Choosing the right wire size is important for safety. When you choose wires for a 220V 15-amp breaker, use 14 AWG copper or 12 AWG aluminum wires. These wires help stop overheating and lower fire risks. Many electricians prefer to choose wires like 12 AWG copper, as it works well with big appliances, reduces voltage drops, and allows for upgrades later. Picking the right wire size helps your circuit work well and follow electrical rules. Always think about safety when you choose wires for your breaker.
Key Takeaways
-
Use 14 AWG copper or 12 AWG aluminum wires for a 220V 15-amp circuit. These wire sizes stop overheating and lower fire risks.
-
Learn about wire thickness and electricity limits. Thicker wires safely carry more electricity, avoiding overloads and short circuits.
-
Pick the right wire covering. PVC bends easily and resists water, while XLPE handles high heat better. Good covering keeps wires safe and lasts longer.
-
Follow local electrical rules. These rules keep you safe and help you avoid fines or accidents.
-
Think about hiring a trained electrician. They install wires correctly and follow safety rules, lowering risks from doing it yourself.
Understanding Wire Gauge and Ampacity
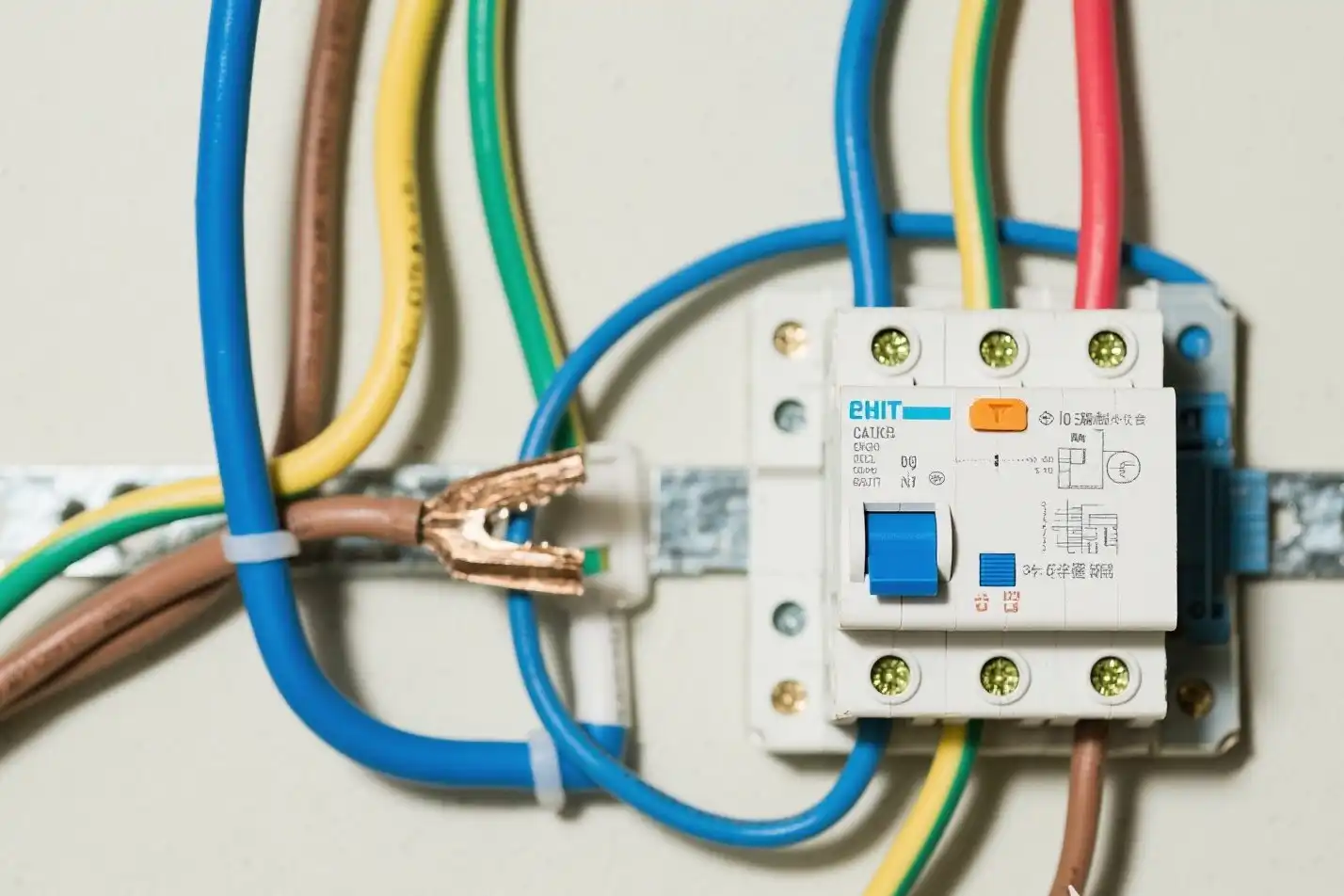
Why wire gauge matters in circuits
Wire gauge is important for keeping circuits safe and working well. It shows how thick the wire is, which affects how much electricity it can carry. Picking the right wire gauge stops wires from overheating, lowers fire risks, and keeps circuits running smoothly.
