacts fast to big faults. An MCB protects against overloads and lets you reset the circuit. This gives you extra safety.
How do I know which device rating to choose?
Check your equipment’s voltage and current needs. Pick a device with a rating just above your normal load. Always follow the maker’s guide and safety rules.
Why do I need certified devices like CE or UL?
Certified devices meet strict safety standards. You lower the risk of fire or damage. You also meet legal rules for your building or project.
What should I do if my protection device trips often?
First, check for overloads or short circuits. Look for signs of damage or loose wires. If the problem continues, ask a qualified electrician for help.
Does SENTOP offer solutions for solar energy systems?
Yes, SENTOP provides protection devices for solar panels, inverters, and connectors. These products help keep your solar energy system safe and reliable.
💡 Tip: Always read the product manual before installing any protection device. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your equipment safe.
See also
What Are the Key Differences Between ATS and STS
The difference between miniature circuit breakers and fuses
What is the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse?
Can I replace a fuse with a circuit breaker?
What Makes Distribution Boxes and Fuse Boxes Different





