Surge voltage is the effect of a high voltage increase within a very brief time period, which may result in destruction of sensitive electrical apparatus. Surge voltage is normally caused by occurrences such as lightning, equipment failure, or switching on/off. For prevention against such surges damaging the apparatus, surge protection devices (SPDs) are utilized. The devices will provide the excessive voltage in the safe pathway, hence preserving the apparatus from destruction.
What is surge voltage?
Surge voltage refers to the drastic fluctuations in voltage that occur in a short period of time. The intensity and duration of these surges may vary depending on the cause.
Reasons for Strong Surge Voltage
The reasons for surge voltage are:
- Flash electric shock: Indirect or direct lightning strokes can generate high voltage surges through power lines.
- Switch surge: Sudden switching of electrical loads can cause temporary voltage spikes.
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD): Static electricity that accumulates on equipment and discharges can generate instantaneous surge voltage, which can annihilate electronic components.
The impact of surge voltage on electrical equipment
Surge voltage can have severe impacts on electrical systems, including:
- Equipment damage: Sensitive parts such as microprocessors and circuit boards can be damaged.
- Data loss: Electronic devices such as computers and servers can experience data damage or loss.
- Risk of fire: In extreme cases, surge voltage can cause overheating and even cause electrical system fires.
What is Surge Protection Device (SPD)?
Surge protection device is an important safety component designed to protect electrical equipment from voltage surges. Surge protectors limit the voltage provided to electrical equipment within a certain threshold by short circuiting the current to ground or absorbing spikes during transients, thereby avoiding damage to the connected equipment.
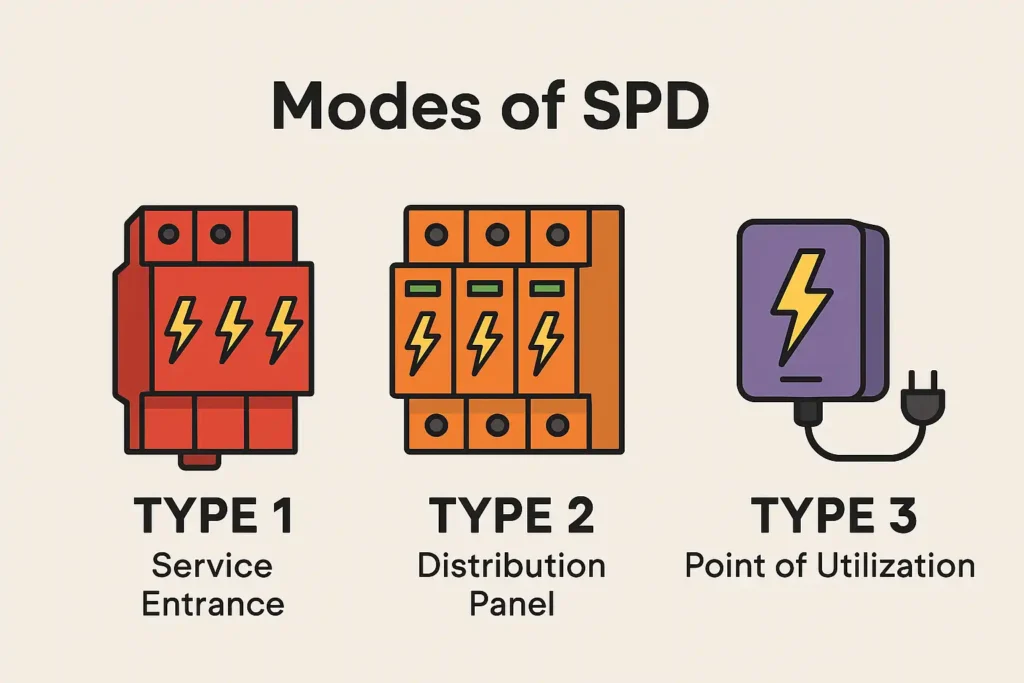
Types of SPD
According to different applications, SPDs are divided into several types (compliant with IEC 61643-11 standard)
- Type 1 SPD: To deal with direct lightning strikes, installed in the main distribution box of the building, with a discharge capacity of over 25kA
- Type 2 SPD: Resist induced lightning and operational overvoltage, suitable for distribution boxes, with a nominal current In ≥ 20kA
- Type 3 SPD: Terminal device protection, such as socket level SPD, suitable for sensitive electronic devices
Key components of SPD
SPD typically includes the following components:
- Varistor: A semiconductor component that absorbs excess voltage.
- Gas discharge tube: When the surge voltage is too high, it guides the excess voltage to the grounding system.
- Capacitor: Used to smooth voltage fluctuations and absorb slight surges.
The working principle of SPD
The core function of SPD is to detect and suppress transient overvoltage. Its working principle can be divided into three stages:
Normal monitoring: Under normal voltage, the internal components of SPD maintain a high impedance state, which does not affect the operation of the circuit
Surge trigger: When the voltage exceeds the threshold, the SPD quickly switches to a low impedance state, discharges the surge current through the grounding system, and clamps the residual voltage to the safe range of the equipment
Automatic recovery: After the surge ends, the SPD component automatically resets to the high impedance state, preparing for the next impact
How to choose to install SPD
The installation location of SPD is crucial for its efficiency. Ideally, SPDs should be installed at the power inlet as much as possible to prevent surge voltage from spreading throughout the electrical system.
Secondly, grounding can be used, with a grounding resistance of ≤ 4 Ω and a lead length not exceeding 0.5 meters to reduce inductance effects
And adopt “Type 1+Type 2+Type 3” graded protection, gradually reducing surge energy
Maintenance and monitoring of SPD
Regular maintenance and checks ensure that SPD can still efficiently protect the electrical system.
- Regular inspection and replacement
SPD should be checked from time to time to ensure its operation as usual. Over time, its components may become old and require replacement to maintain their protective property. - SPD performance monitoring
Automatically track SPD performance to aid in the detection of its triggering state in a timely manner, which implies that the device has been charged with surge voltage. SPD can be replaced before equipment breakdown.
Conclusion
As the core equipment for resisting strong surge voltage, the effectiveness of SPD depends on scientific selection, standardized installation, and continuous maintenance. By implementing graded protection, parameter adaptation, and intelligent monitoring, the lifespan of equipment can be maximized and maintenance costs can be reduced. If you need customized lightning protection solutions, you can consult ONESTO professional manufacturers to obtain systematic services that meet international standards
FAQ
What is the cause of surge voltage?
Surge voltage may be caused by lightning, switch operation, and electrostatic discharge.
How does SPD protect electrical systems?
SPD protects equipment by transmitting overvoltage to the grounding system.
Can SPD eliminate all surge voltages?
SPD can handle most surge voltages, but for high-intensity surges, equipment upgrades may be required.
Where should SPD be installed?
SPD needs to be installed on power entrances, distribution boards, or sensitive equipment to provide comprehensive protection.
Here are some information that you may have just been interested in:
What You Need to Know About Surge Protection Device Lifespan
How to test surge protection device equipment
Five benefits of installing surge protectors in distribution boxes