When choosing a wire gauge, think about how much power it needs to handle. For example:
-
Smaller gauge numbers mean thicker wires that carry more electricity.
-
Bigger gauge numbers mean thinner wires for smaller power needs.
Using the wrong wire gauge can cause problems like overloads, short circuits, or even fires. For example, 6/2 cables work for simple setups, but 6/3 or 6/4 cables are better for bigger power needs. Always follow safety rules, secure connections, and check wiring codes to stay safe.
How ampacity helps pick the right wire size
Ampacity is the most electricity a wire can safely carry without overheating. It’s a key factor when picking the right wire size. Ampacity depends on things like how the wire is installed, how well it handles heat, and how the wires are grouped. Here’s a simple table:
|
What Affects Ampacity |
What It Means |
|---|---|
|
Installation Conditions |
Changes how heat escapes from the wire. |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
Materials around the wire affect its heat level. |
|
Phase Arrangements |
Wire setups change heat and ampacity. |
For a 220V circuit, pick a wire with enough ampacity for the circuit’s power. This keeps the wire from overheating. For example, 14 AWG copper or 12 AWG aluminum wires work for a 15-amp breaker because their ampacity matches the circuit’s needs.
Why 14 AWG copper or 12 AWG aluminum works for 15 amps
You might ask why these wire sizes are good for 15 amps. It’s because of their ampacity and material. A 14 AWG copper wire can carry 15 amps safely. Copper is great at moving electricity, so it wastes less energy and stays cooler.
A 12 AWG aluminum wire is also fine for 15 amps. Aluminum is lighter and cheaper than copper, which makes it useful for some jobs. But aluminum wires need good connections to avoid problems like rust, which can hurt performance.
When deciding between these wires, think about cost, how they’ll be installed, and what your circuit needs. Both options are safe and help your circuit work well.
Choosing Between Copper and Aluminum Wires

Benefits of copper wires for circuit breakers
Copper wires are strong and work well for circuit breakers. They carry electricity easily, wasting less energy and staying cooler. This makes copper a popular choice for homes and businesses.
Tests show copper wires handle high power safely. For example:
-
Copperweld wires worked better than pure copper in grounding tests.
-
A #8 copperweld wire stayed safe after a 46 kA fault. Pure copper broke at 40 kA.
These tests prove copper can handle heavy electrical loads. It’s a reliable option for your circuit breaker.
Advantages of aluminum wires in certain applications
Aluminum wires are useful in some situations. They are lighter and cheaper than copper, which helps in big projects. Industries like car manufacturing use aluminum wires because they weigh less.
|
Application Type |
Growth Rate (CAGR) |
Benefits of Aluminum Wires |
|---|---|---|
|
Cars |
Saves weight, energy, and improves fuel use |
|
|
Trucks |
>5% |
Lighter wires for better efficiency |
Aluminum wires are also easier to install, saving time and effort. But they need good connections to avoid rust or overheating.
Key factors to consider when selecting wire material
When picking copper or aluminum wires, think about these points:
-
Wire Gauge: Pick the right thickness to stop overheating.
-
Insulation Material: Use insulation like PVC to protect the wire.
-
Conductor Material: Copper is strong and conducts well; aluminum is cheaper and lighter.
-
Voltage Rating: Make sure the wire handles your system’s voltage safely.
By checking these factors, you can choose the best wire for your circuit breaker. This keeps your system safe and working well.
Picking the Best Insulation for Your Circuit
Common insulation types for home circuits
When picking wire insulation, there are a few common choices. Each type has its own benefits based on your needs. Here are the most used options:
-
Thermoplastic (PVC): This is a popular and low-cost insulation. It’s flexible, resists water, and handles chemicals well.
-
Thermoset (XLPE): This tough insulation resists heat and scratches. It works great in hot areas.
-
Rubber-based insulation: This type is very bendable. It’s often found in older homes or places needing stretchy wires.
These insulation types work well if installed properly. Good air sealing and careful setup help them perform their best.
Why insulation matters for wire safety and performance
Wire insulation does more than just cover the wire. It keeps the wire safe and working well. Good insulation stops electricity from leaking, prevents short circuits, and shields the wire from damage.
