You usually need a 32A miniature circuit breaker for a 22kW electric vehicle charger. Many experts say a 40A breaker is safer and follows the rules. In Europe, most 22kW chargers use a 400V three-phase supply. This matches the charger’s current rating. The National Electrical Code says to size the breaker at 125% of the continuous load. This helps stop overheating and keeps your wiring safe. Always use the right wiring size and add RCD protection for more safety.
Key Takeaways
- Use a 40A miniature circuit breaker for a 22kW electric vehicle charger. This helps you follow safety rules and stops the breaker from tripping too much. – Use the NEC 125% rule by making the breaker 125% of the charger’s current. This keeps wires from getting too hot and keeps them safe. – Pick the right wire size. Most of the time, use at least 6 mm² copper wire. Use 10 mm² wire if the wire is very long or in a pipe. – Put in an RCD with a 30 mA rating to stop electric shocks. Type A works for most home chargers. Type B is for special cases. – Always check if your electrical panel can handle the charger. Talk to a licensed electrician before you put in a high-power charger.
Miniature Circuit Breaker Size

Direct Answer
If you want to install a 22kW electric vehicle charger, you must pick the right miniature circuit breaker. This keeps things safe and follows the rules. Most 22kW chargers use about 32 amps on a three-phase 400V supply. Many people say to use a 40A miniature circuit breaker instead of a 32A one. This matches what the National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 625 says. The NEC says the breaker should be 125% of the charger’s steady current. This rule helps stop overheating and stops the breaker from tripping too much.
Tip: Always pick a miniature circuit breaker that is the same or bigger than the charger’s current after using the 125% rule. This makes your setup safe and works well.
Never use a breaker that is smaller than what is needed. A breaker that is too small can trip a lot and might not keep your wires safe. A 40A miniature circuit breaker gives you extra safety and follows the rules. If your charger uses more current, you need a bigger breaker. Always look at the charger’s manual and local rules before you decide.
Here are some main reasons why a 40A miniature circuit breaker is better than a 32A one for a 22kW charger:
- The NEC says breakers for steady loads must be at least 125% of the charger’s biggest current.
- A 40A breaker stops too many trips and keeps your home’s electrical system safe.
- Electricians say this size is good for safety and to follow local rules.
- If the breaker is too small, it can trip a lot and may be unsafe.
- Picking the right breaker also means using the right wire size and a special circuit.
Quick Reference Table
