Electrical Safety Standards help make your workplace safer. They protect workers from electric shocks and fires. They also keep your business things safe. These standards help you follow the law.
If you ignore electrical safety, people can get hurt. You could lose property or get in trouble with the law.
Key Takeaways
- Electrical Safety Standards help keep workers safe from harm. They also protect your business from fires and damage.
- Following rules like NFPA 70E and the National Electrical Code helps stop accidents. These rules also help prevent expensive equipment problems.
- Meeting legal requirements helps you avoid fines and lawsuits. It also keeps your business from closing and builds trust with workers and customers.
- Regular training, using the right personal protective equipment, and checking things often lowers risks. These steps help keep everyone safe.
- Look for signs like lights that flicker or outlets that feel warm. Fix problems fast to stop hidden electrical dangers.
Why Electrical Safety Standards Matter
Protecting Employees
You want your workers to be safe every day. Electrical Safety Standards help stop serious injuries. In businesses, workers can get hurt by electricity. Some common injuries are:
- Electric shock can burn skin or make the heart beat wrong. It can also make someone pass out.
- Electrocution is deadly. It happens when electricity goes through the body.
- Falls can happen if a shock makes muscles move suddenly or if the area is unsafe.
- Burns often happen on hands and feet from touching live equipment.
- Cuts and lacerations can come from electrical arcs or sharp things.
- Loud noises from equipment or blasts can cause hearing loss.
You can make these risks smaller by following rules like NFPA 70E. This rule tells you how to work safely, keep equipment in good shape, and control dangers. Train your team, use safety gear, and follow lockout/tagout steps. These actions help stop injuries and keep workers healthy.
Tip: A strong safety culture means more than just following rules. Teach your team to find dangers, report problems, and always work safely.
Safeguarding Assets
Your business needs equipment, buildings, and technology to work. Electrical Safety Standards help protect these important things. Fires and broken equipment can cost a lot of money. Every year, electrical problems cause over $373 million in damage from fires in nonresidential buildings. Factories and industrial places lose about $704 million from fires. Together, businesses lose more than $1 billion each year from fires and broken equipment.
You can stop many losses by following codes like the National Electrical Code (NEC) and NFPA 70B. These rules say you should:
- Build and set up electrical systems to stop overloads and faults.
- Use safety devices like arc-fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) and ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) to turn off power if there is a problem.
- Check and fix equipment often to find hidden dangers, especially in old buildings.
- Hire licensed electricians for repairs and upgrades.
- Keep up with regular maintenance to stop problems before they start.
Following these rules also lowers your insurance risks. Insurance companies might not pay if you do not follow safety codes. Protecting your things keeps your business open and stops costly shutdowns.
Legal Compliance
You must follow the law to keep your business safe. Electrical Safety Standards tell you what rules to follow. If you break these rules, you could get fines, lawsuits, or even have to close your business. Here are some legal problems you might face if you do not follow the rules:
- Fines that can be thousands of dollars.
- Insurance claims denied if you break the rules.
- Forced to close your business until you fix safety problems.
- Longer closures and extra fines if you keep breaking rules.
- Lawsuits from injuries or accidents, which cost money.
- Losing insurance or not being able to renew it.
You can avoid these problems by meeting the rules for your business. Standards help you in many ways:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical Safety Programs | You need programs for checks, repairs, tests, and emergency plans. |
| Employee Training | Workers must get training on safe work and how to use PPE. |
| Lockout/Tagout Procedures | Make sure systems are off during repairs so no one gets shocked. |
| Hazard Communication | Use signs and labels to warn about electrical dangers. |
| IEEE Standards | Follow best ways to lower risks, like arc flash hazard checks. |
| Compliance Inspections | Check often to see if you follow safety rules. |
| Documentation | Keep records of checks, repairs, and training to show you follow the rules. |
| Third-Party Audits | Let outside experts check for problems and help you fix them. |
| Best Practices | Do more than the minimum by using regular checks, risk reviews, and emergency plans. |
Meeting these rules helps you stay out of legal trouble and shows you care about safety. You also earn trust from your workers, customers, and partners.
Key Standards
OSHA Electrical Safety Standards
If you run a business in the United States, you need to know OSHA rules. OSHA makes the main Electrical Safety Standards for workplaces. These rules help keep your team safe from electrical hazards. OSHA splits its rules into two big parts:
- Part 1910, Subpart S for General Industry
- Part 1926, Subpart K for Construction Industry
Each part talks about important things:
- How to design safe electrical systems
- Ways to work safely
- What you must do to keep things working right
- Special rules for certain equipment
You have to make sure your workplace follows these rules. This means checking equipment and using grounding. You must train your workers. You also need to use lockout/tagout steps to control dangerous energy. OSHA wants you to keep records and get ready for inspections. If you work near power lines, you must use tools that do not carry electricity. These rules protect everyone, not just electricians.
OSHA changes its rules by using new industry standards, like NFPA 70B. This helps you follow the newest safety ideas.