Tests show how insulation affects safety:
-
Resistance tests check if wires handle electricity without leaks.
-
Dielectric tests ensure insulation survives high voltage safely.
-
Thickness tests find weak spots that might cause problems.
|
Test Type |
What It Does |
|---|---|
|
Checks insulation quality over time, important for circuits with high resistance. |
|
|
Impulse Dielectric Testing |
Tests insulation under high voltage to ensure no failures. |
|
Insulation Concentricity and Thickness |
Finds uneven spots in insulation that could cause damage. |
Choosing good insulation keeps wires safe and working for a long time.
Best insulation for a 220V 15-amp breaker
For a 220V 15-amp breaker, PVC insulation is a great choice. It handles heat and moisture well, keeping wires safe in homes. PVC is also flexible, making it easy to use in tight spaces.
If you need stronger insulation, try XLPE. It lasts longer, handles higher heat, and resists damage better than PVC. But it costs more and might need expert installation.
Always check the manufacturer’s guide to match insulation with your wire and circuit. Good insulation improves safety and helps wires last longer.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choose Wires for Your Circuit Breaker
Step 1: Find out the circuit’s voltage and amperage
Before picking wires, know your circuit’s voltage and amperage. This helps you choose the right wire size for safety. For a 240-volt breaker, the voltage is 240 volts, and the amperage is 15 amps.
To find these numbers, check your breaker panel or system plans. These plans are like maps showing how parts connect and work. They use symbols to make the system easier to understand.
Schematics give important details about electrical needs. These details help you pick wires that match your circuit’s voltage and amperage.
Looking at schematics also shows how electricity moves through the system. This helps you pick wires that won’t overheat or fail under the circuit’s load.
Step 2: Choose the right wire thickness and material
After finding the voltage and amperage, pick the correct wire thickness and material. Wire thickness, called gauge, affects how much electricity it can carry safely. For a 240-volt, 15-amp breaker, use 14 AWG copper or 12 AWG aluminum wires.
The wire gauge system is a standard way to measure wire sizes. It makes choosing the right cable easier. Safety rules, like NFPA standards, require wires to handle more than 100% of the expected load.
|
Benchmark Type |
What It Means |
|---|---|
|
Wire Gauge System |
A standard way to measure wire thickness. |
|
Safety Factors |
Rules ensure wires can handle more than the expected load. |
Copper wires are strong and carry electricity well, making them great for homes. Aluminum wires are lighter and cheaper, which is helpful for big projects. But aluminum wires need careful setup to avoid rusting.
When deciding on wire material, think about cost, where it will be used, and your circuit’s needs.
Step 3: Pick the best insulation for your wires
Once you know the wire size and material, choose the right insulation. Insulation keeps wires safe by stopping electricity leaks and damage.
For a 240-volt breaker, PVC insulation is a good choice. It’s cheap, flexible, and resists water and chemicals. If your circuit gets very hot, XLPE insulation is better. It handles heat well and lasts longer but costs more.
Follow the “Do” and “Don’t” instructions when picking insulation. Not following them can damage wires or lower their performance.
When choosing insulation, focus on flexibility, strength, and matching it to your wire type. Good insulation makes your wires safer and last longer.
Step 4: Follow local electrical codes for safety
Before setting up a circuit breaker, check your wiring follows local electrical codes. These rules are important for safety and help avoid problems during inspections. They explain what wire size, grounding, and setup methods to use.
Local codes can differ based on where you live. Things like weather and building laws affect these rules. For example:
-
Hot areas may need thicker wires to handle heat.
-
Wet regions might require stronger grounding for safety.
To ensure compliance, read your area’s electrical code guidelines. You can get these from your local government or building office. If you’re unsure, ask a licensed electrician. They can explain the rules and confirm your wiring is correct.
Tip: Always stick to local codes when installing a circuit breaker. This keeps your system safe and avoids expensive inspection issues.
Step 5: Install wires carefully or hire an expert
Putting in wires for a circuit breaker needs planning and care. First, gather tools like wire cutters, strippers, and a voltage tester. Turn off the main power before starting.
Here’s how to install wires:
-
Get the wires ready: Cut them to the right length and remove the insulation at the ends.
-
Attach the wires: Secure them tightly to the breaker terminals.
-
Organize the wires: Run them through conduits or clamps to keep them neat and safe.
-
Check the setup: Use a voltage tester to ensure everything works properly.
If you’re unsure about doing this, hire a licensed electrician. They know how to install wires safely and follow local codes.