You can use this table to quickly see the best miniature circuit breaker size for different charger power and current. This table helps you pick the right breaker for your electric vehicle charger:
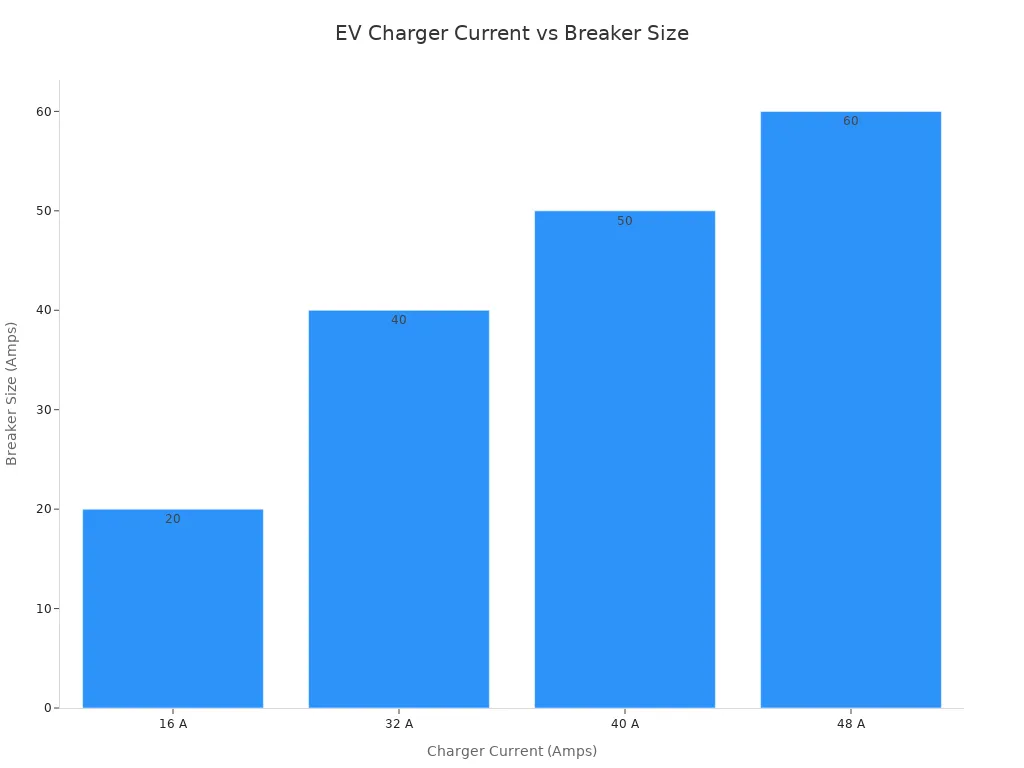
| Charger Power (kW) | Charger Current (Amps) | Voltage (Volts) | Recommended Breaker Size (Amps) | Typical Cable Gauge (AWG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.7 | 16 | 240 | 20 | 12 |
| 7.4 | 32 | 240 | 40 | 8 |
| 9.6 | 40 | 240 | 50 | 6 |
| 11 | 48 | 240 | 60 | 6 |
| 22 | 32 (3-phase) | 400 | 40 (3-phase) | 6 mm² (Europe) |
Note: Always make the miniature circuit breaker 125% of the charger’s rated current for steady loads. For example, a 32A charger needs a 40A breaker.
Most home EV chargers use a 32A or 40A miniature circuit breaker. Bigger chargers, like those for 22kW, may need a three-phase supply and a bigger breaker. Always check if your electrical panel can handle it before you start. If you are not sure, ask a licensed electrician. This helps you avoid mistakes, like picking the wrong breaker type or size.
Calculation
Three-Phase Example
You need to know how much current your 22kW electric vehicle charger draws before you choose a miniature circuit breaker. Most 22kW chargers use a three-phase supply. You can use a simple formula to find the current:
| Parameter | Value / Explanation |
|---|---|
| Power (kW) | 22 kW (target charger power) |
| Voltage (V) | 400 V (typical three-phase voltage) |
| Number of Phases | 3 (three-phase system) |
| Square Root of 3 | ≈ 1.732 (factor for three-phase power) |
| Formula | Power (kW) = Voltage (V) × Current (A) × √3 / 1000 |
| Rearranged Formula | Current (A) = Power (kW) × 1000 / (Voltage (V) × √3) |
| Example Calculation | Current = 22000 / (400 × 1.732) ≈ 31.7 A |
You can see that a 22kW charger on a 400V three-phase supply draws about 31.7 amps. This number helps you pick the right breaker size.
NEC 125% Rule
You must follow the National Electrical Code (NEC) when you select a miniature circuit breaker for your EV charger. The NEC 125% rule says you need to size the breaker at 125% of the charger’s steady current. This rule keeps your wiring safe and prevents overheating.
Here is a step-by-step way to apply the rule:
- Calculate the load current using the formula:
Current (A) = Power (kW) × 1000 / (Voltage (V) × 1.732) - Multiply the current by 1.25 to add a safety margin.
- Choose the next standard breaker size above your result.
For example, if your charger draws 31.7A, you multiply by 1.25. You get 39.6A. You round up to the next standard size, which is 40A. This matches what most electricians recommend for a 22kW charger.
Tip: Always apply the 125% rule once. Do not multiply twice. This keeps your installation safe and meets code requirements.
