Your home’s electrical safety relies on smart choices. Picking the right household residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) is important. This device helps keep you and your family safe. It finds dangerous electrical problems and acts fast. If it detects a fault, it shuts off power right away. This lowers the chance of electric shocks and stops fires. Installing the right RCCB makes your home safer for everyone.
Key Takeaways
- Pick the right RCCB type for your home’s needs. Type AC works for simple devices, while Type A and B protect modern gadgets better.
- Use an RCCB with a 30mA sensitivity for homes. This helps stop electric shocks and lowers fire risks.
- Think about where the RCCB will be installed. Indoor ones need less protection, but outdoor ones must handle weather and temperature changes.
- Test your RCCB every month by pressing the test button. This makes sure it works well and keeps your home safe.
- Ask a licensed electrician to install and check your RCCB. They make sure it’s safe and follows all rules.
Understanding household residual current circuit breakers
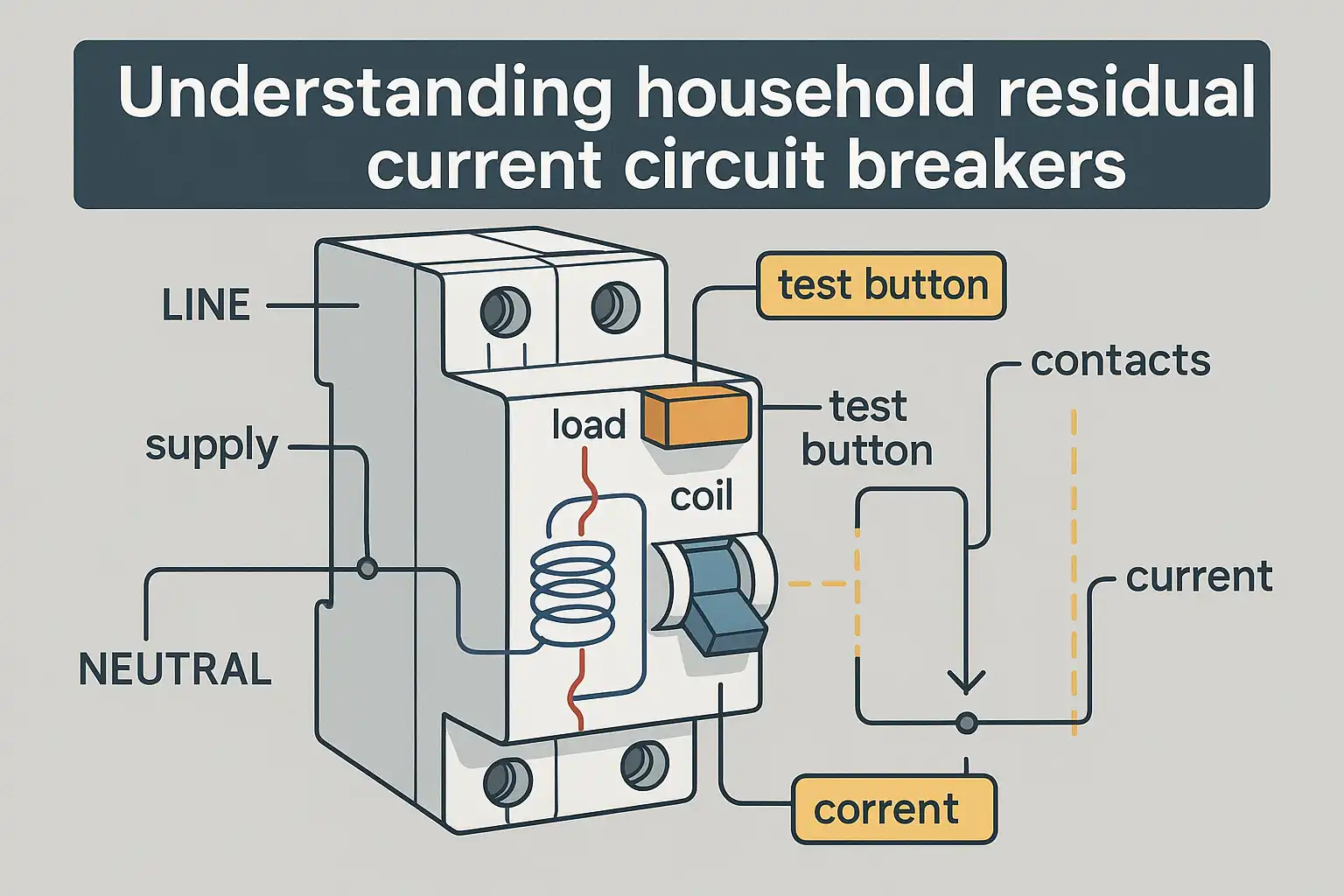
What is an RCCB, and how does it work?
A residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) keeps you safe from electrical dangers. It checks the flow of electricity in your home. It looks for any difference between the live and neutral wires. Normally, the current going in equals the current coming out. This balance means everything is working safely.
If something goes wrong, like current leaking to the ground, the RCCB acts fast. Here’s what happens:
- The current imbalance creates magnetic fields in the sensing coil.
- This activates the relay inside the RCCB, opening the breaker.
- The circuit shuts off immediately, stopping electricity flow.
This process follows Kirchhoff’s Current Law. The law says the current entering and leaving a circuit must match. RCCBs find even tiny leaks caused by faults. This stops dangers like shocks or fires.
Why are RCCBs essential for household safety?
RCCBs are very important for keeping your home safe. They protect you and your family from electrical harm. Here’s why they are so useful:
- Protection Against Electric Shocks: RCCBs trip the circuit when they find current leaks. This stops shocks if someone touches a live wire.
- Fire Prevention: Electrical problems like bad insulation can cause fires. RCCBs cut power quickly to lower fire risks.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Using RCCBs helps your home follow safety rules. This gives you peace of mind.
- Growing Awareness of Electrical Safety: More people now know about electrical dangers. Many homes use RCCBs to stay safer.
RCCBs watch your home’s electricity all the time. They find problems like leaks or overloads and act fast to stop them. Whether you’re fixing your home’s system or building a new one, picking the right RCCB is key to staying safe.
Types of household residual current circuit breakers
Type AC RCCBs: Features and applications
Type AC RCCBs are the simplest kind of residual current circuit breakers. They find and stop sinusoidal alternating current (AC) faults. These faults match the supply’s frequency. Type AC RCCBs work best with basic electrical loads.
Here are some key features and uses of Type AC RCCBs:
- They are great for appliances like lights, ovens, and heaters.
- They fit well in homes with simple and steady electrical needs.
If your home mainly uses standard devices without advanced electronics, a Type AC RCCB could be a good option.
Type A RCCBs: Features and applications
Type A RCCBs give better protection than Type AC models. They detect both sinusoidal AC and pulsating DC currents. This makes them ideal for homes with modern gadgets. These RCCBs are becoming more popular because they protect sensitive electronics.
In 2023, homes used 40% of Type A RCCBs. Businesses and factories used 35% and 25%, respectively. This rise is due to more automation and stricter safety rules.
New smart Type A RCCBs now exist. These let you check and control them remotely. They make safety easier and more convenient. If your home has smart devices or advanced electronics, pick a Type A RCCB.
Type B RCCBs: Features and applications
Type B RCCBs offer the best protection. They detect AC, pulsating DC, and pure DC currents. This makes them perfect for complex electrical setups.
| Feature/Statistic | Description |
|---|---|
| Detection Capability | Finds both AC and DC currents, unlike basic RCCBs. |
| Trip Sensitivity | Trips at 30mA and detects leaks as small as 6mA. |
| Applications | Best for homes, factories, and places with DC-powered tools. |
| Safety Benefits | Stops shocks and fires by quickly finding electrical faults. |
| Versatility | Provides high sensitivity and flexibility for full protection. |
Type B RCCBs are ideal for homes with solar panels or electric car chargers. They ensure top safety for both homes and workplaces.
Single-phase vs. three-phase RCCBs: Key differences
Picking between single-phase and three-phase RCCBs depends on your home’s power setup. Each type has its own purpose and benefits. Knowing how they differ helps you choose the right one for safety.
Single-phase RCCBs
Single-phase RCCBs work with homes that have a standard power supply. Most houses use this kind of system. Here’s what to know:
- Voltage: Runs at 230V, common in most homes.
- Wiring: Has one live wire and one neutral wire.
- Applications: Best for lights, fans, and small kitchen gadgets.
- Cost: Cheaper and simpler to install than three-phase RCCBs.