NFPA 70E and NEC
You will often hear about NFPA 70E and the National Electrical Code (NEC). Both are important for Electrical Safety Standards in businesses. The NEC tells you how to design and put in safe electrical systems. It covers things like cable size, overcurrent protection, and grounding. NFPA 70E tells you how to work safely around electricity. It talks about safe work, training, and safety gear.
These standards help you:
- Put arc flash warning labels on equipment
- Make sure only trained people work on electrical systems
- Set up safe work areas and emergency plans
- Use the right gear to keep workers safe
NFPA 70E changes every three years. It now says you must plan for emergencies and check that workers have the right skills. The NEC and NFPA 70E work together to keep your building and people safe.
International and State Standards
If your business is in more than one country, you may need to follow international rules. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) makes the most common global standards. These rules say how to build, label, and test electrical products. Many countries use IEC rules as their base. For example, the European Union uses IEC rules for most of its electrical safety laws.
In the United States, some states add their own rules to the federal ones. States like California have their own OSHA-approved plans. These plans may ask for more safety steps, extra recordkeeping, or faster reporting. You must follow your state’s rules, which can be stricter than federal rules.
Tip: Always check both federal and state rules to make sure your business meets all Electrical Safety Standards.
Electrical Hazards

Common Risks
Many electrical hazards can happen at work. These hazards may hurt people or damage things. Fires can also start because of them. If you know what to watch for, you can keep everyone safe. Here is a table that lists some common electrical hazards in businesses:
| Electrical Hazard | Description | Associated Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit Overloads | Circuits get too much power and breakers trip or fuses blow. | Power goes out and equipment can break. |
| Disorganized Electrical Panels | Panels are messy or not labeled, so it is hard to find circuits. | It is dangerous to fix things. |
| Inadequate or Faulty Wiring | Old or bad wiring cannot handle the power needed. | Fires can start and people can get shocked. |
| Insufficient Outlets | Not enough outlets means too many extension cords are used. | Cords get hot, circuits overload, and fires can happen. |
| Grounding Problems | Bad grounding makes things unsafe. | Equipment can break and people can get shocked. |
| Improper Installation of Appliances | Appliances are not put in the right way. | Fires and shocks can happen. |
| Aging Electrical Systems | Old systems do not meet new rules or work with new machines. | Power goes out, things break, and people can get shocked. |
⚡ Tip: If lights flicker, outlets feel warm, or you smell burning, there may be hidden electrical dangers.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
If you do not follow electrical safety rules, bad things can happen. Here is what might go wrong:
- More people get hurt at work
- You can get fined or punished by the law
- Projects slow down because of accidents or legal trouble
- People may not trust your company anymore
- You can lose a lot of money from fines and legal costs
- Insurance costs go up because your business is risky
- Insurance may not pay if you did not follow safety rules
Not following safety rules can also cause fires, shocks, and problems that last a long time for your business.
Mitigating Risks
You can make electrical risks smaller by using good safety steps. Here is what you should do:
- Use Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) before fixing anything electrical.
- Pick the right wire size and strong extension cords to stop overheating.
- Cover open electrical parts and fix broken insulation fast.
- Make sure everything is grounded the right way.
- Do not use electrical things in wet places and have an expert check wet equipment.
- Check for fire risks often to find wiring and circuit problems.
- Teach workers about electrical safety so they know what dangers look like and how to stay safe.
Checking often, teaching safety, and letting people report problems helps everyone stay safe at work.
Compliance Steps

Training and Awareness
Your team must learn about electrical safety. Training should happen before anyone works with electricity. It is not just one lesson. You need to teach workers how to spot live parts and check voltage. They must know how to use safety gear. Teach them about hazard recognition and risk assessment. Show safe work practices and lockout/tagout steps. Teach emergency response too. Only qualified people should do electrical work. Retrain your team every three years or when things change. Ongoing training keeps employees alert and lowers accidents. Regular lessons help your business follow new safety rules.
Ongoing training helps everyone spot dangers faster and builds a strong safety culture.