Note: Bad installation can cause dangers like fires or damaged equipment. Always focus on safety when working with electricity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Wires
Picking wires that are too small
Using wires that are too thin can be dangerous. Thin wires overheat and might cause fires. They cannot handle the electricity needed for the circuit. For a 220V 15-amp circuit, use 14 AWG copper or 12 AWG aluminum wires. These sizes carry the current safely without overheating.
Think about how far the power travels in your circuit. Long distances can lower voltage and make wires hotter. To fix this, use thicker wires or ones with less resistance. Keep the wire length short when possible. Check your connections often to make sure they stay tight and work well.
Tip: Always match the wire size to the circuit’s amperage to avoid problems.
Forgetting about insulation type
Not choosing the right insulation can make wires unsafe. Insulation keeps wires safe from damage and stops electricity from leaking. PVC insulation is common for home circuits because it’s flexible and resists water. In hot areas, XLPE insulation is better since it handles heat well.
Bad insulation can cause short circuits, shocks, or fires. Always pick insulation that fits your circuit’s needs. For example, PVC works for a 220V 15-amp circuit, but in tough conditions, stronger insulation like XLPE is better.
Note: Check insulation regularly for damage to keep wires safe and working well.
Skipping local electrical rules
Not following local electrical rules can be unsafe and illegal. These rules help prevent fires and shocks. For example:
|
Mistake |
What Can Happen |
How to Avoid It |
|---|---|---|
|
Breaking electrical rules |
Do regular inspections |
Ignoring these rules can put everyone in danger. Always read your area’s electrical rules before starting. In hot or wet places, you might need thicker wires or better grounding.
Reminder: If you’re unsure about the rules, ask an electrician. They can help you follow the rules and avoid mistakes.
Overlooking voltage drop for long circuits
Not thinking about voltage drop can make circuits unsafe and inefficient. Voltage drop happens when electricity loses power over long distances. This can cause devices to work poorly or even break. For a 220V 15-amp breaker, you must check the distance between the breaker and the devices it powers.
Long circuits need thicker wires to avoid losing too much power. For example, if your circuit is over 50 feet long, 14 AWG copper wire might not work well. You may need 12 AWG copper wire to lower resistance and keep the voltage steady. Always measure your circuit’s length and pick the right wire size.
To figure out voltage drop, use online calculators or ask an electrician. These tools consider wire type, size, and circuit length. Keeping the voltage drop under 3% helps your circuit stay safe and work properly. Ignoring this can cause wires to overheat, raise energy bills, and harm appliances.
Tip: If your circuit is very long, ask a professional to help you choose the right wire size.
Attempting DIY installations without proper knowledge
Trying to install wires without knowing how can be risky. Mistakes can cause short circuits, fires, or electric shocks. Even if you feel confident, electrical work needs special skills and tools to be done safely.
A common mistake is picking the wrong wire size or type. For a 220V 15-amp breaker, use 14 AWG copper or 12 AWG aluminum wires. Using thinner wires can make them overheat and increase fire risks. Another mistake is not securing connections tightly, which can cause loose wires and faults.
If you’re not experienced, it’s best to hire a licensed electrician. They follow local safety rules and make sure your setup is correct. They also have tools to test the circuit and ensure it works safely.
Reminder: Electrical work isn’t something to guess at. Always focus on safety and get expert help if needed.
Picking the right wire for your 220V 15-amp circuit breaker is very important. Use 14 AWG copper or 12 AWG aluminum wires. These wires are safe and stop overheating. Choose insulation like PVC or XLPE to protect the wires and keep them safe. The American Wire Gauge system helps you pick the right wire size for the circuit’s load.
If you’re unsure about wiring or local rules, ask a licensed electrician. They know safety rules and can help avoid mistakes or fines. Testing insulation and picking good wire materials make your circuit safer and more reliable. Following these steps helps you avoid common problems and make smart choices.
Tip: Always focus on safety when working with electricity. Getting expert advice can prevent expensive errors.
FAQ
What happens if you pick the wrong wire size?
Choosing the wrong wire size can make wires overheat. This might cause fires or damage your devices by not delivering power properly.
Can aluminum wires be used for every circuit?
Aluminum wires are good for certain jobs, especially big ones. But they need proper connections to stop rust and stay safe.
How can you check if your wires follow local rules?
Look at your area’s electrical rules or ask an electrician. They can check if your wires meet safety standards.
Is it safe to put in wires without expert help?
If you don’t know how, installing wires can be dangerous. Hiring an electrician makes sure the job is done safely and correctly.
What insulation is best for home circuits?
PVC insulation works well for home circuits. It’s cheap, bendable, and keeps out water, making it a great choice for most houses.
The following information may be of interest to you
Solar grid connected inverter with intelligent monitoring
How to choose the appropriate size of circuit breaker
What size of wire is suitable for a 30 ampere circuit breaker