If your home has basic electrical needs, a single-phase RCCB is enough. It offers good protection for daily use.
Three-phase RCCBs
Three-phase RCCBs are made for places with a three-phase power supply. These are used in bigger homes, businesses, or factories. Key details include:
- Voltage: Runs at 400V, handling more power.
- Wiring: Has three live wires and one neutral wire.
- Applications: Great for air conditioners, pumps, and big machines.
- Efficiency: Spreads power evenly, cutting energy waste.
If your home uses powerful devices or has a three-phase system, this RCCB gives strong protection.
| Feature | Single-phase RCCB | Three-phase RCCB |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 230V | 400V |
| Wiring | 1 live, 1 neutral | 3 live, 1 neutral |
| Applications | Basic household devices | Heavy-duty appliances |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Tip: Find out your home’s power type before picking an RCCB. If unsure, ask a licensed electrician to help you decide.
By learning these differences, you can pick the right RCCB for your system and stay safe.
How to choose the right household residual current circuit breaker
Pick the correct current rating for your home
Choosing the right current rating keeps your home’s electricity safe. The current rating shows the maximum current the RCCB can handle. It prevents unnecessary tripping while keeping your system efficient. To find the right rating, think about these factors:
- Household Power Use: Add up the power used by all devices. Include appliances, lights, and gadgets. Homes with big appliances like ovens or air conditioners may need higher-rated RCCBs.
- Power Distribution: Check how electricity is spread across circuits. Circuits with more load might need RCCBs with higher ratings.
- Future Needs: Plan for adding new devices later. If you want to upgrade your system, pick an RCCB that can handle more power.
Here’s a table to help you decide:
| Specification/Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| PTC Ratings | Real-world performance ratings required by California’s Energy Commission, providing a reliable standard for solar panel efficiency. |
| STC Ratings | Standard test conditions ratings that help set expectations for energy production throughout the year. |
| Efficiency Range | Residential solar panels typically have efficiency ratings between 15% to 23%, influenced by various factors. |
| Environmental Factors | Factors such as temperature, shading, and weather conditions significantly impact solar panel performance. |
| Installation Quality | Proper installation is crucial for maximizing efficiency, including considerations for roof angle and orientation. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of the solar energy system. |
Tip: Ask an electrician to calculate your home’s power needs. They can suggest the best RCCB rating for safety.
Learn about sensitivity levels and why they matter
Sensitivity levels show how well an RCCB finds electrical problems. These levels are measured in milliamperes (mA). They tell the smallest current leak the RCCB can detect. Sensitivity is key for stopping shocks and fires at home.
Here’s why sensitivity is important:
- Personal Safety: RCCBs with 30 mA sensitivity work best for homes. They trip quickly when they find leaks, lowering shock risks.
- Fault Detection: Higher sensitivity catches small problems. This protects your devices and wiring from damage.
- Modern Device Compatibility: Many new gadgets create pulsating DC currents. RCCBs with better sensitivity can detect these currents easily.
Check this table for sensitivity details:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Performance and Tripping Sensitivity | Type A RCDs must trip when detecting AC and pulsating DC residual currents, with typical sensitivity at 30 mA for personal protection. |
| Fault Detection and Tripping Times | Quick response to AC and pulsating DC currents is essential to prevent harm and equipment damage. |
| Expanded Current Sensitivity | Must detect residual currents from modern appliances generating AC and pulsating DC leakage currents. |
| Faster Response Time in Detecting Faults | Designed to react to electrical faults within milliseconds, reducing risks of shocks and fires. |
Note: If your home has smart devices, pick an RCCB with advanced sensitivity for better safety.
Make sure it meets safety standards (e.g., UL, IEC)
Safety standards like UL and IEC ensure RCCBs work reliably. These rules make sure RCCBs protect against electrical dangers. Following these standards means your RCCB is safe and trustworthy.
Here’s why standards are important:
- Quality Checks: RCCBs tested under UL and IEC go through strict tests. This proves they work well in different situations.
- Worldwide Approval: IEC standards are accepted globally. RCCBs that meet these rules can be used anywhere.
- Better Protection: Standards like IEC 61508 focus on safety. They make sure RCCBs stop electrical problems effectively.