Personal Protective Equipment
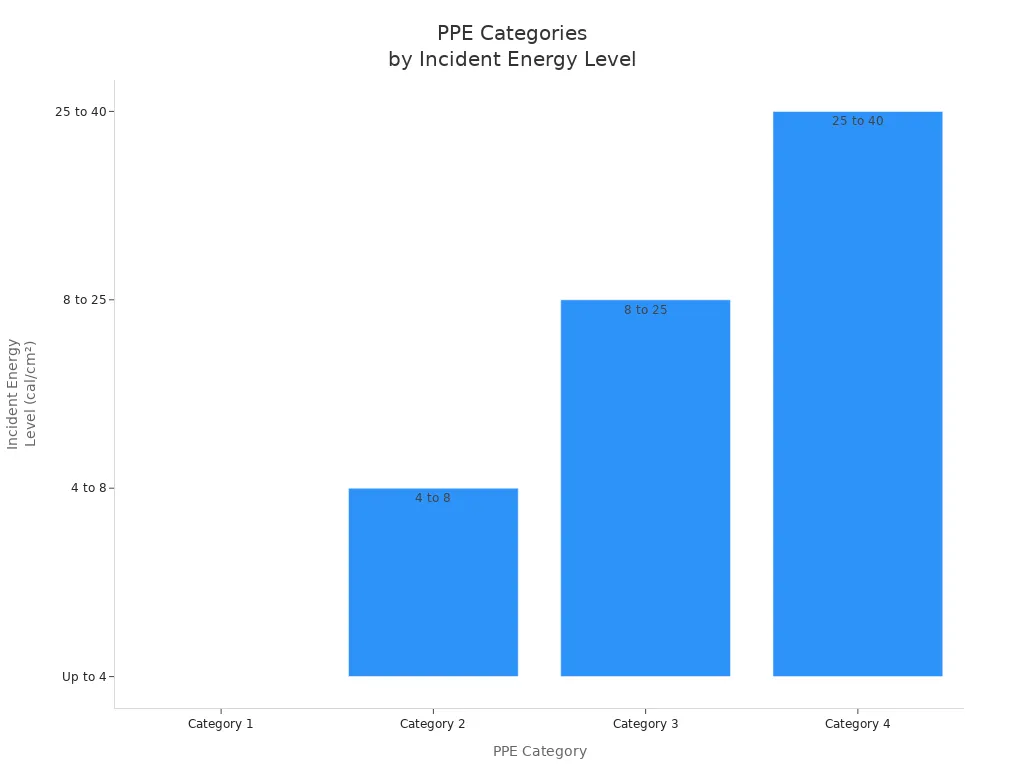
You must give the right PPE for each electrical job. PPE means voltage-rated gloves, flame-resistant clothes, safety glasses, insulated tools, and strong leather shoes. Test gloves before first use and every six months. Insulated tools must match the voltage and place. Use nonconductive ladders and ropes near live parts. Arc flash hazard analyses help pick the right PPE for each job. Train workers to use and care for PPE. The table below shows how PPE changes with hazard levels:
| PPE Category | Incident Energy Level (cal/cm²) | Required PPE Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Up to 4 | Arc-rated clothing, hard hat, safety glasses, leather gloves, leather shoes |
| 2 | 4 to 8 | Arc-rated clothing, hard hat with face shield, safety glasses, leather gloves, leather shoes |
| 3 | 8 to 25 | Arc-rated clothing, hard hat with hood, safety glasses, arc-rated gloves, leather shoes |
| 4 | 25 to 40 | Arc-rated clothing, hard hat with hood, safety glasses, arc-rated gloves, arc-rated shoes |
Inspections and Maintenance
You need to check and fix electrical systems often. Most businesses do full checks every five years. They do smaller checks every year. Inspect systems after changes or accidents. Certified inspectors look for old wiring and overloaded circuits. They check for loose connections and missing safety devices. Visual checks help you find broken switches and scorch marks. They also spot bad wiring. Regular inspections stop accidents and keep your business safe.
Inspections help you find problems early and keep your workplace safe.
Documentation
You must keep clear records to show you follow safety rules. Write down who did the testing and what equipment was checked. Record test results, inspection dates, and repairs made. Use digital systems to store and review records. Businesses make Electrical Maintenance Programs with responsibilities, steps, and inspection plans. Update records after every inspection, training, or repair. Good records prove you follow the law and help you improve safety.
Keeping records up to date shows you care about safety and helps you pass audits.
When you follow Electrical Safety Standards, you keep your team safe. These rules help stop accidents and save money. They also help your business work without problems. Training, inspections, and maintenance make workers feel good and stop delays. You follow the law and your workers trust you more. Put electrical safety first to help your business grow and keep everyone safe.
FAQ
What are electrical safety standards?
Electrical safety standards are rules for working with electricity. These rules help keep workers, equipment, and your business safe from harm.
What happens if you do not follow electrical safety standards?
If you do not follow the rules, people can get hurt. Fires or broken equipment can happen. You might get fined or have legal problems. Insurance may not pay for accidents. Following the rules keeps your business safe and legal.
What should you include in an electrical safety program?
You need to train workers often and check equipment. Make sure you fix things when needed. Set clear rules for using personal protective equipment. Have emergency plans and keep good records.
What is the difference between OSHA and NFPA 70E?
OSHA makes the main safety rules for work. NFPA 70E gives more details for safe electrical jobs. You must follow OSHA by law. NFPA 70E helps you do what OSHA asks.
What are common signs of electrical hazards at work?
Watch for lights that flicker, warm outlets, or burning smells. Breakers that trip a lot are also a sign. These things mean there could be hidden electrical dangers. Tell someone right away to keep everyone safe.
See also
What Should You Know About Replacing Circuit Breakers from Different Brands?
Why Electricians Recommend the Right Wire Size for 60 Amp Circuit Breakers
What size cable is suitable for electric vehicle chargers
What is the suitable 40A miniature circuit breaker for electric car chargers
New Trends and OEM Direction of Micro Circuit Breaker Market in 2025