The NEC 125% rule applies to continuous loads, like EV chargers that run for more than three hours. You must use this rule to avoid undersized breakers and wiring. Manufacturers also use this rule in their recommendations. If you install a charger with a higher current, you need a larger breaker.
Safety & Code
Wiring Size
You must select the correct wire size for your EV charger to keep your installation safe and reliable. The National Electrical Code (NEC) and international standards set clear rules for this. For a 22kW charger, you usually need at least 6 mm² copper wire. If you install the cable in a pipe or run it over a long distance, you should use 10 mm² copper wire. This helps prevent overheating and voltage drop.
| Parameter | Details / Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Power | 22 kW |
| Voltage | 380 V (three-phase) |
| Calculated Current | ~58 A (22000W / 380V) |
| General Wire Size Recommendation | At least 6 mm² copper wire to safely carry ~60A current |
| Special Cases – Pipe Laying | Increase to 10 mm² copper wire due to reduced heat dissipation |
| Special Cases – Long Cable Length (>50m) | Increase to 10 mm² copper wire to reduce voltage drop |
| Summary | Use minimum 6 mm² copper wire; increase to 10 mm² for pipe or long runs |
Tip: Always check the length and path of your cable. Longer runs and tight spaces need thicker wires.
RCD Protection
You need Residual Current Device (RCD) protection for every EV charging point. International safety standards require an RCD with a rated residual operating current not exceeding 30 mA. This device protects you from electric shock and helps prevent fires. For most home chargers, a Type A RCD is enough if your charger has built-in DC fault protection. If your charger does not have this, you must use a Type B RCD, which covers both AC and DC faults.
- Type A RCD: Protects against AC and pulsating DC faults.
- Type B RCD: Protects against AC, DC, and high-frequency faults. Best for commercial or public chargers.
- Always make sure the RCD disconnects all live wires.
If your charger includes a DC monitoring device, you can use a Type A or F RCD with this extra protection. The RCD or DC fault protection can be inside the charger or in your main panel.
Panel Check
Before you install a 22kW charger, you must check your main electrical panel. Most homes need a panel with at least 150A to 200A capacity to support a charger of this size. You should look at the available space for new breakers and see if your panel can handle the extra load.
Follow these steps to make sure your panel is ready:
- Ask a licensed electrician to assess your power supply and wiring.
- Get the right permits and approvals before starting work.
- Upgrade your electrical system if your panel cannot handle the new charger.
- Install the charger and test it for safety.
Note: Always consult a licensed electrician for high-power charger installations. This ensures you meet all code requirements and avoid safety risks.
You need a 40A miniature circuit breaker for a 22kW charger. This size follows the rules and keeps things safe. Always do these things:
- Follow electrical codes so you don’t get shocked or start fires.
- Use the right wires and grounding to lower danger.
- Add RCD protection to find problems and keep everyone safe.
If you don’t check your work or ask an expert, you might have:
- Fires or electric shocks
- Broken charger or car
- Trouble with the law or failed checks
FAQ
What happens if you use a breaker smaller than recommended?
If you use a breaker that is too small, it trips often and may overheat. This can damage your charger and wiring. You risk fire and fail safety inspections.
What wire size should you use for a 22kW charger?
You should use at least 6 mm² copper wire for most installations. If you run the cable through a pipe or over long distances, upgrade to 10 mm² copper wire.
What type of RCD do you need for EV charging?
You need an RCD rated at 30 mA. Type A works for most home chargers with built-in DC protection. Use Type B for chargers without DC fault protection or for commercial setups.
What should you check before installing a 22kW charger?
Check your electrical panel’s capacity. Make sure you have space for a new breaker. Ask a licensed electrician to inspect your wiring and approve the installation.
See also
Din rail 40A 240V a residual current device
How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker for Your Electric Vehicle Charging Setup
What Happens If Your Electric Vehicle Charger Lacks Surge Protection
High quality RCD for electric vehicle chargers