Here’s a table of IEC standards for RCCBs:
| IEC Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| IEC TS 61463 | Bushings – Seismic qualification |
| IEC TS 61464 | Guide for the interpretation of dissolved gas analysis in bushings |
| IEC 61466 | Composite string insulator units for overhead lines with a nominal voltage greater than 1 000 V |
| IEC 61467 | Insulator strings and sets for lines with a nominal voltage greater than 1 000 V – AC power arc tests |
| IEC 61468 | Characteristics and test methods of self-powered neutron detectors in nuclear power plants |
| IEC 61508 | Functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems |
| IEC 61511 | Safety instrumented systems for the process industry sector |
Tip: Look for UL or IEC certification when buying an RCCB. Certified devices meet high safety standards and work reliably.
Think about where to install it (indoor or outdoor)
Where you put your residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) affects how well it works and lasts. Different places have different challenges, like moisture, dust, or temperature changes. Picking the right type keeps it safe and reliable.
Indoor Installation
Indoor spaces are easier to control, but some things still matter:
- IP Rating: For indoors, an RCCB with IP20 is good. It stops small objects like fingers or tools from getting in.
- Ventilation: Make sure the area has airflow to avoid overheating.
- Placement: Put the RCCB in a dry spot that’s easy to reach, like an electrical panel.
Tip: Don’t install the RCCB near water, like sinks or washing machines.
Outdoor Installation
Outdoor setups need stronger protection because of tough conditions. Here’s what to check:
- Weatherproofing: Pick an RCCB with IP65. It blocks dust and water jets.
- Temperature Tolerance: Check if it can handle very hot or cold weather.
- Enclosures: Use a weatherproof box to protect it from rain, snow, and sunlight.
Note: Outdoor RCCBs wear out faster. Check them often to keep them working well.
By thinking about where you’ll install it, you can choose an RCCB that works well indoors or outdoors.
Look for extra features like surge protection and tripping speed
Modern residual current circuit breakers have extra features to make them safer and better. Knowing about these features helps you pick the right one.
Surge Protection
Power surges can harm devices or start fires. Some RCCBs have built-in surge protection. Here’s why it’s useful:
- Appliance Safety: Keeps gadgets like TVs and computers safe from voltage spikes.
- Cost Savings: You won’t need separate surge protectors, saving money and space.
- Longevity: Protects your electrical system from damage, making it last longer.
If your area has lightning or unstable power, get an RCCB with surge protection.
Tripping Speed
How fast an RCCB trips during a problem is very important. Faster trips mean better safety. Here’s what to know:
- Standard Tripping Time: Most RCCBs trip in 30 milliseconds. This is quick enough to stop most dangers.
- Advanced option: Some RCCBs can adjust the trip delay according to specific needs to accurately protect precision equipment.
Tip: Check the maker’s specs for tripping speed. Faster is always safer.
By choosing features like surge protection and quick tripping, you can make your home’s electrical system safer and more efficient.
Installation and maintenance of household residual current circuit breakers
Steps for proper installation
Setting up a household residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) needs care. Follow these simple steps:
- Insert the Breaker: Line up the RCCB with the bus bar. Secure it tightly.
- Wire the Circuit Breaker: Remove wire insulation and connect wires to terminals. Make sure live and neutral wires are in the right spots.
- Test the Circuit Breaker: Push the test button to check if the RCCB trips. This shows it works properly.
- Reattach the Panel Cover: Put the panel cover back on and label the breaker.
- Ground the Circuit Breaker: Attach the ground wire to the ground bus bar to finish.
Tip: Always turn off power before starting. Wear safety gear to stay protected.
Proper installation helps the RCCB work well and keeps your home safe.
Regular maintenance practices
Taking care of your RCCB keeps it working safely. Follow these tips:
- Test Often: Press the test button every month to check its function.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for loose or damaged wires during regular checks.
- Call a Professional: Have an electrician inspect the RCCB once a year.
- Upgrade Old Units: Replace older RCCBs with newer, safer models.
- Keep Records: Write down all maintenance activities for future reference.
Note: Regular checks stop problems before they happen and keep your RCCB reliable.
Safety precautions during installation and maintenance
Safety is key when working with electrical systems. Follow these rules to stay safe:
- Turn Off Power: Shut off the main power before starting any work.
- Use the Right Tools: Have tools like gloves, screwdrivers, and wire strippers ready.
- Read the Manual: Check the RCCB instructions to know its requirements.
