The choice between single-phase or three-phase electricity depends on your power needs. This article compares the two, explaining their differences, advantages, and optimal uses.
Key points
- Single phase power and three-phase power are two basic power supply modes in the power system, and their key differences lie in voltage levels, power carrying capacity, and condition of use
- Single phase power (220V) has a simple structure and low cost, suitable for low-power needs of homes and small businesses (e.g., lighting and domestic appliances)
- Three phase power (380V) is now prevalent to industrial drives, heavy equipment, and data centers due to its high output power, power efficient transmission, and secure supply of electricity
- It is extremely crucial for comprehending the difference between single and three-phase electric supply in determining the respective system based on certain energy requirements, especially at high energy conditions like data centers
Understand single-phase power supply
Single phase power (abbreviated as 1 φ) is a system used to distribute alternating current.
The standard frequency for single-phase power systems is 50 or 60 Hz.
Single phase electricity consists of a live wire (L) and a neutral wire (N), with a voltage of 220V (Chinese Mainland standard), and its current waveform is a single sine wave.
The characteristics of single-phase electricity are simple structure, low installation cost, but limited power transmission capacity, suitable for low-power demand scenarios such as home lighting, small household appliances (such as refrigerators, televisions), etc.
Advantages of single-phase power supply
Single phase power sources have a number of advantages, including simpler design and installation compared to three-phase systems, which render it economical for domestic uses. In addition, it is appropriate for most domestic appliances and easy to use.
As the ideal choice for household power supply, single-phase power supply processing power can reach 2500 watts, which is sufficient to meet most household appliances’ demands and provide efficient and stable performance. Meanwhile, single-phase power supplies have lower costs and are perfectly suitable for decentralized power supply.
Disadvantages of Unidirectional Power Supply
However, single-phase power supplies possess some disadvantages also, mainly low efficiency for heavily demanding applications. It is improper to operate large electric motors and heavy machines exclusively with the support of other machinery such as motor starters and frequency drives because this equipment requires heavy current and produces unstable power supply.
In addition, the fluctuation of single-phase power supply at present is large, which may lead to voltage instability and affect the normal operation of electrical equipment, especially precision equipment or high-power consuming equipment. It may reduce performance or even damage it.
How to measure single-phase power
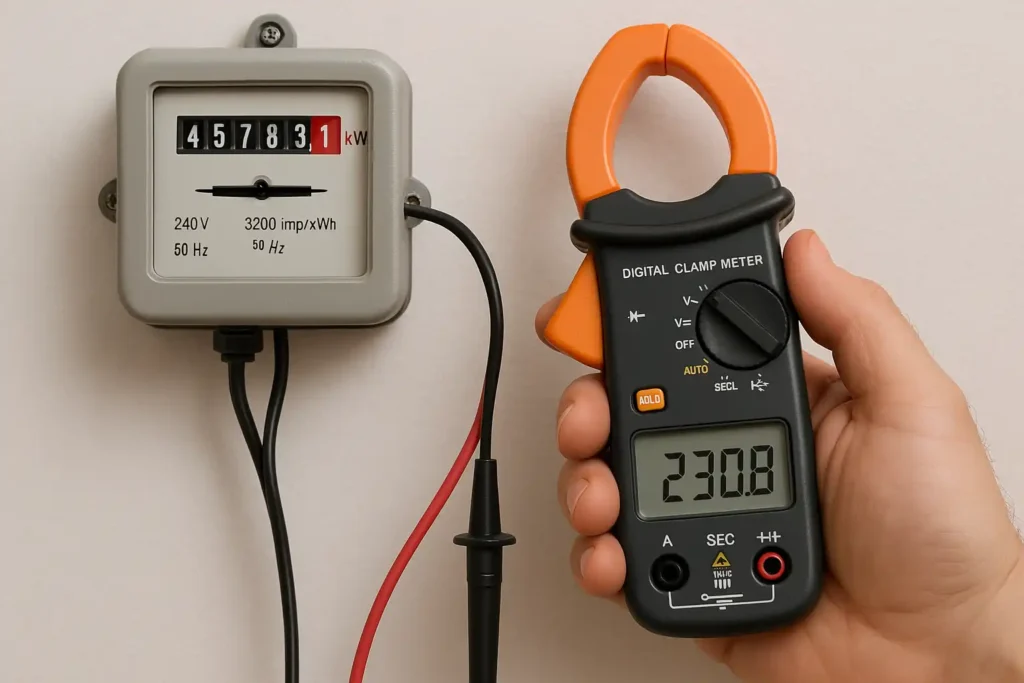

- Measuring voltage and current requires manual calculation of power, only applicable to low-power circuits
- Single-phase power measurement requires a knowledge of basic electrical specifications. The basic formula for single-phase power calculation is kW=(voltage x current x power factor) ÷ 1000. For the normal condition without the concern for power factor, the formula may be simplified as kW=(voltage x current) ÷ 1000.
- To find the present intake of a familiar kilowatt load, calculate current=1000 kW ÷ voltage to make sure your system has the capacity to handle the load without overloading. To take accurate measurements, use root mean square (RMS) voltage and current, using the formula P=Vrms × Arms. For reactive circuits, incorporate the power factor (cos ø) in the calculation.
Explore three-phase power supply
Three phase electricity (abbreviated as 3 ϕ [1]) is a common alternating current (AC) used for power generation, transmission, and distribution.
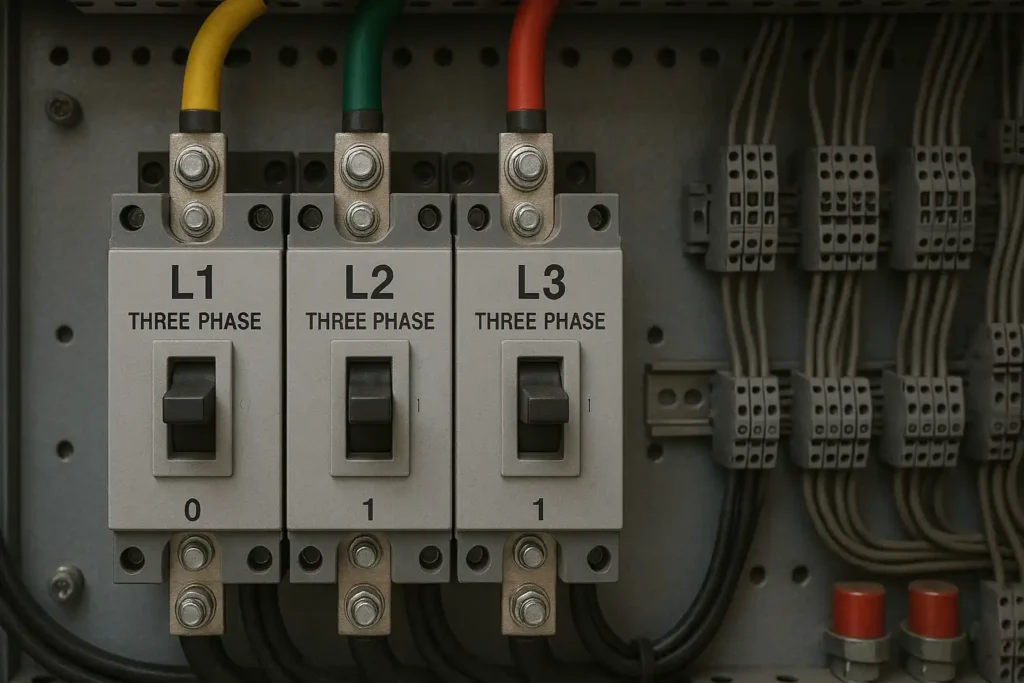
Three phase electricity consists of three live wires (L1, L2, L3) and an optional neutral wire (N). The line voltage between the live wires is 380V, and the phase voltage between the live wires and the neutral wire is 220V.
The phase difference between the three AC potentials of three-phase electricity is 120 °, forming a continuous rotating magnetic field, which makes its power output more stable and efficient, especially suitable for driving high-power equipment such as industrial motors and air conditioning systems
Working principle of three-phase power supply
Three phase electricity achieves the core functions of stable power transmission and rotating magnetic field driven load through three sets of alternating current with a phase difference of 120 °.
Advantages of three-phase electricity
- High power output, suitable for continuous operation and large loads
- High transmission efficiency, with line loss only 50% of single-phase electricity
Disadvantages of three-phase power supply
- Installation is complex and requires professional electrician maintenance
- High initial cost (such as three-phase meters, dedicated lines)
Application of three-phase electricity
Compare single-phase electricity and three-phase electricity
The difference between single-phase and three-phase power systems is significant, which can affect their efficiency and application. The following table highlights the main differences:
| Features | Single-phase Power | Three-phase Power |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Wires | 2 wires (1 live + 1 neutral) | 3 or 4 wires (3 live ± 1 neutral) |
| Voltage Characteristics | 220V, 50/60 Hz AC | 380V, 120° phase difference, balanced transmission |
| Power Output | ≤ 2.5 kW (residential use) | ≥ 10 kW (industrial use) |
| Efficiency | Low efficiency | High efficiency, less power loss |
| Installation Cost | Low | High |
| Application Scenario | Household appliances (lamps, refrigerator) | Industrial motors, data centers, large equipment |
Below, I will also deepen the difference between single-phase power supply and three-phase power supply through videos
Conversion between single-phase and three-phase electricity
- Where there is not three-phase power infrastructure, there is a need for single-phase to three-phase power conversion to enable the operation of three-phase motors. The conversion is one way by utilizing a rotating phase converter, which utilizes an electric motor and generator to generate balanced three-phase power from a single-phase power supply. It is reliable and efficient for overloaded applications.
- Static phase converters utilize capacitors to convert power, another option. While not capable of delivering true three-phase output, they can be utilized for light-duty service. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) first convert single-phase AC power to DC power, and then to three-phase AC power, and can provide frequency and voltage control, and therefore have widespread applications.
- Security measures need to be taken during the process of conversion. Turning off the mains supply and grounding prior to conversion is an inevitable step to prevent accidents and safe conversion.
Summary and Suggestions
- Through the comparison of three-phase electricity and single-phase electricity, we can know that single-phase electricity will be suitable for domestic and small commercial use, while three-phase electricity will be more suitable for industrial use and large devices. Depending on the load requirement and application situation, you can take the correct power supply mode to realize stable and efficient power supply.
- Understanding the working principle and the range of application of single-phase or three-phase electricity is the most crucial thing to make the best decision. Hopefully, the description in this article can help you decide on electricity more wisely.
FAQ:
What is the voltage difference of single-phase electricity compared to three-phase electricity?
Single-phase electricity is normally 220V in voltage, while three-phase electricity is normally 380V.
Why is three-phase electricity most commonly used in industry?
Due to the fact that three-phase electricity is capable of delivering higher power and most suitably adapted to the specifications of high load and heavy-duty equipment.
Is single-phase electricity able to satisfy all household demands?
Yes, single-phase power is enough to supply day-to-day home appliances and lightings.
Are three-phase power systems costly to install?
Yes, installing three-phase power systems is more advanced than installing single-phase power systems and is more capital intensive.
Here are some information that you may have just been interested in:
Choosing Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Solar Inverters
What You Need to Know About Three-Phase Solar Inverters
Selection guide for three-phase automatic transfer switch