- Stay Dry: Never work in wet or damp areas.
- Train Helpers: Make sure anyone helping knows the correct steps.
Alert: Ignoring safety rules can cause injuries or damage your system.
By staying cautious, you can install and maintain your RCCB safely and without problems.
Troubleshooting common issues with household residual current circuit breakers
Frequent tripping: Causes and solutions
If your RCCB trips often, it can be frustrating. It may also mean there’s an electrical problem. Common reasons include broken appliances, too many devices on one circuit, or bad wiring. For example, engineers at La Fe Hospital in Spain found hidden wiring issues causing frequent tripping. They fixed it by testing circuits and isolating the problem areas.
To fix frequent tripping:
- Check Appliances: Unplug devices one at a time to find the faulty one.
- Review Circuit Loads: Make sure circuits aren’t overloaded. Spread out devices if needed.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for loose wires or damaged insulation.
Tip: If the problem continues, call a licensed electrician for help.
RCCB not tripping when expected: What to check
If your RCCB doesn’t trip during a fault, it’s dangerous. Regular testing can catch problems early. In one case, maintenance workers in a factory faced a fire because an RCCB didn’t trip during a test. This shows why proper testing is so important.
Here’s what to check:
| Evidence Description | Explanation |
|---|---|
| RCD Test Button | Press the test button to mimic a fault. Replace the RCCB if it doesn’t trip. |
| User Error in Testing | Disconnect outgoing wires during testing to avoid wrong results. |
| Influence of Downstream Loads | Devices or cables can affect tests. Unplug them before testing. |
| Capacitance Effects | Extra capacitance may slow disconnection. Double-check test results. |
Note: Testing regularly ensures your RCCB works when needed.
Identifying a faulty RCCB and when to replace it
A broken RCCB can put your home at risk. Signs of trouble include frequent tripping, not tripping during tests, or working inconsistently. Internal damage or ground faults can stop the RCCB from protecting your system.
To spot and decide when to replace an RCCB:
- Watch for frequent tripping with electronic devices.
- Check for moisture or dust that might cause false tripping.
- Look for internal wear or damage that stops it from working.
Tip: Replace your RCCB right away if it fails tests or shows damage.
Fixing these problems ensures your RCCB keeps your home safe.
Picking the right household residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) keeps your home safe. Think about important things like matching current and voltage, choosing trusted brands, and having the right sensitivity. Proper setup and regular care make the RCCB work well. Use a 30mA RCCB at home to stop shocks and fires. If you’re unsure, ask a licensed electrician for help.
| Key Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Keeps people safe, stops fires, and protects devices. |
| Type Classification | Home RCCBs are for houses; industrial ones are for factories. |
| Leakage Operating Current | A 30mA RCCB is best for homes but can adjust for devices. |
| Brand Reputation | Pick well-known brands for safety and good support. |
| Rated Current and Voltage Matching | Match RCCB ratings to your home’s load, like 40A or 63A at 220V/380V. |
Tip: Check your RCCB often and get expert advice to stay safe.
FAQ
What is the difference between an RCCB and an MCB?
An RCCB stops electric shocks by finding current leaks. An MCB stops damage from overloads or short circuits. They do different jobs but work together for safety.
Tip: Use both RCCBs and MCBs for full protection.
How often should I test my RCCB?
Test your RCCB every month. Press the test button to check if it trips. Regular tests make sure it works and keeps your home safe.
Note: Replace it right away if it doesn’t trip.
Can I install an RCCB myself?
It’s not safe to install an RCCB yourself. You need electrical skills and safety knowledge. A licensed electrician can install it correctly and safely.
Alert: DIY installation can cause serious dangers.
What does the sensitivity rating of an RCCB mean?
The sensitivity rating shows how small a current leak the RCCB can detect. It’s measured in milliamperes (mA). For homes, 30mA is the best choice. It protects against shocks and fire risks.
Emoji Reminder: ⚡ Always check the sensitivity before buying!
How do I know if my RCCB needs replacement?
Replace your RCCB if it fails the test, trips too often, or looks damaged. A broken RCCB can’t protect you, so act fast to stay safe.
Tip: Have an electrician check it yearly to find problems early.
The following information may be of interest to you
Difference between electromagnetic and electronic RCCB
What Are Residual Current Circuit Breakers and How Do They Work